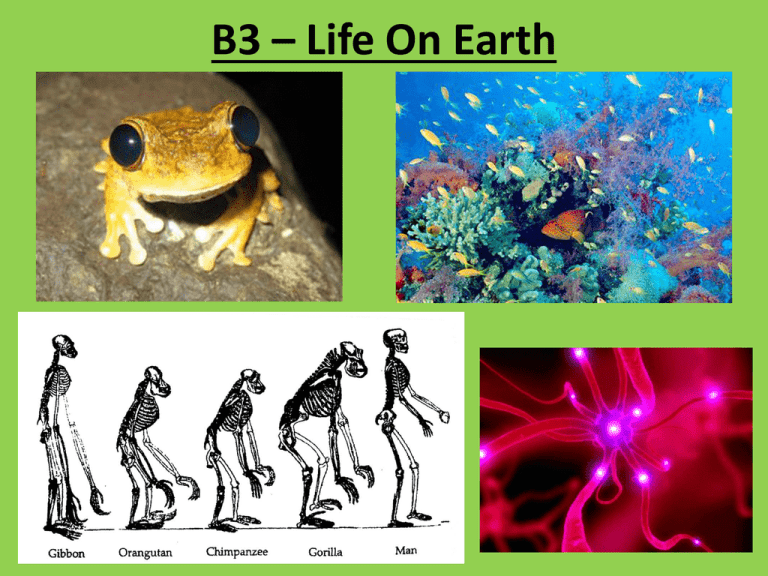
B3 – Life On Earth
Food Webs / Competition
• Living organisms are dependent on the
environment and other species for their survival
• Competition for resources between different
species that are part of the same food web
Rapid Change may cause Extinction
• Environmental Change
• New species introduced (competitor,
predator, disease organism)
• A species in the food web becomes extinct
Extinction due to Human Activity
• Hunting
• Deforestation
• Poaching
• Grey Wolf
– 1740 – Great Britain
– Deforestation and hunting
• Martinique Amazon Parrot
– 1722 – America
– Habitat cleared for
agriculture
• Bali Tiger
– 1937 - Indonesia
– Habitat loss and hunting
• Caribbean Monk Seal
– 1952 – Mexico
– Hunted for meat and oil
Biodiversity
• Biodiversity provides high variety of crops, livestock,
forestry, and fish, which are important sources of
food and medicine for humans.
• Important for sustainable development
Evolution
• All species that have
ever lived evolved from
very simple living
things.
• Life on Earth began
about 3500 million
years ago
• If conditions on Earth at
any stage were
different, natural
selection could have
produced different
results
Evidence for Evolution
• Fossils
• Similarities and Difference in DNA
The Begining of Life
• The first living things
developed from
molecules that could
copy themselves.
• These molecules
were produced by
conditions on Earth
or have come from
elsewhere (asteroid)
Natural Selection
• How evolution happens.
• The natural genetic variation within a population of
organisms means that some individuals will survive and
reproduce more successfully than others in their current
environment.
• This means that more of this organisms genes will be
passed on to the next generation
Environmental and Genetic Variation
• Variation is cause by both of these, but only
genetic variation can be passed on to offspring.
Selective Breeding
• Selective breeding is the process of breeding
plants and animals for particular genetic traits.
Mutations
• Mutations are changes in
DNA caused by radiation,
viruses or other factors.
• Mutations that occur in
sex cells (sperm or egg
cells) can be passed onto
offspring and may
produce new
characteristics (eg: 4
wings instead of 2, red
eyes, etc)
Creating a New Species
• The combined effects of:
– Environmental Changes
– Mutations
– Natural Selection
• Can product a new species over time
Evolution of Multi-cellular Organisms
• Led to nervous and hormonal communication
systems
Receptor and Effector Cells
• Neurones (Nerve Cells) link receptor
cells to effector cells
Central Nervous System
• In vertebrates, the nervous system is
coordinated by the CNS
• The Nervous
System uses
electrical
impulses for
fast, short-lived
responses. It
doesn’t make
permanent,
long lasting
changes
Hormones
• Chemicals which travel in the blood and bring
about slower, longer-lasting responses.
Examples
• Nervous Communication
– Blinking
– Muscle Control
– Heart Beat
• Hormonal Communication
– Puberty (Testosterone, Oestrogen)
– Mood, appetite, sleep (Serotonin)
– Increase heart rate and blood pressure (Dopamine)
Homeostasis
• Nervous and Hormonal systems are involved in
maintaining a constant internal environment
Larger Brain
• Evolution of larger
brain gave early
humans a better
chance of survival
– Smarter
– Quicker
– More social
– More artistic
– Language
Human Evolution
• Common
Ancestor
• Divergence
(Separation) of
Hominid
Species
• Extinction of all
but one of
these species