The Use of EPO-Stimulating Agents in Heart Failure
advertisement

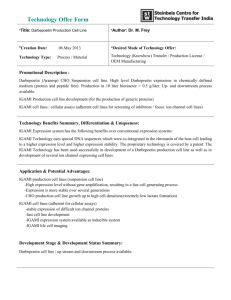
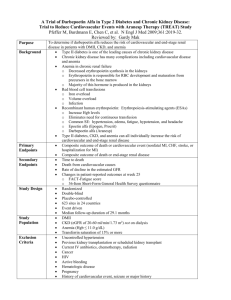
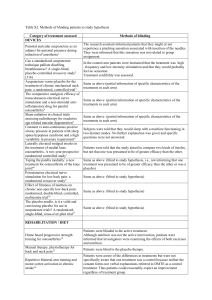
The Use of EPO-Stimulating Agents in Heart Failure Nora Sharaya, PharmD PGY2 Pharmacotherapy Resident Butler University & Community Health Network This speaker has no actual or potential conflicts of interest to disclose in relation to this presentation The Link Between Anemia and Heart Failure Functional Iron Deficiency Hemodilution Activation of the Inflammatory Cascade Anemia Impaired EPO Production Concomitant CKD ISRN Hematol 2012; 2012: 246915 The Link Between Anemia and Heart Failure HF with preserved EF Anemia HF with unpreserved EF ISRN Hematol 2012; 2012: 246915 Mortality A meta-analysis published in 2008 examined 153,180 patients with chronic heart failure Of those patients, 37.2% were anemic After a minimum of six months follow up, 46.8% of patients with anemia died compared to 29.5% of the patients without anemia Based on these results, in patients without an identifiable cause for their anemia, using erythropoietin-stimulating agents has been considered J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008;52:818–2. Complications Increased Risk of Mortality Reduced Exercise Capacity Impaired Quality of Life Increased Risk of Hospitalization J Am Coll Cardiol 2008;52:818–2 ACCF/AHA Guidelines Acknowledge the link between anemia and heart failure • Discuss associated complications No cited recommendation on use of EPO stimulating agents for treatment • Lack of definitive evidence Circulation. 2013; 128: e240-e327. Concerns with EPO Stimulating Agents US Boxed Warning: “Erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESAs) increased the risk of serious cardiovascular events, thromboembolic events, stroke, and mortality in clinical studies when administered to target hemoglobin levels >11 g/dL.” Darbepoetin (Package Insert) van Veldhuisen DJ, et al. Study Design Results Applicability • Randomized, multinational, double-blind, placebo-controlled • n=162 patients In treated patients, there were trends towards improvement in: • Walking distance • NYHA class • Health-care associated QOL • Darbepoetin vs. placebo trended towards : • Randomized to Wto six-minute based dose of SQ walk distance darbepoetin alfa, a o Improvement fixed dose, or in NYHA class placebo Q2W X25W o Improvement targeting Hgb 14.0 in health-care associated QOL • PO iron supplement Eur Heart J. 2007;28:2208–16. Ghali JK, et al. Study Design Results • Randomized, • n=162 (treatment) multicenter, • n=157 (placebo) double blind, • Mostly white males placebo-controlled with NHYA Class III • Randomized to HF darbepoetin alfa • Well-tolerated, but (starting dose, 0.75 no increase in ug/kg) or placebo exercise tolerance subcutaneously Q2W for 52 weeks • A trend towards ↓ mortality and hospitalization Applicability Darbepoetin is well tolerated and showed trends towards improvement: • Exercise tolerance • Mortality • Hospitalization rate Circulation. 2008;117:526–35. Swedberg K, et al. Study Design • Randomized, double-blind, multinational, placebo-controlled • Randomized to darbepoetin alfa 0.75 ug/kg (titrate to Hg>13.0) or placebo SQ Q2W • Iron therapy given if TSAT <20% Results Applicability • n=1136 (treatment) • Do not support • n=1142 (placebo) the use of darbepoetin to • Primary composite reduce the rate of outcome: hospitalization or o Treatment: 576 death from any (50.7%) cause. o Placebo: 565 (49.5%) • Increased embolic and thrombotic events in the treatment group • A low hemoglobin value may be a marker of poor prognosis versus a treatment target N Engl J Med. 2013;368:1210–19. Conclusions Treatment Target Poor Prognostic Sign The Use of EPO-Stimulating Agents in Heart Failure Nora Sharaya, PharmD PGY2 Pharmacotherapy Resident Butler University & Community Health Network Email: nsharaya2@ecommunity.com