Cardiac Enzymes
advertisement

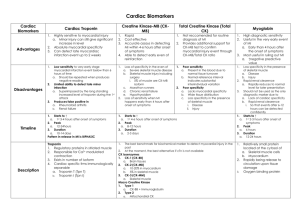
Cardiac Enzymes By Michael W. Bowers CK-MB 3hr, peak 12-24hr lasts 1-3 days Troponin 3-12 hrs, peak 12-24hr, lasts 8-21 days Trop-T and 7-14 Trop-I What is Creatine Kinase? What is Creatine Kinase? • • • • Creatine kinase is an enzyme CK catalyses the conversion of creatine Uses ATP to create phosphocreatine (PCr) and ADP. This CK enzyme reaction is reversible, such that also ATP can be generated from PCr and ADP. • PCr serves as an energy reservoir for the rapid buffering and regeneration of ATP in situ and for intracellular energy transport • Where, Oh Where, is Creatine Kinase MB Isoenzyme? Will Where, Oh Where, is Creatine Kinase MB Isoenzyme? • Myocardium • 1-2% in – Skeletal Muscle – Tongue – Small intestine – Diaphragm What Causes Creatine Kinase Levels to Rise? What Causes Creatine Kinase Levels to Rise? • • • • • • • • • • • Myocardial infarction Cardioversion Cardiac Surgery PCI Hello Cath Lab! Rapid Tachycardia Hypothyroidism Extensive Trauma Rhabdomyolysis (severe muscle breakdown) Muscular dystrophy Myopericarditis Recent cocaine use OK Kids, Let’s Talk Troponin Troponin • Troponin is a complex of three regulatory proteins – Troponin C, troponin I and troponin T • Integral to muscle contraction in skeletal and cardiac muscle, but not smooth muscle • More Cardiac Sensitive and Specific than CKMB Troponin Troponin • Released during MI from myocytes • Heart Muscle Breaks Down • Its subsequent release is prolonged with degradation of actin and myosin filaments • It released in 2–4 hours and persists for up to 7 days. Diff DX of Elevated Troponin • • • • Acute infarction, Renal failure Severe pulmonary embolism causing acute right heart overload Heart failure – – – – – – – – • Myocarditis. Tachy- or bradyarrhythmias, or heart block Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy Cardiac contusion or other trauma including surgery, ablation, pacing, implantable cardioverter-defibrillator shocks, cardioversion, endomyocardial biopsy, cardiac surgery, following interventional closure of atrial septal defects Aortic dissection Aortic valve disease Apical ballooning syndrome - Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy Rhabdomyolysis with cardiac injury Critically ill patients, – especially with diabetes, respiratory failure or sepsis • Acute neurological disease – • stroke or subarachnoid hemorrhage Infiltrative diseases – amyloidosis, hemochromatosis, sarcoidosis, and scleroderma • Inflammatory diseases – myocarditis or myocardial extension of endo-/pericarditis, Kawasaki disease • • Burns, especially if affecting >25 percent of body surface area Extreme exertion Timing • Cardiac enzymes leak slowly into the blood • High levels of cardiac enzymes may take six or more hours after the onset of a heart attack • Pt with chest pain but normal levels of cardiac enzymes = a heart attack cannot be ruled out • Repeated cardiac enzymes tests are normally conducted to confirm diagnosis of a heart attack CK-MB 3hr, peak 12-24hr lasts 1-3 days Troponin 3-12 hrs, peak 12-24hr, lasts 8-21 days Trop-T and 7-14 Trop-I • • • • • • • • • • • • Hurst’s The Heart Up to date http://www.publicsafety.net/serum.htm ucl.ac.uk homemed.co.za wikipedia www.duhs.edu.pk/curriculum Webmd jwilliames.wordpress.com animalcapshunz.icanhascheezburger.com buildingpersonalstrength.com awakeningbusiness.com