Trauma Team Training

Trauma Team Training
Take Home Clinical Points
Essential CRM skills
• Know your environment
• Anticipate and plan
• Effective team leadership
• Active team membership
• Effective communication
• Be situational aware
• Manage your resources
• Avoid and manage confli cts
• Be ware of potential errors
Trauma Apps
• I Phone Westmead Trauma App
– https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=air.
au.com.lpn.WestmeadApp&hl=en
• Android Westmead Trauma App
– https://itunes.apple.com/au/app/westmeadtrauma/id785943004?mt=8
Airway
Airway Pearls
• Plan your Airway Intervention
– Equipment
– Team Briefing (Plan A, B and C)
– ‘Checklist’
• Goal is to Oxygenate and Ventilate (not intubation)
• Optimise Haemodynamics and Oxygenation Prior to induction
• Anticipate a difficult airway (team brief as above)
• A Neutral position is slightly flexed at the neck so put a towel or SAM splint behind the head
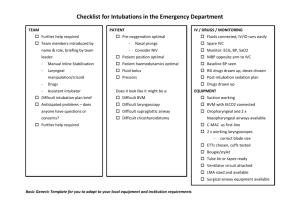
Checklist
Example
ITIM – Difficult Airway Management 1
Failure to Intubate
Call for Help
Maintain Cricoid (if used) and Inline
Place Oral Airway and 2 person BVM with 100% O2
Attempt to
Ventilate and Keep
Sats>90%
ITIM – Difficult Airway Management 2
Are the SATS>90% with the BVM??
Optimise Position,
Use Adjuvant(s) for
Intubation
Yes No
Attempt to Ventilate using LMA
Able to keep
Sats>90%: If yes
Proceed to Right
Unable to keep
Sats<90%
Surgical Airway
Make 2 nd attempt at
Intubation
Consider Waking the patient or obtaining further resources
Consider Surgical
Airway
Drugs for RSI - Discussion
• RSI is usual Technique for Trauma Intubation
• Dose reduce Sedative Agent = Thiopentone (if used) 0.5mg – 2mg /kg (rather than 5mg/kg)
• Consider Ketamine 1mg -2mg/kg or
Midazolam 0.05mg – 0.1mg/kg
• Fluid prior to induction may be appropriate
(vasopressors are not usually appropriate)
• May need to increase dose of Suxamethonium
• Need to allow all drugs more time to act
• Propofol is (generally) NOT recommended
Abdomen Protocols
Haemorrhage
Where is the Bleeding
• ‘PLACES’
– Pelvis
– Long Bone
– Abdomen
– Chest
– Externally and Epistaxis
– Scalp
Chest Protocols
Sternal Injury
Penetrating Chest Injury
Code Crimson and
Massive Transfusion
Massive Transfusion
• Prof Koutts Protocol (October 2012) – Is available on the Westmead intranet
• Consider 1g Tranexamic Acid Early (within 3 hours)
Principles of Massive Transfusion
Penetrating Abdominal Wounds
Head Injury
Neuroprotective Measures
• Head up 30 degrees
• IV Fluid (Relative Hypervolaemia)
• Avoid Hypotension and Hypoxaemia
• Reduce ICP and maximise Cerebral Perfusion
Pressure (CPP) (Monroe Kellie Doctrine)
– CO2 30-35
– No tight ties, conservative C spine precautions
– Drugs – Induction, Sedation and Paralysis
– ICP Monitoring (invasive) and Seizure Meds:
• recent evidence suggesting against
Hypertonic
Saline
Continued to next slide…
Trauma Call Criteria
Cognitive Aids
5 Cs OF COMMUNICATION
1.Clarity
Give and receive instructions & information (be specific, be succinct, avoid jargon, CLOSE LOOPS)
2.Coordination
(use people’s names, confirm you hear instructions, relay information via leader)
3.Cohesion
(clarify goals, share information, invite input, summaries and updates, acknowledge effort, speak calmly, use humour)
4.Concern to be freely expressed use graded assertiveness attention /enquiry /clarify /demand)
5.Conflict to be avoided/ managed
(clarity, consensus, decision)
GRADED ASSERTIVENESS
1. Bring to Attention:
2. Enquire (make an enquiry or offer an alternative as a suggestion):
”Are you going place an IV in that fractured arm?”
3. Clarify
“ I feel uncomfortable about this, please explain what you are doing”
4. Demand a Response or Take Control of the Case:
“ Sir you MUST LISTEN” KEY PHRASE
“Stop – you must listen to me ”
Alternative Mnemonic
**CUSS = ‘Concern’, ‘Unsure’, ‘Safety’, ‘STOP!’
CONFLICT RESOLUTION:
4 STEP NEGIOTIATION PROCESS
1
.State what actually happened or what you observed
(be specific)
2.State how you feel about it and find out their perspective
3. Say what you want to happen next
4. Agree on the next step
Time critical situations may require an abbreviated approach.
Authority
: Deliver directive
No authority
: Graded assertiveness
7 NON-TECHNICAL TEAM TASKS
1.Assemble right team
- skill mix / numbers / phone consults
2.Plan & prepare
- organisational / patient specific / plan A & B
& C
• Equipment (type/location/working order/ training)
• Colleagues ( names , skill mix, roles, brief team)
• Situational awareness (pt load & mix, anything else that will impact on your resources)
3.Manage resources
- make decisions / allocate tasks / get help
4.Manage people
- roles & goals / familiarity & trust / update
5.
Communicate effectively – CCCCC
6.Monitor & evaluate
- cross check / team update & confirm / documentation
7.Support each other
- awareness of roles & support & feedback