Fiji Banded Iguana
advertisement

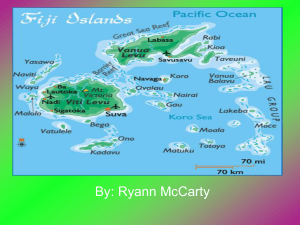
Fiji Banded Iguana By Darian & Kaitlin It’s Latin name is “brachylophus fasciatus.” The name, Brachylophus, is derived from two Greek words: brachys meaning "short" and lophos meaning "crest" or "plume", denoting the short spiny crests along the back of this species. The specific name, fasciatus, is a Latin word meaning "banded". Biome Tropical Rainforests •Temperatures are from 31-26C all year round. •There is a wet season where it rains almost constantly. They can get 2000-3000mm of rain on the coast and up to 6000mm in the mountains. Distribution •10,000 found iguanas over 29 different islands. •Endangered •They can be found in high trees or low laying swamps. Community • • • • • • • • Found in the Fiji’s islands. Are often in the ivi tree. Fijian banded are tree dwelling and favour swampy forest and lowland. Rarely come down from trees except to lay eggs. Habitat is disappearing due to land clearing, agriculture and threaten by introduce species such as feral cats, goats and mongooses. It forages for tropical leaves, flowers, fruit. Fiji has over 3000 plant species , animals such as mongooses, bats, and cane toads. 100 species of birds and 25 which are endemic . Niche Fiji Crested Iguana Fiji Banded Iguana • Fiji Banded Iguana are more slender ,smaller, and smoother than their endemic relative the Fiji Crested Iguana. • Thought to be herbivores, as they eat leaves, fruit, and flowers of trees and shrubs, particularly hibiscus flowers of the Vau tree and fruit such as banana and papaya. Limiting factors • A biotic factor connected to iguana, is the hibiscus flowers from the Vau tree. • Water from swamps, contributes toward types of food and quality. • Eat many tropical fruits and plants. • Captive hatchlings have been reported eating insects and such, however the adult will not eat them. • Deforestation has caused them to loose their homes and would make them go down to lower ground, where their predators live. This has given them greater extinction rate. • Found in tropical areas to give an assorted amount of food. Adaptations • • • • • • • • Bury eggs so humans and other predators can’t find them. Females guard their eggs, which is uncommon for iguanas. If threatened, they have taught themselves to aggressively defend their territory which terrify locals. Males will darken the blue bands, and fake attack a predator . This keeps predators like mongooses away and help keep them alive. Also the color bands on the males change from green to blue, grey or black depending on their mood. Fiji Banded Iguana spend their days foraging, basking and watch their territories during the day and go to the treetops at. The Fiji Banded Iguana is diural which mean the animal is active during the day and a sleep at night. The tail are extremely long which makes up more than two thirds of the lizards total length and uses it balance as climbs though the forest branches Good at climbing and also swimming. More slender ,smaller, and smoother than their endemic relative the Fiji Crested Iguana. Taxonomy • Kingdom: Anamalia – multicellular • Phylum: Chordata – Has a spine • Class: Sauropsida – Classified as a reptile • Order: Squamata – Contains scales • Suborder: Iquania – lizard • Family: Iguanidae – Family of lizards, composed of iguanas and relates species • Genus: Brachylophus • Species: B. fasciatus Bibliography http://www.flickriver.com/photos/11304433@N00/sets/72157600035466039 http://www.rainforest-facts.com/australasia-oceania-rainforests.html http://www.arkive.org/fiji-banded-iguana/brachylophus-fasciatus http://seapics.com/feature-subject/reptiles/fiji-iguana-pictures.html http://www.digimorph.org/specimens/Brachylophus_fasciatus/ Google images Wikipedia naturefiji.org