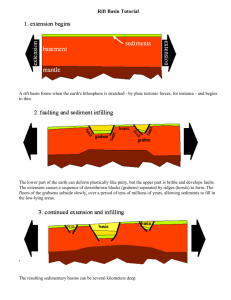
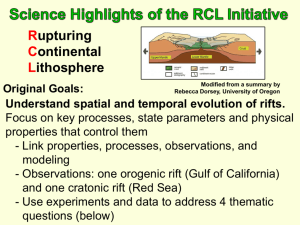
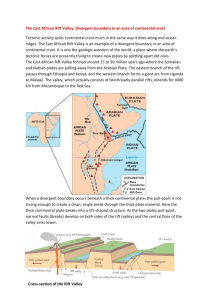
Document
advertisement

QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Wadati-Benioff zone: zone of seismicity created by slip between upper surface of slab and lithosphere of the upper plate QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Reminder / change in schedule Friday is a discussion of the paper “How Erosion Builds Mountains” by Pinter and Brandon. Paper is on electronic reserve On Wednesday, we will talk about tectonic basins Rift to drift: a story of extension Four main stages related to Wilson cycle RIFT VALLEY stage, prior to continental splitting; caused by upwelling of hot mantle material? Example: East African Rift YOUTHFUL stage: thermal effects dominate for about 50 my after the onset of seafloor spreading. Example: Red Sea MATURE stage: subdued regional subsidence. Example: most of the present Atlantic continental margins FRACTURE stage: subduction starts Fates of continental rift elements Development of ocean basin and passive margins aulocogen (failed rift arm) interior rifts (prone to reactivation) QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Currently active continental rifts East African rift zone Rio Grande rift Lake Baikal, Russia Salton trough, California (transtensional) Dead sea rift (transtensional) Some former continental rifts Rhine Graben, northern Europe Triassic grabens, East coast U.S. Keweenawan rift - northern midwest, U.S. base of all passive margins Elements of extensional system High- and low-angle normal faults Brittle-ductile transition Dikes lower crustal intrusion Lower crustal and lithospheric attenuation Thermal and uplift history Advection: heat transfer through magmatism Higher heat flow due to thinner crust and lithosphere, asthenosphere nearer surface thermal uplift components isostatic uplift components ISOSTASY Isostasy: the state of gravitational equilibrium between the Earth's lithosphere (analogous to iceberg) and asthenosphere (analogous to seawater). Tectonic plates ‘float’ at an elevation which depends on their thickness and relative density; thus high areas will have large lithospheric ‘roots’. Where a balance is achieved between topography and size of roots, lithosphere is said to be in isostatic equilibrium. Igneous activity Extension typically involves ‘bimodal’ volcanism, characterized by rhyolite and basalt Contrasts with andesitic volcanism of arcs QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Rift basin sedimentation sediment depocenters: accommodation space may be 10s of km deep immature sediments (lots of feldspar, lithic fragments) half grabens common Fault-controlled patterns of sedimentation: alluvial fans and debris flows Along-strike changes = segmentation of depocenters Depocenter symmetry will reflect structural symmetry Pure Shear Simple Shear Conceptual models of rift evolution passive vs. active rifting Passive - in response to far-field stress Active - in response to upwelling of asthenospheric mantle rift tip propagation: Gulf of California influence of previous structure: Tertiary formation of the Atlantic Ocean hot spots, triple junctions and aulocogens Rift to drift: a story of extension http://www.mines.utah.edu/geo/courses/UOnline/slideshow/contrift_1.html Establishing a passive margin