IC61 - DRAFTING I
advertisement

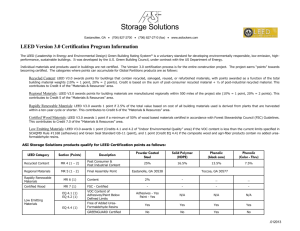
IC61 - DRAFTING I Essential Standard 1.00 Understanding Fundamental Concepts and Trends of Drafting IC61 - DRAFTING I Essential Standard 1.02 Understanding Industrial Design, Sustainable Design, and LEED Industrial Design What is Industrial Design? The Short Answer? Industrial Design (or I.D.) is the Design of all of the Stuff that we use every day. Industrial Designers: DESIGN things like cars, bikes, furniture, tools and equipment, computers, medical devices, house wares, toys – all the stuff you see in stores, all the stuff people use at home and work every day, the things that most people think just appear somehow. Sometimes the term Product Design is substituted for Industrial Design. 2013 International Design Excellence Awards So, what isn’t Industrial Design? Fashion Designers: design Clothing and Fabrics. Graphic Designers: design Websites, Computer apps, Magazines, Advertising, Packaging & more. Similar to I.D. but usually only 2-Dimensional. Architects, Engineers, Urban Planners, Interior Designers and Landscape Architects design the Places and Spaces in which we live. Do you understand? Prove it. Take a few minutes to make your own list of 6 items, in this room, that were probably designed by an Industrial Designer. Can you also list 2 things that were probably designed by a Graphic Designer? How about 1 thing by an Architect? And lastly, 1 thing by an Engineer? Do you really understand? DO IT. You will now work in small groups to Design a Better: 1. Pencil Sharpener 2. Stapler 3. Hole Punch 4. Rolling Desk Chair 5. Computer Mouse. A better Mousetrap? See Handout for Instructions. Sustainable Design What is Sustainable Design? The Short Answer: Sustainable design seeks to reduce negative impacts on the environment, and the health and comfort of building occupants, thereby improving building performance. Sustainable Design Objectives: Reduce Consumption of Non-Renewable Resources (More on this later) Minimize Waste Raw Materials Used in Construction Packaging: Pre-Use and Post-Use Reduce – Reuse - Recycle Create Healthy, Productive Environments Use Non-Toxic & Recycled Building Materials Use of Natural Lighting & Ventilation What is a Non-Renewable Resource? Once it is used, it is gone forever, or it can’t be reused for anything else. Examples of Non-Renewable Energy? How We Waste Energy What is a Renewable Resource? It is easily Replaced and/or can be Reused or Recycled. Examples of Renewable Energy? Using Wind Power What is a Renewable Resource? Is Wood a Renewable Resource? Sometimes Yes (Bamboo) Sometimes No (Slow growing Hardwoods) Is an Aluminum Window Frame a Renewable Resource? Yes. Aluminum building products can be easily Recycled. Sustainable Design Principles: Optimize Site Potential Minimize Non-Renewable Energy Consumption Use Environmentally Preferable Products Protect and Conserve Water Enhance Indoor Environmental Quality Optimize Operational and Maintenance Practices U.S. General Services Administration Sustainable Facilities Tool help designers: Optimize Site Potential Minimize Non-Renewable Energy Consumption Use Environmentally Preferable Products Protect and Conserve Water Enhance Indoor Environmental Quality Optimize Operational and Maintenance Practices Use this online tool to list at least 2 practices for each of the Sustainable Design Principals Sustainable Facilities Tool (http://sftool.gov/) LEED What is LEED? The Short Answer: LEED stands for Leadership in Energy & Environmental Design But, what IS LEED? LEED is a green building tool that addresses the entire building lifecycle by recognizing best-in-class building strategies, thereby reducing its overall impact on the environment. LEED is a program that provides third-party verification of green buildings. Building projects satisfy prerequisites and earn points to achieve different levels of certification. How does LEED work? Projects earn points to satisfy green building requirements in specific categories. Within each of the LEED credit categories, projects must satisfy prerequisites and earn points. The number of points the project earns determines its level of LEED certification. What are the 5 Main Credit Categories? (They should sound familiar) Sustainable sites credits encourage strategies that minimize the impact on ecosystems and water resources. Water efficiency credits promote smarter use of water, inside and out, to reduce potable water consumption. Energy & atmosphere credits promote better building energy performance through innovative strategies. Materials & resources credits encourage using sustainable building materials and reducing waste. Indoor environmental quality credits promote better indoor air quality and access to daylight and views. There are also 3 Neighborhood Development Categories, 2 Home Credit Categories and 2 Bonus Credit Categories. What are the 4 LEED Certification Levels? CERTIFIED: 40 – 49 Points SILVER: 50 – 59 Points GOLD: 60 – 79 Points PLATINUM: 80 Points and above Why should you design a LEED Certified Building? To Lower Operating Costs and Increase its Resale Value. To Conserve Energy, Water and other Natural Resources. To Create a Healthier and Safer Building for its Occupants. To Qualify for Money-Saving Incentives, like Tax Rebates and Zoning Allowances. Why should you design a LEED Certified Building? What are you going to make me find out about LEED? Do you remember those Extra Categories I mentioned earlier? “There are also 3 Neighborhood Development Categories, 2 Home Credit Categories and 2 Bonus Credit Categories.” That’s right, you are going to find out what they are. www.usgbc.org is the place to look. You are also going to provide examples of things to do that meet the requirements of the 5 Main Categories. But that is for tomorrow. Review What is Industrial Design? Industrial Design (or I.D.) is the Design of all of the Stuff that we use every day. What is Sustainable Design? Sustainable design seeks to reduce negative impacts on the environment, and the health and comfort of building occupants, thereby improving building performance. What is LEED? LEED (Leadership in Energy & Environmental Design) is a green building tool that addresses the entire building lifecycle by recognizing best-in-class building strategies, thereby reducing its overall impact on the environment. It is a tool for achieving Sustainable Design.