Final_analog of vestibular dysfunction
advertisement
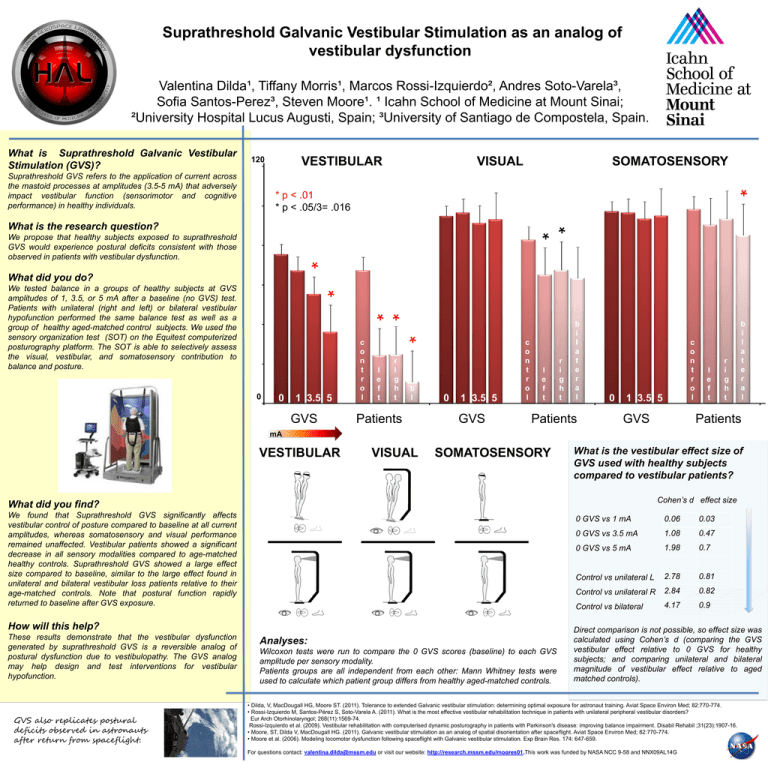
Suprathreshold Galvanic Vestibular Stimulation as an analog of vestibular dysfunction Valentina Dilda¹, Tiffany Morris¹, Marcos Rossi-Izquierdo², Andres Soto-Varela³, Sofia Santos-Perez³, Steven Moore¹. ¹ Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai; ²University Hospital Lucus Augusti, Spain; ³University of Santiago de Compostela, Spain. VESTIBULAR 120 Suprathreshold GVS refers to the application of current across the mastoid processes at amplitudes (3.5-5 mA) that adversely impact vestibular function (sensorimotor and cognitive performance) in healthy individuals. VISUAL SOMATOSENSORY * What is Suprathreshold Galvanic Vestibular Stimulation (GVS)? * p < .01 * p < .05/3= .016 * * What is the research question? We propose that healthy subjects exposed to suprathreshold GVS would experience postural deficits consistent with those observed in patients with vestibular dysfunction. * What did you do? * We tested balance in a groups of healthy subjects at GVS amplitudes of 1, 3.5, or 5 mA after a baseline (no GVS) test. Patients with unilateral (right and left) or bilateral vestibular hypofunction performed the same balance test as well as a group of healthy aged-matched control subjects. We used the sensory organization test (SOT) on the Equitest computerized posturography platform. The SOT is able to selectively assess the visual, vestibular, and somatosensory contribution to balance and posture. ** 0 1 3.5 5 GVS * 0 c o n t r o l l e f t r i g h t b l Patients 0 1 3.5 5 GVS c o n t r o l l e f t r i g h t b i l a t e r a l Patients 0 c o n t r o l 1 3.5 5 GVS l e f t r i g h t b i l a t e r a l Patients mA VESTIBULAR VISUAL SOMATOSENSORY What is the vestibular effect size of GVS used with healthy subjects compared to vestibular patients? Cohen’s d effect size What did you find? We found that Suprathreshold GVS significantly affects vestibular control of posture compared to baseline at all current amplitudes, whereas somatosensory and visual performance remained unaffected. Vestibular patients showed a significant decrease in all sensory modalities compared to age-matched healthy controls. Suprathreshold GVS showed a large effect size compared to baseline, similar to the large effect found in unilateral and bilateral vestibular loss patients relative to their age-matched controls. Note that postural function rapidly returned to baseline after GVS exposure. How will this help? These results demonstrate that the vestibular dysfunction generated by suprathreshold GVS is a reversible analog of postural dysfunction due to vestibulopathy. The GVS analog may help design and test interventions for vestibular hypofunction. GVS also replicates postural deficits observed in astronauts after return from spaceflight. Analyses: Wilcoxon tests were run to compare the 0 GVS scores (baseline) to each GVS amplitude per sensory modality. Patients groups are all independent from each other: Mann Whitney tests were used to calculate which patient group differs from healthy aged-matched controls. 0 GVS vs 1 mA 0.06 0.03 0 GVS vs 3.5 mA 1.08 0.47 0 GVS vs 5 mA 1.98 0.7 Control vs unilateral L 2.78 0.81 Control vs unilateral R 2.84 0.82 Control vs bilateral 4.17 0.9 Direct comparison is not possible, so effect size was calculated using Cohen’s d (comparing the GVS vestibular effect relative to 0 GVS for healthy subjects; and comparing unilateral and bilateral magnitude of vestibular effect relative to aged matched controls). • Dilda, V, MacDougall HG, Moore ST. (2011). Tolerance to extended Galvanic vestibular stimulation: determining optimal exposure for astronaut training. Aviat Space Environ Med; 82:770-774. • Rossi-Izquierdo M, Santos-Pérez S, Soto-Varela A. (2011). What is the most effective vestibular rehabilitation technique in patients with unilateral peripheral vestibular disorders? Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol; 268(11):1569-74. Rossi-Izquierdo et al. (2009). Vestibular rehabilitation with computerised dynamic posturography in patients with Parkinson's disease: improving balance impairment. Disabil Rehabil ;31(23):1907-16. • Moore, ST, Dilda V, MacDougall HG. (2011). Galvanic vestibular stimulation as an analog of spatial disorientation after spaceflight. Aviat Space Environ Med; 82:770-774. • Moore et al. (2006). Modeling locomotor dysfunction following spaceflight with Galvanic vestibular stimulation. Exp Brain Res. 174: 647-659. For questions contact: valentina.dilda@mssm.edu or visit our website: http://research.mssm.edu/moores01.This work was funded by NASA NCC 9-58 and NNX09AL14G