Lecture Goals
• Introduction to the major groups of
zooplankton
• Discussion of common and distinguishing
characteristics of these groups
• Important controls on distribution and
abundance of zooplankton
Approach to Freshwater Animals
• Descriptions of major groups, organized
taxonomically when possible
• Some morphology, but I will focus on life history
and ecology
• Life History: changes experienced by an
individual between birth and death that
determine habitat requirements, ecology, and
reproductive output
• Ecology: interactions among species, or
between the focal species (stage) and physical
habitat
What are zooplankton?
• Microscopic animals that float freely in the
water column
• Very important as primary consumers –
converting energy from phytoplankton to a
form that can be used by larger animals
• Important food base for secondary
consumers, including fish
Major groups of freshwater
zooplankton
• Rotifers
• Cladocerans
• Copepods
Rotifers
• 50 μm – 3 mm
• Smallest metazoan
Taxonomy
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
http://tolweb.org/tree/
Rotifer Taxonomy
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Rotifera
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
Rotifer Diversity
**High diversity in morphology
Cyclical
Parthenogenesis*
STRESS
Resting Eggs
Cyclical
Parthenogenesis
Rotifer Life Cycle
No Molting → Cell Expansion
Rotifer Colonies
Major groups of freshwater
zooplankton
• Rotifers
• Cladocerans
• Copepods
Cladocerans
0.5 mm – 3 mm
Cladoceran Taxonomy
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Arthropoda
Class: Crustacea
Orders: Cladocera
Family: Daphniidae and
Bosminidae
Genus
Species
Cladoceran Families
Daphniidae
Bosminidae
**High diversity in morphology
Cyclical
Parthenogenesis*
Cladoceran Eggs
Cladoceran Life Cycle
Cyclical
Parthenogenesis
Ephippium
Cyclical
Parthenogenesis
Major groups of freshwater
zooplankton
• Rotifers
• Cladocerans
• Copepods
Copepods
1.0 mm – 8.5 mm
Copepod Taxonomy
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Arthropoda
Class: Crustacea
Orders: Cyclopoida,
Calanodia, Harpacticoid
Family
Genus
Species
Copepod Orders
Cyclopoid
Calanoid
Harpacticoid
**Low diversity in morphology
Copepod Egg
Sacs
Cyclopoid
Copepod Egg
Sacs
Calanoid
Copepod Egg
Sacs
Harpacticoid
Copepod Life Cycle
Controls on Zooplankton
Distribution and Abundance
• Temperature Nutrients
• Physical Phactors Phish Phytoplankton
• Vertical Migration
• Parthenogenic ↔ Sexual Cycles
• Predation among Zooplankton
Controls on Zooplankton
Distribution and Abundance
• Temperature Nutrients
• Physical Phactors Phish Phytoplankton
• Vertical Migration
• Parthenogenic ↔ Sexual Cycles
• Predation among Zooplankton
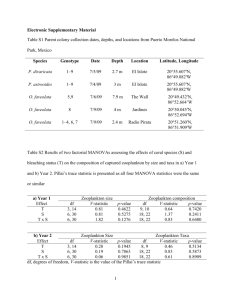
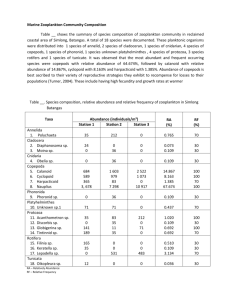
Zoop Distribution and Abundance:
Temperature
Nutrients
Controls on Zooplankton
Distribution and Abundance
• Temperature Nutrients
• Physical Phactors Phish Phytoplankton
• Vertical Migration
• Parthenogenic ↔ Sexual Cycles
• Predation among Zooplankton
Zoop Distribution and Abundance:
Physical Phish Phytoplankton
Zooplankton
Population
Dynamics
Controls on Zooplankton
Distribution and Abundance
• Temperature Nutrients
• Physical Phactors Phish Phytoplankton
• Vertical Migration
• Parthenogenic ↔ Sexual Cycles
• Predation among Zooplankton
Zoop Distribution and Abundance:
Vertical Migration Pattern
• Variation with stage and sex
• Light is proximal cue
• 3 main hypotheses
Vertical Migration Hypotheses:
Predation
Vertical Migration
Hypotheses:
Food Quality
Vertical Migration
Hypotheses:
Growth and
Feeding Efficiency
as a Function of
Temperature
“Hunt warm, rest
cool”
High Feeding
Efficiency
High Growth
Efficiency
Controls on Zooplankton
Distribution and Abundance
• Temperature Nutrients
• Physical Phactors Phish Phytoplankton
• Vertical Migration
• Parthenogenic ↔ Sexual Cycles
• Predation among Zooplankton
Zoop. Distribution and Abundance:
Parthenogenic -Sexual Cycles
VS.
Parthenogenic -Sexual Cycles
Asplanchna
Paramecium
+
Amictic ♀♀
=
Amictic ♀♀
Parthenogenic -Sexual Cycles
Chlamydomonas
Asplanchna
Paramecium
+
Amictic ♀♀
+
Euglena
=
Parthenogenic -Sexual Cycles
Enlargement
=
Mictic
♀♀
Large Mictic ♀♀
Mictic ♂♂
Mictic ♀♀ with
“Humps”
Controls on Zooplankton
Distribution and Abundance
• Temperature Nutrients
• Physical Phactors Phish Phytoplankton
• Vertical Migration
• Parthenogenic ↔ Sexual Cycles
• Predation among Zooplankton
Zoop. Distribution and Abundance:
Predation among zooplankton
Predation Among Zooplankton
Cyclomorphosis
Cyclomorphosis: Elongation
Cyclomorphosis: Enlargement
Asplanchna
Mictic
♀♀
Large Mictic ♀♀
Cyclomorphosis:
Production of Lateral Spines
Cyclomorphosis:
Reduction in Spines
Keratella
Zooplankton in Streams and Rivers
Low-Flow Areas
Backwaters
Reservoirs
Alternate Copepod Life Cycle
Cocopods
Copepuffs