Eclampsia drill
advertisement

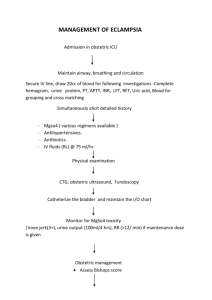
Eclampsia Drill Dr Sharda Patra( Asso. Prof) Prof Manju Puri Department of Obstetrics & Gynecology Lady Hardinge Medical College & Smt SK Hospital New Delhi Eclampsia Drill Eclampsia is an important obstetric emergency which if not managed promptly can lead to life-threatening complications like cerebral haemorrhage, pulmonary edema, abruptio placentae maternal and fetal death Any pregnant woman presenting with convulsions in later half of pregnancy should be treated as eclampsia until proved otherwise The management of eclampsia involves Immediate management Subsequent management One should remember that first few minutes following a fit are very crucial and should be handled very fast due to risk of cerebral hypoxia and aspiration which can have serious consequences. . Immediate management…. Principles Speed Skills Priorities Immediate management ….. Stabilize the woman Call for Help Remember A; B; C of resuscitation Control convulsion Control blood pressure Initial Resuscitation Airway Place the woman on her left side to reduce the risk of aspiration of secretions, vomit and blood Put an airway in between the tongue and palate to prevent tongue bite and falling of tongue Suction of the secretions is done through this airway by connecting it to a suction machine. Give oxygen (if available15 l /min ) and continue longer if cyanosis persists Stay with the patient to ensure that her airway is clear Initial Resuscitation Breathing Assess – count respiratory rate .Look, Listen, Feel. Ventilate if necessary Circulation Assess pulse , BP. CPR if necessary Secure intravenous access with a cannula (16G ) Send blood for BG, CBC, platelets, clotting screen, KFT, LFT, Uric acid, Serum electrolytes Catheterize the patient to empty the bladder , record output and monitor output subsequently Do a urine examination for proteins Treat and prevent further fits Administer Magnesium Sulphate (MgS04) Regimes: Pritchard or Zuspan Pritchard Loading dose Maintenance dose 4g IV 20% solution over 5 to 10min plus 10g IM (5 g 50% solution deep I/M in each buttock) 5g I/M every 4h in alternate buttock till 24 hrs after the last seizure or delivery which ever is later Zuspan Loading dose Maintenance dose Loading dose 4g IV 20% solution over 5 to 10min 1 to 2 g / h by controlled infusion pump x 24h after the last seizure Mg So4 :Preparation and Administration MagSo4 available in 25%, 50% strength Initial loading dose 14gms 14gms 4gm IV 10 gms IM Preparation and administration 25% ampoules (2ml) contains 0.5 gm magso4 IV 4gms 50% amps (2ml) contains 1gm of magso4 Take 4amps (8ml) dilute with 12ml saline to make it 20ml Take 8amps (16ml) dilute with 4ml saline to make it 20ml 20ml solution contains 4gms Magso4 ( 4gm/20ml 20% Sol) IV 4gm 20ml is given slow IV over 5-10mins Keep an eye on respiratory rate , facial flushing , Preparation and Administration 10gms IM 50% amps (2ml) contains 1gm of magso4 Take 5amps (10ml) undiluted 5gms deep IM(10ml) in each buttock If convulsion recurs Give 2gm IV 20% solution over 5-10mins and continue the maintenance dose Monitoring during magnesium sulphate Therapy Respiratory rate >14/ min Presence of patellar reflexes (knee jerk) Urinary output- 25ml/hr or 100ml/4hrs Repeat doses of magnesium sulphate must be withheld or delayed if: The respiratory rate is less than 14 per minute Patellar reflexes are absent Urinary output is less than 100 ml over preceding 4 hours Antidote: In case of respiratory depression or arrest: Give calcium gluconate 1 g (10 ml of 10% solution) IV slowly Assisted ventilation using mask and bag, anesthetic apparatus or intubation CAUTION Magnesium sulfate should be used with caution in women with Impaired renal function. Patients with a heart block or myocardial damage including a history of cardiac ischaemia Controlling blood pressure Antihypertensive drugs should be given if the diastolic blood pressure is 110 mmHg or more. The aim is to keep the diastolic blood pressure between 90–100 mmHg to prevent cerebral haemorrhage Drug of choice- Labetolol, Nifedepin Labetolol 1. 20 mg I.V over 2mins wait for 10 mins if no response 40 mg iv 80 mg iv (can be increased upto 220 mg) 2. 10 mg IV 20 mg iv 40 mg iv Target : Decrease in diastolic BP To 90-100 mgHg 40 mg iv 80 mg iv Nifedipine 10 mg tabs orally to repeat every 20 mins up to a maximum dose of 200 mg Subsequent management Once the patient is stabilized and fits have ceased , then a pervaginum examination is done to assess cervical status Consider for termination of pregnancy if not in labor Essential care Turning the woman two–hourly to avoid hypostatic pneumonia mouth care, (no oral fluids are given) monitor the urinary output. Observations: Restlessness or twitching which may herald the onset of another fit Color is observed for cyanosis which indicates the need for oxygen Temperature four hourly. Hyperpyrexia may occur Pulse and respirations are recorded hourly, or more often Blood pressure is recorded at least hourly earlier if >=160/110 Ut contractions and FHS is checked Input output is recorded accurately. A L G O R I T H M Do not leave the patient alone Place in left lateral position CALL FOR HELP Airway Assess Maintain patency Give oxygen Breathing Assess Protect Airway Ventilate if required Circulation Evaluate pulse and BP Secure IV access Control of convulsions Control of Hypertension Loading dose : 4gm IV 20ml is given slow IV over 5-10mins followed by 10gms , 5gms deep IM (10ml) in each buttock If fits recur- 2gms , 20% IV Maintenance dose- 5gms IM in alternate buttocks 4 hourly Monitor- Resp rate>16 Presence of Knee jerk Urinary output >25ml/1hr If Mag toxicity- Inj Calcium Gluconate , 10% 10ml , 10mins IV Labetolol 10mg IV , give 20mg IV if noresponse after 10mins, then 40mg, 40mg, 80mg max 220mg Nifedipine 10mg orally , repeat after 20mins if noresponse , max 200 mg, target BP- dbp-90-100 mmHg Delivery A DRILL …….. Eclampsia The need for good clinical skills to be able to recognize and act promptly Be in control of the situation Need to care for the family, who will be extremely distressed to see the woman have a fit; Need for gentleness, so as not to harm the woman if she is unconscious, or stimulate further fits; Need to respect the woman’s dignity at all times; Need for strict attention Thanks