Aquatic Plants ppt email version
Aquatic Plants
Aquatic Ecology
Mr. Werner
PLANTS (MACROPHYTES)
TAXONOMY and DIVERSITY
Macro-algae (Chara) – Several forms
Flowering Plants – 2 dozen families (several hundred species)
4 categories: Floating unattached, Floating attached, Submerged, Emergent
AQUATIC MACROPHYTE HABITAT
Attached, Floating, submerged, emergent,
SWIMMING AND ESCAPE BEHAVIOR none
FEEDING PREFERENCES AND BEHAVIOR
Photosynthesis
LIFE CYCLE AND DIAPAUSE
The seed bank
ECONOMIC IMPORTANCE AND MANAGEMENT
Large: Ecologically important
Sometimes nuisances
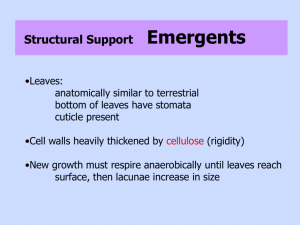
EXTERNAL STRUCTURE, APPEARANCE and ANATOMY
Typical plant structures: roots (rhizome, holdfast) stem (single cell in macro-algae) leaves flowers
“Plants are inside-out animals.”
Tim Allen
The importance of aquatic macrophytes in freshwater systems
• Aquatic macrophytes play a vital role in ecosystems.
• They are primary producers and an important food source.
• They provide a substrate for algae and shelter for invertebrates and young fish.
• They offer nesting sites or birds and mammals
• They aid in nutrient cycling.
• They catch sediments and help stabilize river and stream banks.
Rhizomes
1. Floating unattached plants
• Roots, if present, hang free in the water and are not anchored to the bottom.
Duckweed
2. Floating attached plants
• …have leaves which float on the surface, but their stems are beneath the surface, and their roots anchor the plant in the substrate.
3. Submerged plants
Elodea nuttallii • … the entire plant is below the surface.
4. Emergent aquatic macrophytes
• …have roots below and stems and leaves above the water’s surface.
Sedges - Carex
Textbook
a.
Sedge - Wetlands b.
Grass – Emergent c.
Lily pads – Floating Attached d.
Sundew - Emergent e.
Duckweed – Floating Unattached c.
b.
d.
e.
Representative of aquatic submerged macrophytes
Chara (macroalgae)
Pond weeds (narrowleafed water weed)
Boad-leafed water weed
Utricularia (bladder wort)
Milfoil
(Myriophyllum)
For Picture see Fig. 5.7 p.136 in Textbook
Life Cycle
• Reproduce once a year
• Macro-algae = release motile gametes
• Flowering Plants = flowers on stalks, pollinated by wind or insects/birds.
• Seeds mature during warm season & enter diapause stage in winter.
The speed of the water determines the type of plants found.
• Fast water encourages low, encrusting forms
Lentic Systems
• Slow flowing or lentic bodies can have large leafy forms present.
Factors affecting plant growth
• Light is the most important factor in determining the presence of plants
• Light levels beneath the surface can be affected by many factors such as:
– Depth
– Turbidity (sediment)
– Shading (trees etc.)
– Water color (chemical staining)
– Ice formation