8th-Grade-Eras
advertisement
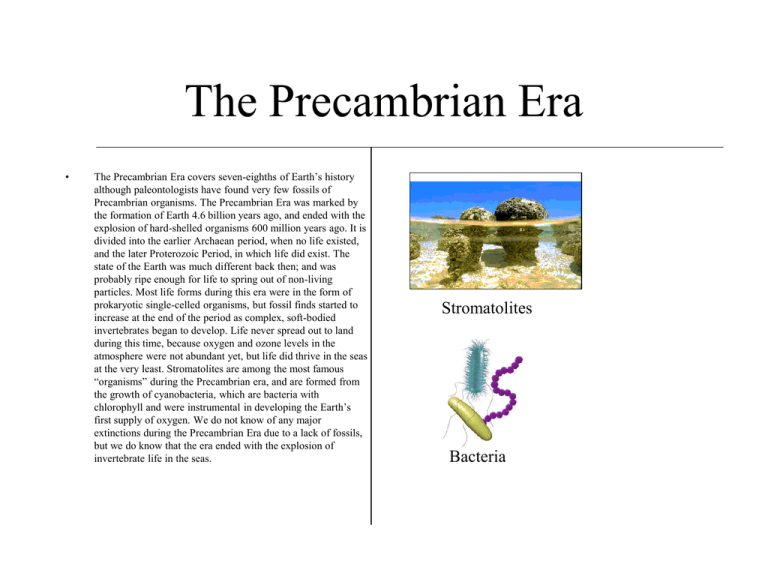
The Precambrian Era • The Precambrian Era covers seven-eighths of Earth’s history although paleontologists have found very few fossils of Precambrian organisms. The Precambrian Era was marked by the formation of Earth 4.6 billion years ago, and ended with the explosion of hard-shelled organisms 600 million years ago. It is divided into the earlier Archaean period, when no life existed, and the later Proterozoic Period, in which life did exist. The state of the Earth was much different back then; and was probably ripe enough for life to spring out of non-living particles. Most life forms during this era were in the form of prokaryotic single-celled organisms, but fossil finds started to increase at the end of the period as complex, soft-bodied invertebrates began to develop. Life never spread out to land during this time, because oxygen and ozone levels in the atmosphere were not abundant yet, but life did thrive in the seas at the very least. Stromatolites are among the most famous “organisms” during the Precambrian era, and are formed from the growth of cyanobacteria, which are bacteria with chlorophyll and were instrumental in developing the Earth’s first supply of oxygen. We do not know of any major extinctions during the Precambrian Era due to a lack of fossils, but we do know that the era ended with the explosion of invertebrate life in the seas. Stromatolites Bacteria The Paleozoic Era • The Paleozoic Era was an era that lasted from around 600 million years ago to 230 million years ago. During the Cambrian Era, the first period of the Paleozoic Era, there was an abundance of hard-shelled organisms, including the famous trilobite, which has been found in many areas around the world. Additionally, the first vertebrate, a small fish, came into existence during the Cambrian Epoch, although life was still restricted to the seas. During the next period, the Ordovician period, seas had spread across much of North America, and many new animals, including shellfish, coral, and fishlike vertebrates had developed. Life finally spread onto the land in the following Silurian period, and the land had now exhibited arachnids and simply plants. The following period, the Devonian period, was also known as “The Age of Fishes” due to the proliferation of fish in the seas. The same period also marked the proliferation of plant life on land as well as the first amphibians. The first reptiles on the Earth appeared in the following Carboniferous period, which is responsible for many of the oil deposits that we have today. The climate of the Earth was very hot and moist, but cooled down in the following Permian period, which was characterized by the first conifers (a type of gymnosperm) as well as the formation of glaciers in many areas. The Appalachian Mountains also formed during this period, but a mass extinction spelled the end of this period and of the Paleozoic Era, as 90% of all species of life on Earth had disappeared in this mass extinction; all within a few million years. Trilobite Coelacanth Ammonites Diplocaulus The Mesozoic Era • • • • The Mesozoic Era covered the period from 230 to 65 million years ago. The Mesozoic Era is often known as the “Age of Dinosaurs” because these reptiles were the largest, the most powerful, and the most conspicuous animals of the era. They basically dominated the Earth in the Mesozoic Era, which is divided into three periods: The Triassic, the Jurassic, and the Cretaceous Periods.These three periods exhibited their own unique share of dinosaurs, although the most conspicuous dinosaurs, such as the Tyrannosaurus Rex, were found in the Cretaceous Period, the period in which dinosaurs were at their peak. The era also marked the birth of the Rocky Mountains, as well as the first birds, and mammals, both of which come from reptiles. Flowering plants (angiosperms) also first appeared in the Mesozoic Era. While the early Mesozoic was dominated by unusual plants, the first modern gymnosperms began to appear during this era. The end of the Mesozoic Era is among the most famous events in the history of the Earth. 65 million years ago, 75% of the species on Earth went extinct, including the dinosaurs, while the cause of the mass extinction remains controversial. During the Mesozoic Era, Pangaea began to split apart, and seas were forming between the continents. Europe was flooded during this era, and became dry again only during the Cretaceous period. A great rift zone helped drive Europe and North America apart, while Northern Africa also started to rift apart. Tectonic activity on the Earth was particularly active during the late Mesozoic Era, and there were many other events related to the shifting of the continents. Tyrannosaurus Rex Archaeopteryx Ichthyosaur Conifers The Cenozoic Era • The Cenozoic Era enclosed the period of time from the extinction of the dinosaurs 65 million years ago to the present day, and is divided into two periods: The Tertiary Period, and the Quaternary Period. The era is often called the “Age of Mammals” because mammals thrived and became widespread across the Earth during this era. Birds and flowing plants (angiosperms) also thrived during this era, while reptiles were now only living in a fraction of their former glory. The Earth developed to the point as we know it today, and several mountain ranges, including the Alps and the Himalayas formed. The climate of the Cenozoic era varied greatly; the Earth was relatively warm at some times, but the era had also possessed numerous ice ages. We may currently be living in an intergalactic ice age in fact; which is basically a time period in between ice ages. In the beginning of the period, the Earth was recovering from the mass extinction at the end of the Mesozoic Era, but the survivors of the extinction thrived, with few competitors or predators. Small mammals eventually evolved into the larger mammals that we recognize today, although many small mammals still obviously exist today. Additionally, this period also marked the evolution of apelike creatures into humans, who now have so much control over the world that the world is now in the mercy of the hands of humans. There has been a recent mass extinction that has just begun a century ago, as more and more species become extinct due to the actions of impetuous and selfish humans. The mass extinction is still continuing today, and could possibly be an extinction similar to those of previous eras if humans do not change their actions. Sabre-tooth cat Homo erectus Wooly Mammoth Flowering Plant (Angiosperm)