immune with stress
advertisement
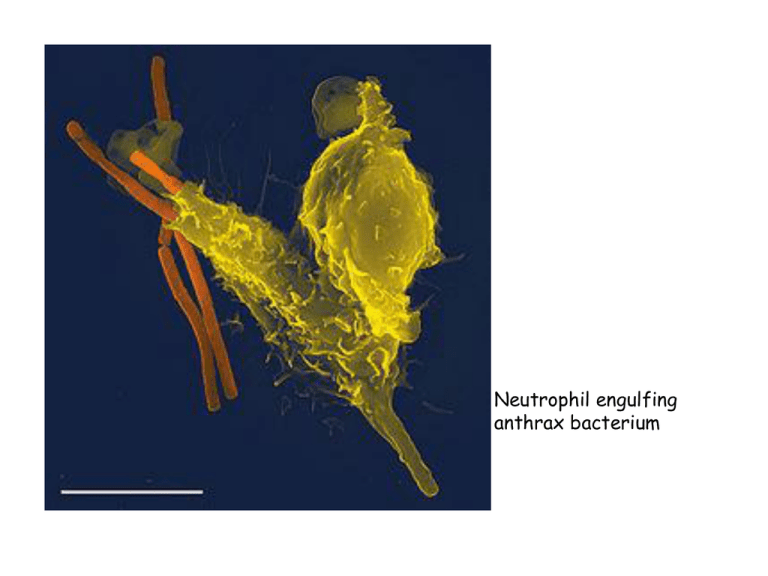
Neutrophil engulfing anthrax bacterium Vertebrate Immune System INNATE humoral complement antitoxins bacteriolysins cellular 1. 2. 3. 4. Inflammation Kill and clear any non-self Natural Killer Cells Basophils Eosinophils Phagocytes a) Macrophges b) Neutrophils c) Dendritic cells Fast acting, non specific Does not confer long lasting protection ADAPTIVE cellular humoral T-cell B-cell 1. Helper T cell Th0 Th1 Th2 2. Cytotoxic T cell Inflammation Kill specific pathogens B-cell Producing antibodies Mark pathogens for destruction and clearance Slower response, but highly specific Leaves memory cells Macrophage cytotoxins Cytotoxic Cytotoxic Cytotoxic Cytotoxic Cytotoxic Cytotoxic T Tcell Tcell Tcell Tcell Tcell cell CD8+ CD8+ CD8+ CD8+ CD8+ CD8+ T cell CD8+ Perforin granulysin Presenting antigen Interleukin 2 Macrophage T cell Helper T CD4+ Helper T cell Helper T cell Helper T cell Helper T cell Helper T cell Helper T cell cell IFN γ Helper Th1 Th1 memory Interleukin 2 Interleukin 4 Interferon γ Il4 Helper Th2 Il4 Il5 Il6 Il10 Il13 B cell memory IFN γ Tumor Necrosis Factor Activate more macrophages Macrophage B cell unactivated B cell ACTIVATED STRESS • Sympathetic Nervous System (Epinephrine and Norepinephrine): – Increases inflammation—increases adhesion molecules from macrophages—allowing all cells to stick into tissues better – Increase inflammation—Th1 cells have receptors for Epinephrine and Norepinephrine • Glucocorticoids: Acute • Glucocorticoids: Chronic Effect of stress on T cell response ACUTE STRESS • Sympathetic Nervous System (Epinephrine and Norepinephrine): – Increases inflammation—increases adhesion molecules from macrophages—allowing all cells to stick into tissues better – Increase inflammation—Th1 cells have receptors for Epinephrine and Norepinephrine • Glucocorticoids: Acute – Enhances IFNγ action on Th1 • Glucocorticoids: Chronic Effect of stress on T cell response ACUTE CHRONIC STRESS • Sympathetic Nervous System (Epinephrine and Norepinephrine): – Increases inflammation—increases adhesion molecules from macrophages—allowing all cells to stick into tissues better – Increase inflammation—Th1 cells have receptors for Epinephrine and Norepinephrine • Glucocorticoids: Acute – Enhances IFNγ action on Th1 • Glucocorticoids: Chronic – Reduce numbers of lymphocytes (T>B), basophils, eosinophils, macrophages Fig. 1. Juxtaposition of typical stressors for wild animals and known effects of stressors on immune function in domesticated rodents Immune function Habitat modification Invasive species Pollution Immune enhancement basal immune function Inclement weather Social status change Scope of baseline shift (or GC insensitivity) contingent on experience (#, timing or intensity of prior stressors) Infection Injury Aggressive interaction Parasite detection Predation Minutes-hours Immune suppression Food restriction Hours-days Days-weeks Weeks-months Duration of stressor Protective up-regulation Protective down-regulation Allostatic overload Vertebrate Immune System INNATE humoral complement antitoxins bacteriolysins acute cellular 1. 2. 3. 4. Inflammation Kill and clear any non-self Natural Killer Cells Basophils Eosinophils Phagocytes a) Macrophges b) Neutrophils c) Dendritic cells Fast acting, non specific Does not confer long lasting protection chronic ADAPTIVE cellular humoral T-cell B-cell 1. Helper T cell Th0 Th1 Th2 2. Cytotoxic T cell Inflammation Kill specific pathogens B-cell Producing antibodies Mark pathogens for destruction and clearance Slower response, but highly specific Leaves memory cells Definitions • Adaptive arm—humoral: responsible for extracellular pathogen control through generation of antibodies (B cells) specific to particular components of pathogens (antigens) • Adaptive arm—cell mediated: responsible for intracellular pathogen control (cytotoxic T cells), and upregulating both cell mediated (Th1) and humoral (Th2) adaptive immune • Innate arm—cell mediated: cells that destroy non-self • Innate arm—humoral—proteins, acellular components identify and destroy non-self • Leukocytes—all white blood cells • Lymphocytes—specific leukocytes, two sizes – Large, granular: natural killer cells – Small: T and B cells • MHC—recognition of self Macrophage cytotoxins Cytotoxic Cytotoxic Cytotoxic Cytotoxic Cytotoxic Cytotoxic T Tcell Tcell Tcell Tcell Tcell cell CD8+ CD8+ CD8+ CD8+ CD8+ CD8+ T cell CD8+ Perforin granulysin Presenting antigen Interleukin 2 Macrophage T cell Helper T CD4+ Helper T cell Helper T cell Helper T cell Helper T cell Helper T cell Helper T cell cell IFN γ Helper Th1 Th1 memory Interleukin 2 Interleukin 4 Interferon γ Il4 Helper Th2 Il4 Il5 Il6 Il10 Il13 B cell memory IFN γ Tumor Necrosis Factor Activate more macrophages Macrophage B cell unactivated B cell ACTIVATED