Control of Clostridium difficile
advertisement

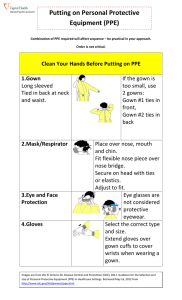
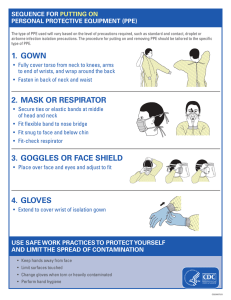
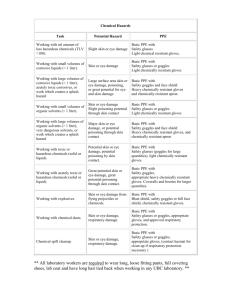
Agent: is a sporeforming, gram-positive anaerobic bacillus that produces two exotoxins: toxin A and toxin B. These cause colon dysfunction and cell death. infection may manifest as ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Mild diarrhea Pseudomembranous colitis (PMC) Toxic megacolon Perforations of the colon Sepsis Death Gram stain of C. difficile From Public Health Image Library Watery diarrhea, often foul-smelling Fever Loss of appetite Nausea Abdominal pain/tenderness is shed in feces, even after symptoms resolve Any surface, device, or material (e.g., toilets, bathing tubs, and electronic rectal thermometers) that becomes contaminated with feces may serve as a reservoir for the spores. spores can survive for long periods (months to years) on surfaces. Spores are transferred to patients primarily by the hands of healthcare personnel who have touched a contaminated surface or item. Image: http://www.cdiff-support.co.uk/about.htm Increasing incidence and severity Recent outbreaks of severe disease caused by epidemic strain of (BI/NAP1/027)with increased virulence, antibiotic resistance Persons at greatest risk More disease reported in “low-risk” persons UTMB has treated patients with the new epidemic strain ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Advanced age Severe underlying disease Immunosuppression GI surgery or manipulation ◦ Healthy persons in community, peripartum women Historically uncommon, now epidemic More resistant to fluoroquinolones Carries extra toxin known as binary toxin There is an 18-base pair deletion in the regulatory gene (tcdC) responsible for toxin production. This strain produces 16 times as much toxin A and 23 times as much toxin B in vitro. More severe disease, higher mortality, more frequent relapses Implement for patients with watery diarrhea not explained by non-infectious conditions. For patients isolated on basis of symptoms: isolation can be discontinued if test is negative If the laboratory test for is positive, patient must remain isolated for duration of hospitalization. If a test is positive, do not order a later test as a “test of cure” or to discontinue isolation. . You will be wearing a gown and gloves to enter the room. If you are performing a procedure that may splatter respiratory secretions to your face, you will need facial protection-a face shield or goggles and a mask. Gown first Mask or respirator Goggles or face shield Gloves Combination of PPE is not the same for all types of precautions. Extended Contact Precautions requires the use of a gown and gloves. Source: CDC Note: clean hands before donning PPE. Select appropriate type and size Opening is in the back Secure at neck and waist If gown is too small, use two gowns ◦ Gown 1 ties in front ◦ Gown 2 ties in back Source: CDC Don gloves last Select proper type and size Insert hands into gloves Extend gloves over cuffs of isolation gown Keep gloved hands away from face Avoid touching or adjusting other PPE Remove gloves if they become torn; perform hand hygiene before donning new gloves Limit surfaces and items touched. Source: CDC Contaminated-outside front ◦ Areas of PPE that have or are likely to have contact with body sites, materials, or environmental sources where the infectious organism may reside Clean-inside of gown, outside back of gown, ties on head (mask) and back (gown) ◦ Areas of PPE that are not likely to have been in contact with the infectious organism Source: CDC 1. 2. 3. 4. Gloves Face shield or goggles (if worn). Avoid touching front of goggles or shield to remove. Gown Mask or respirator (if worn). Avoid touching the front of the maskuse ties or elastic to remove. Source: CDC Grab outside edge near wrist Peel away from hand, turning first glove inside-out. Hold in opposite gloved hand. Slide ungloved finger under wrist of remaining glove. Peel off from inside, creating a bag for both gloves. Discard Clean hands •Unfasten ties •Peel gown away from neck and shoulder •Turn contaminated outside away from inside •Fold or roll into a bundle •Discard Source CDC Clean your hands after PPE removal If your hands become visibly contaminated during the process of PPE removal, wash hands before to continuing to remove PPE. For Extended Contact Precautions: ◦ You may use alcohol hand sanitizer BEFORE patient contact. ◦ You must use CHG soap and water AFTER contact For all other types of isolation, either hand sanitizer or CHG soap is effective both before and after patient contact. Most hospital-grade disinfectants are not effective against If the surface can tolerate (sodium hypochlorite) use a , which can be purchased pre-diluted or made fresh (1 part bleach, 9 parts water). If the surface does not tolerate ,a thorough physical cleaning is necessary. Because patients may be moved and their equipment may accompany them, supervisors for Environmental Services and Clinical Equipment Services will be notified of new cases of . If you enter a room with equipment, you will see the sign. If you are scheduling a patient for procedures/ tests off the unit or transferring the patient to another unit, be sure to include information about isolation during the scheduling process and as a part of the handoff. . As a general rule, the room of patient in will be available as soon as Environmental Services has finished cleaning and disinfecting the environment. In some cases, cultures will be taken before and after the terminal clean as a quality control measure. Healthcare Epidemiology will coordinate with the appropriate Environmental Services supervisor/staff member. The room may be released as soon as cultures are collected.