sciencejep Ch.12to16
advertisement

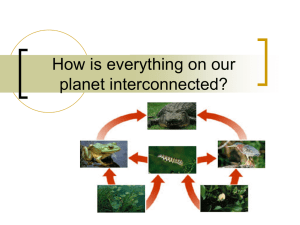
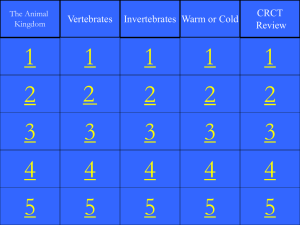
Middle School Science Jeopardy! Chapters 12-16 Ch.12 Invertbr Ch.12-13 Invertbr Ch.14 Biomes Ch.15 Ecosyst Ch.15 Interact Ch.16 Human Impact 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 500 Invertebrates 100 These invertebrates are found only in water and have stinging tentacles to help capture prey. Q: What are Cnidarians? Invertebrates 200 These animals have a tube-shaped body. Food enters at one end & exits at the other. They take in oxygen through their skin and must live in moist environments. Q: What are worms? Invertebrates 300 This class of invertebrates may live on land, freshwater, or saltwater. They have a muscular foot and a mantle or layer of folded skin that protects their internal organs. Q: What are mollusks? Invertebrates 400 This class of invertebrates live in the ocean. Their bodies have radial symmetry and they have a water vascular system. Their tube feet allow them to move on the ocean floor. Q: What are echinoderms? Invertebrates 500 An exoskeleton completely covers the body of an arthropod. For land arthropods, this structure keeps cells and tissues from drying out. However, arthropods must shed this exoskeleton as they grow and are vulnerable to predators when they molt. Q: What are advantages and disadvantages of an exoskeleton? Invertebrates 100 These invertebrates have 3 . body sections (head, thorax, abdomen) and six legs. Q: What are insects? Invertebrates 200 This class of invertebrates includes both spiders and insects. They have many pairs of legs and other parts that extend from their bodies. Q: What are arthropods? Vertebrates 300 This class of animals is warm blooded, has hair, and feeds its young milk. Q: What are mammals? Vertebrates 400 This external animal structure allows for more flexibility and ways of moving. Q: What is the advantage of an endoskeleton? Vertebrates 500 Newts and salamanders are examples of this class of vertebrates. Q: What is an amphibian? Ecosystems/Biomes 100 Living parts of an ecosystem (plants or animals) are called this. Q: What are biotic factors? Ecosystems/Biomes 200 Non living parts of an ecosystem are called this. (Water, Sunlight, Soil, Temperature, Air, etc.) Q: What are abiotic factors? Ecosystems/Biomes 300 The number of living organisms that a given area can support. Q: What is carrying capacity? Ecosystems/Biomes 400 Cattail ^ caterpillar ^ frog ^ Heron This is an example of what type of energy flow? Q: What is a food chain? Ecosystems/Biomes 500 A type of model that illustrates the feeding relationships between many different producers and consumers in a complex feeding pattern that overlaps and is interconnected. Q: What is a food web? Ecosystem Interactions 100 Biome, ecosystem, community, population, organism Q: What are the 5 levels of organization in an environment? Ecosystem Interactions 200 An interaction between two species that benefits both species. Q: What is mutualism? Ecosystem Interactions 300 McDougal-Littel or Holt Q: What are the two science books for grades 6? Ecosystem Interactions 400 A relationship between two species in which one species benefits while the other is not affected (neither harmed or helped). Q: What is commensalism? Ecosystem Interactions 500 The establishment of a new biological community in an environment that is barren (little or no topsoil present at first). Q: What is primary succession? Ecosystem Interactions 100 A relationship between two species where one species benefits and the other is harmed. Q: What is parasitism? Ecosystem Interactions 200 This generally describes the climate and types of plants found in similar places around the world.. Q: What is a biome? Ecosystem Interactions 300 The living and non-living factors that interact with each other to form a stable environment including only organisms and their local environment. Smaller than a biome. Q: What is a community? Ecosystem Interactions 400 The establishment of another ecological community after a major disturbance (like fire, flood) within a stable environment where topsoil still remains after the disturbance. Q:What is secondary succession? Ecosystem Interactions 500 Mutualism, Commensalism, Parasitism. Q: What are the 3 types of symbosis? Human Impact 100 Resources that cannot be replaced quickly enough by natural means. Q: What are non-renewable resources? Human Impact 200 Resources that can be managed and used over and over again. Q: What are renewable resources? Human Impact 300 Coal, Petroleum, natural gas, silver, gold, etc. are examples of these Q: What are non-renewable resources? Human Impact 400 The number and variety of life forms in an ecosystem as a measure of this. Q: What is biodiversity? Human Impact 500 Polluting the air, water, or soil. Destroying or changing animal habitats. Using up natural resources at too fast a rate. Q: How have humans negatively impacted the environment?