Crime Scene Investigation and Evidence Collection
advertisement

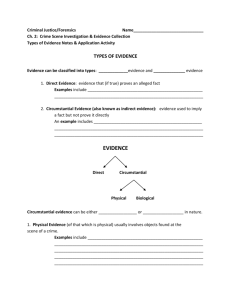
Crime Scene Investigation and Evidence Collection Physical Evidence • Any and all objects that can establish that can establish that a crime has or has not been committed or can link a crime and its victim or perpetrator – In order to be useful it must be collected, preserved and properly analyzed by forensic experts – The CSI Myth…Crime laboratories do not solve crimes yet only enhance the ability of investigators to solve crimes by providing them with data. Types of Evidence Direct vs Circumstantial Direct • First hand observations such as … – Eyewitness Accounts – Police Dashboard Cameras – Surveillance Cameras • Confessions are also considered to be Direct Evidence Circumstantial • Indirect evidence that can be used to imply a fact yet does not directly prove it • Provides a link between a suspect and a crime Scene. – Can be physical or biological in nature Circumstantial Evidence Physical vs Biological Physical • Fingerprints, footprints, shoe prints, tire impressions, tool mark impressions, synthetic fibers, weapons, bullets, shell casings ect… • Reduces # of suspects only to a smaller group of people – Exception- fingerprints can be individualized and sometimes other physical evidence can be individualized Biological • Body fluids (blood, semen, saliva), hair, natural fibers, plant part (such as pollen) ect... • Usually reduces # of suspects to smaller group or even a single individual – Often more persuasive in court Types of Evidence Class vs Individual Class • Evidence that narrows the identity of a criminal down to a certain group (classification) of people • Does not narrow suspects down to a single suspect or criminal. • Can exclude some suspects – Example- ABO Blood Type, Rh+ / Rh – Blood Type, Shoe size ect… Individual • Evidence that narrows the identity of a criminal down to a single individual. – Examples– • DNA (biological) • Fingerprints (physical) • Some other physical evidence – Fragments that fit together like a jigsaw puzzle • Handwriting * Types of Evidence Trace Evidence • Small but measurable amounts of physical or biological evidence found at a crime scene – Examples… write down a few • • • • • • • • • Fiber from clothing Broken glass fragments Paint chips fingerprints on glass Soil on shoes or tracked into a home Drop of blood on a T shirt Hair on a brush Pollen on clothing Pet hair on clothes or rugs Locard’s Exchange Principle • Whenever two people contact with each other, a physical transfer occurs • exchange of trace materials/evidence may occur between two people or a person and their other environmental surroundings