THYROID 1.16.15 - Southern Regional AHEC
advertisement

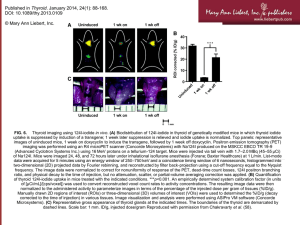
Fayetteville VA Medical Center Grand Rounds January 16, 2015 Fayetteville, NC Thyroid Update Stanley A. Tan MD, MS, MPH, PhD, DTM&H, FACE, FACC, FCCP Disclosure Statement • Nothing to disclose Objectives • After this grand rounds presentation, you should be able to: – 1. Diagnose and manage hypothyroidism & hyperthyroidism – 2. Evaluate and manage thyroid nodule(s) and goiters – 3. Describe and manage thyroid cancers Thyroid Anatomy • • • • • Largest endocrine organ in body—20 g Right and left lobes Isthmus Pyramidal lobe Goiter = enlargement of thyroid – Diffuse – Nodular Thyroid Physiology • Iodide + tyrosine – MIT & DIT • • • • • MIT + DIT = T3 2 DIT = T4 Thyroglobulin – storage Thyroid binding globulin – circulation Deiodinase – T4 T3 Thyroid Physiology • Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Thyroid Axis – TRH (stimulates TSH & Prolactin) – TSH – T4 & T3 – Negative feedback • Thyroid C-cell – Calcitonin – Thyroid Medullary Carcinoma (MEN type II) Thyroid Diagnostic Evaluation • TSH • Free T4 – Old tests: T4, T3 uptake, FTI • T3—Total & Free T3 • Thyroid Peroxidase Antibody – Old test: Anti (thyroid) microsomal antibody • Thyroglobulin Antibody • Thyroglobulin Thyroid Imaging • Thyroid Ultrasound Scan – Anatomical • RAI Thyroid Uptake & Scan – Physiologic & Anatomical – Uptake • High: Graves’, Hashimoto Thyroiditis, Plummer’s • Low: Hypothyroidism, exogenous thyroid or iodine, Subacute Thyroiditis – Scan • • • • Graves—Diffuse Hashimoto—Diffuse or patchy Plummer’s—Multi hot nodules Cold nodule—1-5 % malignancy FNA Thyroid Biopsy • Solitary Nodule • “Cold” nodule – If negative, observe; repeat ultrasound scan 6 mo, rebiopsy if larger; continue observe if stable – If indeterminate, thyroid suppression; ultrasound 6 mo later, rebiopsy if larger or not shrinking Hypothyroidism • Symptoms – Weight gain, tired, sleepy, cold intolerance, constipation • Signs – Myxedema facie, dry skin, scalp hair loss, brittle nail, periorbital edema, decreased DTR – Goiter • Hashimoto thyroiditis, adenomatous • No goiter: Idiopathic Primary Hypothyroidism Hypothyroidism • Diagnostic Studies – TSH, Free T4, Thyroid Peroxidase Antibody – Thyroid Ultrasound Scan • Therapy – Levothyroxine – Dessicated Thyroid – Liothyronine Hyperthyroidism • Graves – – – – Graves opthalmopathy Goiter Hyperthyroidism Thyroid Stimulating Immunoglobulin (TSI) • Hashimoto Thyrotoxicosis – Thyroid Peroxidase Antibody • Plummer’s Disease – Hyperthyroid Multinodular Goiter Hyperthyroidism • Subacute Thyroiditis – Painful Goiter – Elevated Sed Rate – Decreased RAI Thyroid Uptake • • • • Acute Suppurative Thyroiditis Struma Ovarii Exogenous thyroid Secondary—TSH producing pituitary tumor Goiter • Diffuse – – – – – Hashimoto Thyroiditis Graves’ Disease Subacute Thyroiditis Postpartum, Silent, Painless Thyroiditis Adenomatous Goiter • Multinodular – Plummer’s Disease – Adenomatous Multinodular Goiter • Solitary Nodule Evaluation of Thyroid Nodule • FNA Thyroid Biopsy – Solitary Nodule – Dominant Nodule in a Multinodular Goiter – “Cold” Nodule • If benign, observe, repeat ultrasound scan in 6 mo • If indeterminate, suppress, repeat scan, rebiopsy if not shrinking or enlarging Thyroiditis • • • • • Hashimoto Thyroiditis Subacute Thyroiditis Postpartum, Silent, or Painless Thyroiditis Acute Infectious Thyroiditis Riedel’s thyroiditis Hashimoto Thyroiditis • Chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis • Associated Polyglandular auto-immune disease (Schmidt’s Syndrome) • Thyroid Peroxidase Antibody • Transient hyperthyroidism (Hashimoto Thyrotoxicosis), euthyroidism, then hypothyroidism Thyroid Cancer • • • • • Thyroid Papillary Carcinoma Thyroid Follicular Carcinoma Thyroid Medullary Carcinoma Undifferentiated Thyroid Carcinoma Lymphoma Thyroid Carcinoma • Thyroidectomy • High dose I-131 radiation therapy • Synthroid suppression – Non-detectable TSH • Yearly Thyroglobulin level • RAI Total Body Scan – Year anniversary – Thyrogen stimulated Thyroid Carcinoma • Thyroid Papillary Carcinoma – Local lymph node invasion • Thyroid Follicular Carcinoma – May be mixed with papillary – May be T4 producing—can cause hyperthyroidism with metastases – Hematogenous metastases to bone Thyroid Medullary Carcinoma • Thyroid C-Cells • Calcitonin • MEN Type II – Sipple Syndrome – Pheochromocytoma, Thyroid Medullary Carcinoma, Parathyroid Adenoma – Autosomal Dominant • Surgery