UG-GTZ_-_prunus_Presentation-_ ICIPE

BIO-PROSPECTING PRUNUS
AFRICANA IN UGANDA
By
David L.N. Hafashimana (Ph.D)
National Forestry Resources Research Institute
(NaFORRI),
UGANDA
Background
• Bio-prospecting? Or Collaborative Research?
• Prunus africana – African medicinal plant, widely distributed – wide variations genetically & chemically.
• Commercial extraction & Export of bark a threat
• Long term survival lies in successful plantations
• Diverse plantations – higher chances of survival and market satisfaction
Background …
Project:
DEVELOPMENT OF STRATEGIES FOR THE
CONSERVATION AND SUSTAINABLE USE OF
P. AFRICANA TO IMPROVE THE
LIVELIHOODS OF SMALL-SCALE FARMERS
Coverage: Some countries in Eastern, Central and Southern Africa (eg. Cameroon, South
Africa, Uganda, Tanzania, Madagascar, Kenya,
Tanzania etc)
Partners involved
Project objectives
• Improve incomes and livelihoods of rural communities – improved germplasm
• Support national and trans-boundary insitu and ex-situ conservation strategies – establishment of gene reserves
• Strengthen capacities of nationals for mgt of forest genetic resources
Location of sample areas- Uganda
Why the bother
• Debarking taking place for bio-prospecting in different places, Africa-wide
Why the bother …
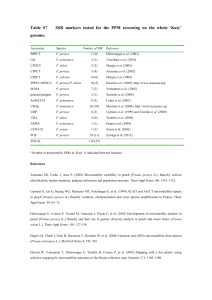
Chemical composition and Diversity of Prunus in 8 Uganda forests
Forest Docosanol (mg/g of β-sistosterol (mg/g Mean diversity dry bark) of dry bark) estimate (H)
Kibale 225 137
Mt. Rwenzori 225 150
0.2021
0.1206
Mt. Elgon
Bwindi
Bugoma
132
129
127
109
124
113
0.1757
0.1471
0.1670
0.1928 Kasyoha-
Kitomi
Kalinzu
125 101
100 103 0.1967
Mabira 29 108 0.1881
Source: Malinga M. and Boffa, J.M. (2004). Assessment of bark quality and genetic diversity of Ugandan Prunus
Africana populations for the development of on-farm cultivation and export markets. World Agroforestry Centre,
Nairobi, Kenya and Forestry Resources Research Institute, Kampala, Uganda. (Unpublished report).
Highlights of the MTA
• Type of Agreement Material Transfer
Agreement – (in line with Ugandan law)
• Type and quantity of resource(s) Prunus africana bark (for Chemical analysis) and leaves
(for genetic analysis); Small quantities for research/ analysis – (In Austria)
• Purpose of collection and expected results –
Research; results to be returned for use in mother garden (Gene reserves) establishment
Highlights …
• Location of research and development
• a)Partly in Provider country (collection, multiplication and scaling out/ planting) and b) Partly in User country (Chemical and genetic analysis – samples from different participating countries)
Highlights ….
Possible third party involvement -
Transmission to any third party, to be referred to the provider for a fresh
Agreement with the third party
Conditions if there is a change in use along the line –
Yes, New PIC and new agreement/ amendment to old agreement required for change of use
Highlights …
Type of benefits –
Non-monetary benefits
-Information sharing,
-Technology transfer
Some monetary benefits
-Funding for sample collection and
- Provision of some Scientific equipment for sample collection
Highlights …
Direct contribution to poverty alleviation, if any:
Anticipated through the improved planting stock/ germplasm to be availed to the communities for multiplication and planting for subsequent sale of the Prunus bark – proceeds to go to participating communities directly
Highlights ….
In any ABS transaction, the provider country needs to know what it needs and guide the users on what is acceptable and what is not in accordance with national law and national needs, interests and priorities.
Conclusion
We can use Biodiversity for Poverty
Eradication; Sustainability is Vital