Jellyfish- Powerpoint
advertisement

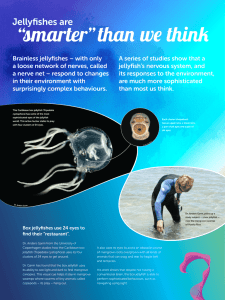
JELLYFISH No bones. No brains. But what a sting! FACTS ON JELLYFISH Belong to the Phylum “Cnidaria” Radial Symmetry Medusa shape Fertilize externally -sperm & egg released in water 2 Layers -epidermis -outer - gastrodermis -inner mesoglea -jelly between the layers Stinging cells called “ cnidocytes”. Habitat Jellyfish are found in every ocean. They live in both deep and shallow coastal waters. Feeding Jellyfish eat tiny plankton, invertebrates, larvae, and small fish. Jellyfish have sensors in their tentacles that can detect movement around them. When movement is detected, stingers shoot out and paralyze the prey. The jellyfish then uses its tentacles to bring the prey to its mouth and ingest it. Movement Jellyfish usually drift or move gracefully through the ocean, occasionally you will see them swimming. Jellyfish swim by pulsations of their umbrella or bell shape. It is coordinated by a very simple nervous system. Appearance Jellyfish often appear clear or pale blue color. But they can also be yellow, deep blue, bright purple, pale lilac, bright orange, deep red. When they are disturbed at night, they give off a cold bright light called luminescence. More Facts Made up of 95% water more than 200 species of jellyfish Jellyfish have a short lifespan, the longest surviving species living only two to six months ocean sunfish and leatherback turtles are two of the jellyfish predators LIFE CYCLE