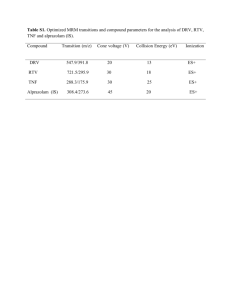
Roles of protease inhibitors for HIV infected children - HIV-NAT
advertisement

Roles of protease inhibitors for HIV infected children By Kulkanya Chokephaibulkit, MD Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Mahidol University WHO Recommendation When to Start ART in Children: 2013 WHO Recommendation for 1st Line ART: 2013 WHO Recommendation for 2nd Line ARV 2013 US Recommended First Line Regimens • NRTI + NNRTI or PI: • Choice of NNRTI or PI – ≥6 years: atazanavir/ritonavir (AI*) – ≥3 years: efavirenz (AI*) – ≥42 weeks postmenstrual and ≥14 days postnatal: lopinavir/ritonavir (AI) • Choices of NRTI – ≥3 months: abacavir + (lamivudine or emtricitabine) (AI) – Adolescents, Tanner Stage 4 or 5: tenofovir + (lamivudine or emtricitabine) (AI*) – Any age: zidovudine + (lamivudine or emtricitabine) (AI*) First-line ART with a PI vs NNRTI an open-label, randomised (PENTACT-1): Time to switch 71% were still on 1st line 57% were virologic suppress on 1st line The PENPACT-1 (PENTA 9/PACTG 390) Study Team. The Lancet. Feb 1, 2011:1-11. LPV/r Better Than NVP in Infants 2-36 Month-Old Who Had No Exposure to NVP: 6 African countries and India (N=288) May be NVP require step-up dosing, or LPV/r is more forgiving. Violari A. NEJM 2012;366:2380-9 เกณฑ์ การเริ่มยาต้ านไวรั สในเด็กติดเชือ้ เอชไอวี 2013 (Draft) อาการแสดง ทางคลินิก หรื อ อายุ < 1 ปี อายุ 1-5 ปี > 5 ปี เริ่มการ รั กษา CDC cat B, C หรื อ WHO stage 3, 4 CDC catB, C หรื อ WHO stage 3, 4 ระดับ CD4 ที่ควรพิจารณาเริ่มยาต้ านไวรั ส % CD4 หรื อ ระดับ CD4 เริ่มการ รั กษา %CD4 <25 OR CD4 <500cells/mm3 1-3 yr CD4 < 1000 cell 3-5 yr CD4 < 500 cell ยาต้ านไวรัสในเด็กติดเชือ้ เอชไอวี ARV naïve Thai guideline 2013 (draft) Preferred < 1 year 1-3 years 3-12 years > 12 years AZT (ABC) /3TC/LPV/r AZT (ABC)/ 3TC + LPV/r or NVP AZT (ABC)/ 3TC + EFV TDF/3TC + EFV AZT /3TC /NVP Alternative AZT (d4T) /3TC/NVP d4T/3TC + LPV/r or NVP If anemia d4T first 6 mo. TDF/ 3TC + EFV (NVP) AZT/ 3TC + EFV or NVP If anemia d4T first 6 mo. Proposed Second Line ARV Regimen for Thai Children (2013) Failing first line Preferred Second line AZT+3TC +NNRTI TDF + 3TC + LPV/r* TDF or ABC +3TC +NNRTI AZT + 3TC + LPV/r* AZT+3TC+LPV/r TDF (ABC) + 3TC + EFV (if no NNRTI-R) TDF (ABC) +3TC + DRV/r (if NNRTI-R) ABC+3TC+LPV/r TDF + AZT+ EFV (if no NNRTI-R) TDF+ AZT + DRV/r (if NNRTI-R) • *If cannot tolerate LPV/r or developey dyslipidemia, replace with ATV/r • Avoid using ddI due to problems of absorption, formulation, interaction, AE สูตรยาต้ านไวรัสที่ใช้ ในเด็ก ภายใต้ หลักประกันสุขภาพถ้ วนหน้ า 2013 (จานวน 5565 คน) EFV based NVP based PI based 0.01 29% PI+NRTI others 21% EFV+NRTI NVP+NRTI 49% First Antiretroviral Regimens in Asian Children: TreatAsia 2010 (11 sites from Cambodia, Indonesia, India, Malaysia, and Thailand), N=1655 Hansudewechakul R. JAIDS 2010:55:503-9 Others 4% PI-based 6% EFV-based 29% At start of HAART (Median) Age = 7 year-old CD4% = 8% CD4 count (>6 yo) = 100.5 NVP-based 61% Switch Rate NNRTI to PI = 4.1/100 person-year PI to NNRTI = 3.8/100 person-year Outcomes of Second Line PI Regimen in Asian Children (TApHOD data) 153 children who were receiving PI for >24 weeks Median age 10 yo. 83% used LPV/r At 48 weeks At 96 weeks Immune recovery 61% 70% UD HIV-RNA 60% 65% Hyper TG (>130 mg%) 73% 66% Bunupuradah T. Antivir Ther 2013 High virologic response rate after second-line boosted protease inhibitor-based antiretroviral therapy regimens in children from a resource limited setting Puthanakit T. AIDS Research and Therapy 2012. http://www.aidsrestherapy.com/content/9/1/20/abstract Lopinavir/r in Children Pros Cons • Well known efficacy • Excellent short term safety • Cheapest • Pediatric formulation available • Co-formulate with RTV • The first PI recommended in most guidelines • Long term metabolic complications • High pill count • OD not approved for children Atazanavir/r in Children Pro Con • OD • Less dyslipidemia • Recommended as preferred PI in children >6 yo • Not for <6 year-old • Hyperbilirubinemia • Need RTV boosting (no co-formulation) • More expensive Efficacy of Atazanavir in Children 6-18 Year-Old at 24 Weeks of Rx 15-25 kg: 150/80 mg; 25-32 kg: 200/100 mg, 32-39 kg: 250/100 mg; >39 kg: 300/100 mg 180 • Safety: Cough 21% 171 Jaundice 13% Fever 19% Increase bilirubin 49% 160 140 116 120 100 80 60 40 Rx naïve (24/41) Rx experienced 59 (14/58) 24 20 0 % with VL < 50 CD4 gain http://www.aidsmap.com/en/news/80F577BE-9DFE-4796-B4A7-BC9E0CB33149.asp Characteristics of Lipodystrophy from Protease Inhibitors • Fat gain on abdomen, breast, and dorsocervical hump • Fat loss from peripheral extremities • Fat gain in visceral organs Dyslipidemia found 40%-80% in children, associated with receiving PI and lipodystrophy1-3 Prevalence of Dyslipidemia in a European cohort of HIV-infected children and adolescents (N=426), 60% receiving PI4 Fasting Hypertriglyceridemia 66% 45% 21% Hyper-cholesterolemia 49% 28% 1% Glucose intolerance 5% 4% 1.Lapphra K. J Med Assoc Thai. 2005. 2. Taylor P. Pediatrics 2004. 3. Amaya RA. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2002, 4. Alam NM. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2012 March 1; 59(3): 314–324 Frequency of abnormal lipid profile in Thai adolescents Siriraj, Bangkok, 2013 HIV-infected N = 100 Healthy Total = 50 P value CHOL > 200 mg/dl 25 (25%) 12 (24%) 0.867 LDL > 130 mg/dl 16 (16%) 8 (16%) 0.733 HDL < 35 mg/dl 8 (8%) 0 (0) 0.017 TG > 150 mg/dl 37 (37%) 1 (2%) <0.001 49% receiving PI V. Poomlek. 7th IAS 2013, KL, MOPE047 Metabolic Syndrome in children and adolescents: The clusters of metabolic risk factors (International Diabetes Federation) FBS > 100 mg/dl BP>130/85m mHg Waist circumference > P90 HDL<40 mg/dl (<50 mg/dl in female >16 yo Presence of metabolic syndrome increases the risk of DM and CVD TG>150 mg/dl The cIMT in association with on PI > 6 months in HIV-infected Thai adolescents cIMT (mm) Receiving PI > 6 months (n=53) Receiving PI < 6 months or P value never(n=47) Proximal CCA 0.393 (0.284-0.478) 0.369 (0.289-0.448) 0.019 Distal CCA 0.40 (0.273-0.475) 0.381 (0.311-0.441) 0.022 ICA 0.353 (0.283-0.514) 0.345 (0.26-0.431) 0.179 Overall cIMT 0.379 (0.284-0.451) 0.372 (0.287-0.423) 0.02 The values were presented in median (range) Risk of Myocardial Infarction in Patients Exposed to Specific Individual Antiretroviral Drugs : The Data Collection on Adverse Events of Anti-HIV Drugs (D:A:D) Worm SW. JID 2010;201:318-30. Contribution of risks factors for CAD in HIV-Positive Persons 1.04 1.25 1.47 Estimated effect (95%CI) on the odds ratio of a first CAD event for: - genetic risk score quartile (black dots), - HIV-related variables (gray triangles) - traditional CAD risk factors (gray squares). Rotger M. CID 2013 Jul;57(1):112-21. Estimated chronic kidney disease and antiretroviral drug use in HIV-positive patients CKD defined as confirmed (persisting for 3 months) decrease in eGFR to 60 ml/min per 1.73m2 or less if eGFR at baseline above 60 ml/min per 1.73m2 or confirmed 25% decrease in eGFR if baseline eGFR 60 ml/min per 1.73m2 or less). Mocroft A. AIDS 2010;24:1667-78. After failing second line or AE from second line regimens, what’s next? • Integrase inihibitor: RAL • PI: DRV/r • NNRTI: ETV New regimen should compose of 2-3 fully active drugs An Adolescents who resist to everything Date 26/11/1996 Age 5Y1M 23/3/1999 7Y3M 9/10/2001 9Y9M 18/3/2003 10/8/2004 17/7/2007 11Y3M 12Y8M 15Y7M 20/8/2007 15Y8M 22/1/2008 28/4/2009 Regimen Start AZT+ddI Start AZT+3TC+EFV Start AZT+3TC+IDV/r “ “ “ Start TDF+3TC+LPV/r 16Y1M “ 17Y4M “ CD4 CD4% 312 6.43 VL - Remark 514 2.07 - 27 0.69 - 357 654 468 9.44 16.55 14.87 72,000 <400 4,830 V-Resistant NRTI=M41L, D67N, K70R, M184V, K219Q NNRTI=A98G, G190A LPV and TDF became available 544 - 12.49 - 997 8,240 V-Resistant RT=M41L, D67N, T69N, K70R, A98G, M184V*, G190A, H208Y*, T215S* PR=L10F, G16E, K20I, M36I, M46I, K55R, H69K, L89M, L90M, I93L The genotype of AC076 Date Age 28/4/2009 17Y4M 28/7/2009 17Y7M 27/4/2010 18Y3M 6/7/2010 18Y7M 18/1/2011 19Y1M Regimen “ CD4 % Remark 544 12.49 8,240 V-Resistant RT=M41L, D67N, T69N, K70R, A98G, M184V*, G190A, H208Y*, T215S* PR=L10F, G16E, K20I, M36I, M46I, K55R, H69K, L89M, L90M, I93L “ 376 14.53 Start AZT/3TC+TDF +DRV/r “ “ VL - 435 11.01 9,910 418 14.96 <40 ได้ ยา DRV จาก Dance Program Case Failure With Extensive Resistance Date. Age Regimen 22/9/98 1Y5M Start CD4 CD4% VL 956 15 - 890 30 - Remark AZT+3TC 30/10/01 4Y7M Start ddI+d4T+EFV 18/11/03 6Y8M “ 1,240 27 - 14/2/06 8Y11M Start 814 26 - 627 22 Only NNRTI available. (Should not be done.) Lipodystrophy. AZT+3TC+EFV 14/8/07 10Y5M “ 10,400 V-Resistant NRTI = D67N, K70KR, M184V,T215F, K219Q, G333E NNRTI = Y188L 26/2/08 10Y11M Start 898 22 - Check IDV level ok 3TC+IDV+LPV/r 19/8/08 11Y5M “ 884 27 <40 11/8/09 12Y5M Start 595 32 <40 AZT/3TC+DRV/r Hyperlipidemia. Darunavir/r The third line PI of choice Pros • Most potent PI • Works in patients resisted to other PIs • Less dyslipidemia • Well tolerate • Approve from 3 year-old Cons • Expensive • Need RTV boosting, no co-formulation • OD only in >12 yearold Risk of triple-class virological failure in children with HIV: a retrospective cohort study Incidence per 100 person-years (95% CI) of triple-class virological failure in children with HIV by duration of antiretroviral therapy *At end of year 9. The Pursuing Later Treatment Options II (PLATO II) project team for the Collaboration of Observational HIV Epidemiological Research Europe (COHERE)*. The Lancet 2011;377:1580-7. DELPHI: Darunavir EvaLuation in Pediatric HIV-1Infected treatment-experienced patients • Patients – ARV treatment-experienced, HIV-1-infected pediatric patients (aged 6–17 years, on HAART ≥12 weeks, HIV-1 RNA ≥1000 copies/mL) • Objective – Evaluate safety, tolerability and efficacy of Darunavir/r plus an OBR over 48 weeks in an open-label, Phase II study (TMC114-C212) • 6–17 years old • On HAART ≥12 weeks • HIV-1 RNA ≥1000 copies/mL • (N=80) 20–<30kg: Darunavir/r 375/50mg bid (n=20) 30–<40kg: Darunavir/r 450/60mg bid (n=24) ≥40kg: Darunavir/r 600/100mg bid (n=36) ARV = antiretroviral; HAART = highly-active antiretroviral therapy; OBR = optimized background regimen (≥2 ARVs) Bologna R, Spinosa-Guzman S, et al. 15th CROI 2008. Abstract 78LB Summary of antiretrovirals used at screening (N=80) NRTIs NNRTIs PIs 3TC ABC AZT d4T ddI TDF FTC EFV NVP LPV SQV APV TPV ATV NFV IDV ENF 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 Patients who had used drug at screening (%) PIs = protease inhibitors Meyers T, et al. 5th IAS 2009. Abstract 2133 NRTIs used in the OBR NRTI used, n (%) Group A (N=22) Group B (N=22) Lamivudine 12 (55) 10 (45) Abacavir 8 (36) 5 (23) Zidovudine 6 (27) 7 (32) Emtricitabine 4 (18) 3 (14) Tenofovir 12 (55) 8 (36) Stavudine 7 (32) 5 (23) Didanosine 5 (23) 10 (45) Spinosa-Guzman S, et al. 4th IAS 2007. Abstract TUPEB125 DELPHI: baseline characteristics Darunavir/r (N=80) Demographics 57 (71) Male, n (%) Age at screening, years (± SD) 6–<12 years, n (%) 12–17 years, n (%) Perinatal infection, n (%) 24 (30) 56 (70) 62 (78) Disease characteristics CDC classification C, n (%) Mean (± SD) log10 HIV-1 RNA Median CD4 cell count, cells/mm3 (range) Median CD4% (range) Mean duration of known HIV infection, years (± SD) 40 (50) 4.64 0.80 330 (6–1505) 17 (0.7–47) 10.7 (3.2) SD = standard deviation Bologna R, Spinosa-Guzman S, et al. 15th CROI 2008. Abstract 78LB DELPHI: baseline characteristics (cont’d) Darunavir/r (N=80) Previous ARV treatment Median number of ARVs (range) PIs: ≥1, n (%) NNRTIs: ≥1, n (%) NRTIs: ≥2, n (%) Enfuvirtide (ENF), n (%) 9 (3–19) 77 (96) 63 (79) 80 (100) 8 (10) Median number IAS USA mutations1 Primary PI mutations (range) PI RAMs (range) NNRTI RAMs (range) NRTI RAMs (range) 3 (0–6) 11 (0–19) 1 (0–4) 4 (0–8) 1. Johnson VA, et al. Top HIV Med 2006;14:125–130 PI = protease inhibitor; RAMs = resistance-associated mutations Bologna R, Spinosa-Guzman S, et al. 15th CROI 2008. Abstract 78LB DELPHI: Virologic response to Week 48 (ITT-TLOVR) ≥1 log10 HIV-1 RNA reduction HIV-1 RNA <400 copies/mL HIV-1 RNA <50 copies/mL Response rate (%) 100 80 65% 59% 48% 60 40 20 0 0 2 4 N = 80 8 12 16 20 24 32 Time (weeks) 40 48 80 ITT = intent-to-treat; TLOVR = time-to-loss of virologic response Blanche S, et al. AIDS 2009;23:2005–13 DELPHI: Mean change in CD4 cell count to Week 48 (ITT-NC=F) Mean change in CD4 count (cells/mm3 ±SE) 200 150 +147 100 50 0 0 2 4 8 12 16 N = 80 20 24 32 Time (weeks) 40 48 80 NC=F = non-completer considered failure Blanche S, et al. AIDS 2009;23:2005–13 DELPHI: Effect of number of baseline DRV resistance-associated mutations on virologic response – Week 48 analysis Responders At least 1 log10 decrease VL <50 copies/mL DRV resistanceassociated mutations at baseline N n % n % 0 39 29 74 23 59 1 17 12 71 8 47 2 15 9 60 7 47 ≥3 9 2 22 0 0 Blanche S, et al. AIDS 2009;23:2005–13 DELPHI: AEs regardless of causality – Week 48 analysis‡ N=80 Mean exposure (weeks) 60 Incidence n % 1 adverse event (AE) 74 93 1 grade 3 or 4 AE 21 26 1 serious AE 11 14 1 AE leading to permanent discontinuation 1 1* Death 0 0 ‡Since first intake of drug; *Grade 3 anxiety considered unrelated to DRV/r Blanche S, et al. AIDS 2009;23:2005–13 DELPHI: Grade 2–4 treatment-related clinical AEs (incidence ≥1%)* – Week 48 analysis N=80 Mean exposure (weeks) 60 Incidence n % Diarrhea 1 1 Rash 1 1 *Laboratory abnormalities reported as AEs not shown in the table Blanche S, et al. AIDS 2009;23:2005–13 DELPHI: Grade 2–4 laboratory abnormalities (incidence ≥1%) – Week 48 analysis Mean exposure (weeks) Incidence N=80 60 ANC decreased n 10 % 13 Pancreatic amylase 9 11 ALT increased 5 6 AST increased 4 5 Lipase 3 4 ANC = absolute neutrophil count; ALT = alanine aminotransferase; AST= aspartate aminotransferase Blanche S, et al. AIDS 2009;23:2005–13 DELPHI: Mean lipid levels at baseline and Week 48 Baseline Week 48 2.8 250 Left axis mg/dL; right axis mmol/L 6.5 250 p<0.01 Mean concentration Normal values p<0.05 p<0.001 p<0.05 200 2.3 200 5.2 150 1.7 150 3.9 100 1.1 100 2.6 50 0.6 50 1.3 0 0.0 0 0.0 Triglycerides Total cholesterol LDL calculated HDL SI unit scales are different due to different conversion factors (0.0113 for triglycerides and 0.0259 for cholesterol) Blanche S, et al. AIDS 2009;23:2005–13 Lipid Changes at Week 48 with Baseline in PI Studies Small Changes of Lipid Profile Following DRV/r and ATV/r METABOLIK: Week 48 Jules Levin. 10th International Congress on Drug Therapy in HIV Infection, Glasgow, November 7-11, 2010 เกณฑ์ การอนุมัตกิ ารใช้ ยา DRV ของ สปสช (มีเฉพาะขนาดเม็ด 300 มก) 1. ไม่ เป็ น terminal ill 2. ข้ อใดข้ อหนึ่ง – 2.1 Failing while on PI regimen > 6 months with triple class mutation, >2 major PI mutation ([D30N, V32I, M46I, M46L, I47A, I47V, G48V, I50L I50V, I54L, I54M, T74P, L76V, V82A, V82F, V82L, V82S, V82T, I84V, N88S, L90M], but still susceptible to DRV and available effective backbone – Intolerance to PI 3. Likely to have good compliance Darunavir Pediatric dose (6- <18 Year-old) Recommended dose for treatmentexperienced pediatric patients (6 to < 18 years of age) Body weight (kg) Dose DRV/r (mg) ≥ 20 kg–< 30 kg 375 / 50 mg b.i.d. ≥ 30 kg–< 40 kg 450 /60 mg b.i.d. ≥ 40 kg 600 /100 mg b.i.d. ขนาดยาที่แนะนาในเด็กไทย ปรับตามยาเม็ดที่มี ขนาด 300 มก เท่ านัน้ นา้ หนัก* (กิโลกรัม) ขนาดยาที่แนะนาในเด็กไทย (สปสช) กินพร้ อมอาหาร 12–<15 DRV 300 มก. bid (ร่ วมกับ RTV 50** หรือ 100 มก.) 15–<30 DRV 450 มก. เช้ า, 300 mg เย็น (ร่ วมกับ RTV 50** หรือ100 มก.) 30–<40 DRV 450 มก. bid (ร่ วมกับ RTV 100 มก.) ≥40# DRV 600 มก. bid (ร่ วมกับ RTV 100 มก.) DRV Pharmacokinetic in Thai Children Using RTV 100 mg boosting for all Median plasma concentration (mg/l) 10 ● 20-30kg, ■ 30-40kg, ▲ >40kg BID dosing DRV/r Standard DRV/r Thai 20 to < 30kg 375/50 375/100 30 to < 40kg 450/60 450/100 ≥ 40 kg 600/100 600/100 8 6 4 2 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 Time (h) Available in 75mg, 150mg, 300mg, 400mg, 600mg tablets Chokephaibulkit K, Ananworanich J, et al Antiviral Therapy 2012 Food effect of DRV Sekar V. Clin Pharmacol 2007;47:479-84 Resistance Pattern in 44 Thai Children Who Fail Second Line Regimens Ananworanich J. OUTCOMES OF THIRD-LINE ANTIRETROVIRAL THERAPY CONTAINING DARUNAVIR, ETRAVIRINE OR RALTEGRAVIR IN THAI CHILDREN WITH HIV INFECTION 4th International Workshop on HIV Pediatrics 20-24 July 2012, XIX International AIDS Conference 22-27 July 2012. OUTCOMES OF THIRD-LINE ANTIRETROVIRAL THERAPY CONTAINING DARUNAVIR, ETRAVIRINE OR RALTEGRAVIR IN 44 THAI CHILDREN WITH HIV Ananworanich J. OUTCOMES OF THIRD-LINE ANTIRETROVIRAL THERAPY CONTAINING DARUNAVIR, ETRAVIRINE OR RALTEGRAVIR IN THAI CHILDREN WITH HIV INFECTION 4th International Workshop on HIV Pediatrics 20-24 July 2012, XIX International AIDS Conference 22-27 July 2012. OUTCOMES OF THIRD-LINE ANTIRETROVIRAL THERAPY CONTAINING DARUNAVIR, ETRAVIRINE OR RALTEGRAVIR IN 44 THAI CHILDREN WITH HIV Ananworanich J. OUTCOMES OF THIRD-LINE ANTIRETROVIRAL THERAPY CONTAINING DARUNAVIR, ETRAVIRINE OR RALTEGRAVIR IN THAI CHILDREN WITH HIV INFECTION 4th International Workshop on HIV Pediatrics 20-24 July 2012, XIX International AIDS Conference 22-27 July 2012. Treatment Simplification LPV/r วันละครั ง้ เทียบกับ วันละสองครั ง้ (+ optimized NRTIs) ในอาสาสมัครที่เคย ได้ รับการรั กษามาก่ อน แต่ ไม่ เคยได้ รับยา LPV/r (VL>1000) องค์ การอาหารและยา ประเทศสหรัฐอเมริกาได้ รับรองการใช้ ยา LPV/r วันละครัง้ สาหรับผู้ใหญ่ ท่ เี คยได้ รับการรั กษามาก่ อนที่มี =< 2 key mutations (พฤษภาคม 2010) N=300 each arm แสดงให้ เห็นว่ า ยา Lopinavir/Ritonavir วันละครัง้ ไม่ ด้อยไปกว่ า วันละสองครัง้ ในผู้ใหญ่ ท่ เี คยได้ รับยาต้ านไวรัสมาก่ อน R. Zajdenverg. M06-802 study. 5th IAS. Cape Town 19-22 July 09 Switching LPV/r from BID to OD in Children on 2nd Line Rx with VL<50 copies/mL: N=11 All had VL < 50 copies/ml at 12, 24, and 48 weeks of OD dosing • AUC for OD and BID were not different • Cmin in OD was lower than in BID. 7 children had Cmin < 1 mcg/mL. • Taking EFV (N=6) with LPV/r OD associated with lower Cmin , but no effect on AUC Chokephaibulkit K, et al. JAC 2012, Aug 23. doi:10.1093/jac/dks332 DIONE: 24 Week Efficacy, Safety, Tolerability and Pharmacokinetics of Once Daily DRV/r in Treatment-Naïve Adolescents, 12 to <18 years Flynn P et al. 2011 6th IAS Conference, Rome, Italy Abs WePDB0101 HIV RNA <50 c/mL 200 Response (± SE): HIV-1 RNA <50 copies/mL (ITT-TLOVR; %) 92% 80 175 100 40 DRV/r (N=12) 20 CD4 cell count increase 150 60 Mean (± SE) change in CD4 cell count (cells/mm3) (NC=F) 100 0 BAS 2 4 8 Time (weeks) 16 24 11/12 (92%) patients achieved HIV-1 RNA <50 copies/mL (ITT-Time Loss of Viral Response) 12/12 (100%) by FDA snapshot algorithm One patient with one DRV RAM (V11I) at baseline was a responder at Week 24 DRV/r (N=12) 50 0 BAS 2 4 8 Time (weeks) 16 24 Mean CD4 cell count increased by 175 cells/mm3 2 patients reported AEs at least possibly related to treatment (all grade 1 or 2) No patient discontinued DRV/r due to an AE No deaths ARIEL: PK substudy • Optional for patients with confirmed HIV-1 RNA <50 copies/mL at Week 32 • DRV/rtv 40/7 mg/kg qd dose determined with population PK model using data from the Week 2 analysis • Ten patients participated: 5 female; 7 weighed ≥15kg, 3 weighed 14 to <15kg DRV AUC0–24h geometric mean, μg•h/mL (SD) DRV C0h geometric mean, ng/mL (SD) ARIEL qd sub-study (n=10) Adult (ARTEMIS)1 (N=335) Adults, % 115 (40.6) 89.7 (27.0) 128 3029 (1715) 2027 (1168) 149 • No treatment-related or grade ≥2 AEs were reported • All patients retained HIV-1 RNA <50 copies/mL during the two-week substudy AUC0–24h=AUC between 0 to 24 hours 1. Janssen data on file ARIEL: PK substudy Virologically suppressed (<50 copies/mL) patients at ≥ Week 24 switched to DRV/r 40/7mg/kg qd 14,000 DIONE Week 2 (n=12) ARTEMIS* Week 4 (n=9)1 ARTEMIS* Week 24 (n=13)1 ARIEL substudy Weeks 32–40 (n=10) 12,000 DRV plasma concentration (ng/mL) • 10,000 8000 6000 4000 2000 0 0 *Adults 4 8 12 16 20 24 Time (hours) 1. Janssen data on file Pharmacokinetics and 48-weeks efficacy of once daily darunavir/ritonavir in virologic suppressed HIV-infected Thai children: a pilot study Weight band BID OD 20 to <30 kg. DRV 375 + RTV 100 DRV 450 + RTV 100 30 to <40 kg. DRV 450 + RTV 100 DRV 600 + RTV 100 ≥ 40 kg. DRV 600 + RTV 100 DRV 900 + RTV 100 6/8 children maintained virologic suppressed to 48 weeks of OD dosing Chokephaibulkit K, 7th IAS 2013, Kuala Lumpur. Abs# MOPE047 Conclusions: Recommended DRV/rtv pediatric dosing 3 to <6 years ARVexperienced 10 to 15kg: 20/3mg/kg bid 15 to 20kg: 375/50mg bid 6 to <12 years ≥20 to <30kg: 375/50mg bid ≥30 to <40kg: 450/60mg bid ≥40kg: 600/100mg bid 10 to 15kg: 35/7mg/kg qd ARVnaïve 15 to 30kg: 600/100mg qd 30 to 40kg: 675/100mg qd US and EU US only 12 to <18 years 40kg: 800/100mg qd DRV: drug interaction data available No dose adjustment of DRV or co-administered drug Tenofovir (TDF) Clarithromycin (CLAR) Atazanavir (ATV) Ketoconazole (KTZ) (max dose 200mg) Efavirenz (EFV) Paroxetine (PAR) Sertraline (SER) Didanosine (ddI) Modify dose or schedule of co-administered drug Atorvastatin (ATORV) Sildenafil (SIL) Pravastatin (PRA) Ethinyl estradiol (EE) Norethindrone (NE) Digoxin Nevirapine (NVP) Etravirine (ETR) TMC125 Ranitidine (RAN) Omeprazole (OME) Indinavir (IDV) Enfuvirtide (ENF) Methadone (MTD) Not recommended Saquinavir (SQV) Lopinavir (LPV) Back D. et al Antivir Ther. 2008; 13:1-13 Raltegravir/Etravirine/r-Darunavir Combination in Adolescents with Multidrug-Resistant Virus Percent (N=12) 100 100 90 92 80 70 83 75 60 VL <400 VL <50 50 40 42 30 20 42 25 10 0 Month 8 1 3 6 9 Of treatment Thuret I. AIDS 2009;23:2364-6. THANK YOU