5th Grade Science – Chapter 5
advertisement

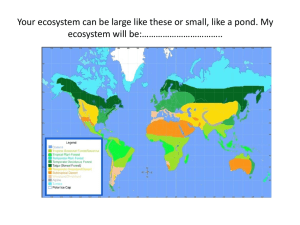
Chapter 5 Interactions in Ecosystems 5th Grade Science What is an Ecosystem? • ____________ - all living and non-living things Ecosystem in an area. • An ecosystem is any place where _______ are living found. Population • ___________ - a group of organisms of one species that live in an area at the same time. Ex: a group of oak trees or an ant colony Community Community - made up of all of the populations in • __________ an area. – Members of a community depend on each other for food reproduction ________, _________, and _____________. shelter Non-living parts of an ecosystem include: -_________________ air -_________________ water soil -_________________ -__________________ temperature Ecosystem Interactions interact • Living and non-living things _______ in an ecosystem. depend • Living things ________ on non-living things for survival. role • Each part of an ecosystem has a ______, a job or function that they perform. • The whole system works to meet the needs of all of the parts. Populations in an Ecosystem • ____________ can live and grow only where Populations their needs can be met in the ecosystem. • If the needs of the population are not met: smaller – The number of members will get _________ – Some members might ________ away move survive – Some will not __________. Biomes Tropical Rainforest Biomes - located near the • __________________ equator and are warm all year long. • Tropical Rainforests have more species _________ than all other ________. biomes • Tropical Rainforest Species: – _________ Kinkajou Basilisik Lizard – ____________ – __________ orchids Deciduous Forest Biomes • Grow in cooler places that do not have large amounts of ____. rain Deciduous Trees • ____________ - lose their leaves - oaks, elms, maples. diseases • Populations fluctuate due to _______, _________, overcrowding __________. predators • Why do trees lose their leaves in the winter? • Why is overcrowding a problem in the forest? Grassland Biomes grasslands • ___________ - biomes covered with many types of grasses and few trees. decaying • ___________ grasses form ________ soils. fertile small • _______ amount of rain • Animals: bison _______, ________, _________ antelope Prairie dogs - eat the grasses that the prairie provides. • ________ in the grasslands are wolves and predators bison Populations in the Grassland decrease • _________ when habitat changes - ______, climate ________, ________________ enemies Water and food supply • ____________________ Declining population of wolves - grasslands changed into farmlands. Prairie dogs decreased in numbers because their food source was taken away and they had less space to roam. Gray wolves • ___________ - lightly populated in Northern States Taiga Biome • _________ biome that covers much of Canada forest and Russia in places that are cold and fairly dry. • Most trees in the _____have needles – pines tiaga • Needles are _______ that conduct leaves photosynthesis and provide food for the tree. • Needles have a ______coating that prevent water waxy loss • tree • Animals – bears, elk, moose and wolves – fur to keep warm Desert Biomes desert - areas that receive less than 25 • ______ centimeters of rain or snow each year. Root systems close to • Desert plants have large _________ the surface that allow them quickly take up water from rain. • Animals – sleep during the day and look for food at night to avoid the high temperatures • Largest deserts are found in ______ and SW ____ Africa Asia Tundra Biome • _______ biome with little _______. cold rain • _____________ area of the world Most Northern • ___________ Limiting Factors include the amount of water, food, and space or shelter that is availible to an organism. • ______________ - the number of organisms Carrying capacity that can live in a place Limiting factor in the tundra • ____________________ -short time of warm weather Water Ecosystems rivers 1. ___________ 2. ___________ Wetlands 3. ___________ Coral Reefs The Deep Sea 4. ___________ Water ecosystems include animals that spend much of their time on land. adapted Plants and animals are _________ to live in this environment. Wetlands Wetland • ________ - partly covered with water or is flooded at least part of the year. sawgrass • _________ wetland has many different types of grasses – ex. Everglades Swamp • _________ - wetland with many trees and bushes. • __________ - places where rivers flow into Estuaries oceans. Benefits of Wetlands filters • _________ - plants, soils, and microorganisms • _________ - plants, soils, and microorganisms Cleaners clean the water food shelter to many wetland • Provides _____ and ______ species. Coral Reefs Coral Reefs • __________ grow in areas where there are not many nutrients – extra nutrients will help the enemies of coral to grow and harm the coral. • Coral reefs _______ shore lines from ocean protect storms • Coral reefs have provided ________ medicines • As corals grow and die, their ________ parts skeletal pile up to make the reefs The Deep Sea cold dark and has very high • The deep sea is ____, ____, ______________. Water pressure sunlight • ________ cannot reach these depths – no plants grow. • Animals bodies are _______ to live under the adapted crushing pressure of the water. Competition • Organisms in an ecosystem compete over: space – ________ – ________ water light – ________ – ________ food mates – ________ – An organisms that cannot compete may die or move away to get its needs met. Competition cont’d • Animals of the same species may compete with each other and with organisms of other species for resources. • Plants compete for resources such as water space light _______, ________, _________, and ________. nutrients Invasive species native • _____________ - may outcompete ________ species for resources Symbiosis • ___________ - a long term relationship Symbiosis between different species. • In symbiosis, one of the species is always helped ________, the other species in the relationship is either _______, _________, or helped harmed ____________. Not affected • A symbiotic relationship where one species is parasites - feed on other harmed involves _______ host organisms - _______. Food chains and Food Webs • Every organism needs energy _______ in order to live • Energy moves through an ecosystem in Food chains Energy chains ___________, ___________, or ____________ Food webs Producers • __________ - organisms that make their own food such as ________, __________, and plants protists other _____________. microorganisms • Producers get the energy that they need from sun the _______. Consumers consumers • ___________ - organisms that cannot make their own food animals • All ________ are consumers herbivores • ___________ - only eat plants • ___________ - predators, eat only other carnivores prey animals called ______ • __________ - eat plants and animals omnivores decomposers • ___________ - eat waste or dead organisms