Data interoperability
advertisement

(3) Data scope in INSPIRE
Vlado Cetl
European Commission
Joint Research Centre
Institute for Environment
and Sustainability
Digital Earth and Reference
Data Unit
www.jrc.ec.europa.eu
Serving society
Stimulating innovation
Supporting legislation
Outline
•
•
•
•
Training: INSPIRE Basics
EC JRC
INSPIRE Data Themes
Data Interoperability
Data Specifications
Examples
2/29
INSPIRE components
Training: INSPIRE Basics
EC JRC
3/29
INSPIRE data themes
Annex I
1. Coordinate reference
systems
2. Geographical grid systems
3. Geographical names
4. Administrative units
5. Addresses
6. Cadastral parcels
7. Transport networks
8. Hydrography
9. Protected sites
Annex II
1.
2.
3.
4.
Elevation
Land cover
Ortho-imagery
Geology
Training: INSPIRE Basics
EC JRC
Annex III
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Statistical units
Buildings
Soil
Land use
Human health and safety
Utility and governmental
services
7. Environmental monitoring
facilities
8. Production and industrial
facilities
9. Agricultural and
aquaculture facilities
10.Population distribution –
demography
11. Area management/
restriction/regulation
zones & reporting units
12. Natural risk zones
13. Atmospheric conditions
14. Meteorological
geographical features
15. Oceanographic
geographical features
16. Sea regions
17. Bio-geographical regions
18. Habitats and biotopes
19. Species distribution
20. Energy Resources
21. Mineral resources
4/29
INSPIRE data themes
•
The INSPIRE working group on Reference Data and Metadata
(RDM) (2002): Reference Data and Metadata Position Paper
• Provide an unambiguous location for a user's information
• Enable the merging of data from various sources
• Provide a context to allow others to better understand the
information that is being presented
• INSPIRE Environmental Thematic Coordination Group (2002):
Environmental thematic user needs - Position Paper
• a review of policy documents including existing and planned
environmental legislation;
• a review of papers available from existing formal and informal
working groups;
• consultation with stakeholders in different environmental policy
areas
• expert judgement based on the experience of EEA staff and
EIONET
Training: INSPIRE Basics
EC JRC
5/29
Data interoperability
The starting point …
user
...
dataset
Training: INSPIRE Basics
EC JRC
• Access to spatial data in various
ways
user
dataset
...
• User has to deal with interpreting
heterogeneous data in
different formats, identify, extract
and post-process the data he
needs
lack of interoperability
dataset
6/29
Data interoperability
user
... and what INSPIRE is
aiming at
user
...
...
Network
Service
Network
Service
Network
Service
dataset
dataset
dataset
Training: INSPIRE Basics
EC JRC
• Provide access to spatial data via
network services and according to a
harmonised data specification to
achieve interoperability of data
! Datasets used in Member States may
stay as they are
! Data or service providers have to
provide a transformation between their
internal data model and the harmonised
data specification
7/29
INSPIRE IRs vs. TG
Training: INSPIRE Basics
EC JRC
8/29
Why common Data Specifications?
• Member States should make available
data within the scope of INSPIRE using
•
the same spatial object types (and definitions)
•
the same attributes (and definitions, types,
code lists) and relationships to other types,
e.g. BuildingHeight, BuildingSize
•
a common encoding (GML application
schemas)
•
common portrayal rules
• This facilitates interoperability and panEuropean/cross-border applications
(e.g. information systems, reporting
systems, forecasting models)
Training: INSPIRE Basics
EC JRC
9/29
DS Development - Stepwise Approach
Development of conceptual framework and specification
methodology (by Data Specification Drafting Team)
•
•
DS-D 2.3 Definition of Annex Themes and Scope
•
DS-D 2.5 Generic Conceptual Model (GCM)
•
DS-D 2.6 Methodology for Specification Development
•
DS-D 2.7 Guidelines for Encoding
Development of data specifications for each spatial data
theme (by different Thematic Working Group) based on the
•
•
conceptual framework
•
common specification development methodology
•
and on the INSPIRE roadmap
• Preparation of the Implementing Rules based on data
specifications (by the Commission)
Training: INSPIRE Basics
EC JRC
10/29
Data interoperability – standards stack
Training: INSPIRE Basics
EC JRC
11/29
Data interoperability – standards stack
Training: INSPIRE Basics
EC JRC
12/29
Data interoperability – Stakeholders
•
Thematic working groups – 19
TWGs for Annex II&III
•
TWG Facilitators
•
TWG Editors
•
Domain experts
•
•
•
•
EC INSPIRE Team (DG ENV, DG
JRC, DG ESTAT)
Technical coordination = JRC INSPIRE team
Data Specifications Drafting Team
(DS DT)
Stakeholders
•
Legally mandated organisations (LMOs)
•
Spatial data interest communities (SDICs)
Training: INSPIRE Basics
EC JRC
13/29
Finding the appropriate level of
interoperability
Training: INSPIRE Basics
EC JRC
14/29
Conceptual Framework
•
To provide a repeatable data
specification development
methodology and general
provisions for the data
specification process, which is
valid for all spatial data themes
•
The GCM is using a set of
interoperability elements
Fundamentals
Training: INSPIRE Basics
EC JRC
Requirements
Reference model
Architectural
support
for
interoperability
Terminology
Multi-lingual text and cultural
adaptability
Use of ontologies
Coordinate referencing and
units of measurements
Registers and Registires
Data Modelling
Object referencing
Spatial and temporal aspects
Rules for application schemas
and feature catalogues
Shared application schemas
Consolidated model repository
Multiple representation
Extension points
Data Management
Identifier management
Consistency between data
Data and information quality
Metadata
Conformance
Data capturing rules
Data transformation guidelines
Rules for data maintenance
Portrayal
Data delivery
15/29
TG & IR
Training: INSPIRE Basics
EC JRC
16/29
IR & TG development cycle
Training: INSPIRE Basics
EC JRC
17/29
IR & DS development cycle
Training: INSPIRE Basics
EC JRC
18/29
Cross-theme data interoperability
Reporting
Waste
SD:Species distribution
PD: Population
Distribution
EL:Elevation
PRTR
SEVESO
Urban Planning
ER:Energy
Resources
US: Utilities and
Governmental Services
(Waste Management)
PF:Production and
industrial facilities
AF:Agricultural and
aquaculture facilities
SO:Soil
HB:Habitats and biotopes
Training: INSPIRE Basics
EC JRC
BU:Buildings
AM:Area management/ restriction/
regulation zones & reporting units
Waste Management
Plans
Environmental Impact
Assessment
Risk Management
…
19/29
Key pillars of data interoperability
Conceptual
data models
• objects types,
properties &
relationships
• cross-domain
harmonizatio
n
• based on a
common
modelling
framework
• managed in a
common UML
repository
Training: INSPIRE Basics
EC JRC
Encoding
• conceptual
models
independent
of concrete
encodings
• standard
encoding:
GML, but also
possible to
derive other
encodings
(e.g. based
on RDF)
Harmonised
vocabularies
• to overcome
interoperabilit
y issues
caused by
free-text
and/or multilingual
content
• allow
additional
terms from
local
vocabularies
Registers
• provide
unique and
persistent
identifiers
for reference
to resources
• allow their
consistent
management
and
versioning
20/29
Key pillars of data interoperability
Conceptual
data models
Encoding
Harmonised
vocabularies
Registers
• conceptual
• to overcome
• objects
• provide
models
interoperabili
types, in INSPIRE
and
described
Conceptual
Frameworkunique
documents
independent
ty issues
properties &
persistent
of concrete
caused by
relationships
identifiers
encodings
free-text
for
• crossand/or multireference to
• standard
domain
lingual
resources
encoding:
harmonizatio
content
GML, but
n
• allow their
also
• allow
consistent
• based on a
possible to
additional
managemen
common
derive other
terms from
t and
modelling D2.6:Methodology
encodings
local
versioning
framework
for Specification
D2.7:
Guidelines
D2.10.3: Common
D2.9:
O&M
D2.5:
Generic
(e.g.
based
vocabularies
for Encoding
data models
Guidelines
Conceptual
Model in Development
• managed
on RDF)
a common
Training: INSPIRE Basics
21/29
EC JRC
UML
How to read the data specifications
Foreword
General Executive Summary
Theme-specific Executive Summary
1. Scope
2. Overview (incl. 2.2 informal description)
3. Specification scopes
4. Identification information
5. Data content and structure
5.2 Basic notions
5.3 – 5.x Application schemas (incl. UML diagrams and
feature catalogues)
6. Reference Systems
How to read the data specifications
7. Data Quality
7.1 DQ Elements
7.2 Minimum DQ requirements and recommendations
8. Metadata
8.1 Additional requirements and recommendations for MD
elements defined in the MD Regulation
8.2 MD Elements for interoperability
8.3 Recommended theme-specific MD elements
9. Delivery (incl. Encodings)
10. Data Capture
11. Portrayal (incl. layers, styles)
How to read the data specifications
Annex A: Abstract Test Suite
Annex B: Use cases
Annex C: Code list values
Other Annexes (e.g. examples)
How to read the data specifications
Training: INSPIRE Basics
EC JRC
25/29
Data specification thematic extensions
INSPIRE data application schemas
total number
INSPIRE Annex II Themes
1
3
4
1
3
1
Extended Application
Schema
Core Application Schema
INSPIRE Annex III Themes
+
INSPIRE Data
specifications contain
138 Use cases
Training: INSPIRE Basics
EC JRC
26/29
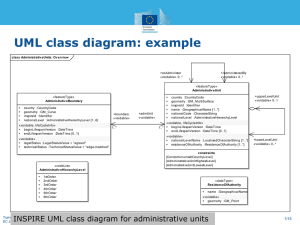
UML class diagram: example
class Administrativ eUnits: Ov erv iew
+/administeredBy
«voidable» 0..*
+coAdminister
«voidable» 0..*
«featureType»
Administrativ eUnit
«featureType»
Administrativ eBoundary
+
+
+
+
country :CountryCode
geometry :GM_Curve
inspireId :Identifier
nationalLevel :AdministrativeHierarchyLevel [1..6]
«voidable, lifeCycleInfo»
+ beginLifespanVersion :DateTime
+ endLifespanVersion :DateTime [0..1]
«voidable»
+ legalStatus :LegalStatusValue = "agreed"
+ technicalStatus :TechnicalStatusValue = "edge-matched"
«codeList»
Administrativ eHierarchyLev el
+
+
+
+
+
+
Training: INSPIRE Basics
EC JRC
1stOrder
2ndOrder
3rdOrder
4thOrder
5thOrder
6thOrder
+boundary
«voidable»
1..*
+admUnit
«voidable»
+
+
+
+
+
+
country :CountryCode
geometry :GM_MultiSurface
inspireId :Identifier
name :GeographicalName [1..*]
nationalCode :CharacterString
nationalLevel :AdministrativeHierarchyLevel
+upperLevelUnit
«voidable» 0..1
«voidable, lifeCycleInfo»
1..* + beginLifespanVersion :DateTime
+ endLifespanVersion :DateTime [0..1]
«voidable»
+ nationalLevelName :LocalisedCharacterString [1..*]
+ residenceOfAuthority :ResidenceOfAuthority [1..*]
+lowerLevelUnit
«voidable» 0..*
constraints
{CondominiumsAtCountryLevel}
{AdmininstrativeUnitHighestLevel}
{AdministrativeUnitLowestLevel}
«dataType»
ResidenceOfAuthority
+
name :GeographicalName
«voidable»
+ geometry :GM_Point
27/29
INSPIRE Data specifications - examples
•
•
•
•
AU
CP
EL
…
Training: INSPIRE Basics
EC JRC
28/29
More information
INSPIRE
•
•
http://inspire.jrc.ec.europa.eu/
•
INSPIRE Data Specifications
•
Overview
•
http://inspire.jrc.ec.europa.eu/index.cfm/pageid/2
Data models
•
•
http://inspire.jrc.ec.europa.eu/index.cfm/pageid/2/list/datamodels
Schemas
•
•
http://inspire.ec.europa.eu/schemas/
Training: INSPIRE Basics
EC JRC
29/29
Vlado Cetl
vlado.cetl@jrc.ec.europa.eu
http://inspire.jrc.ec.europa.eu/
Thank you for your attention!
Training: INSPIRE Basics
EC JRC
30/29