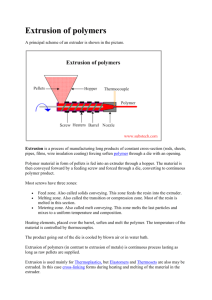
PROCESSING OF
PET BOTTLES
MOHAMMED ALZAYER
CHRIS CLAY
XINHANG SHEN
Mat E 453
December 11th, 2014
Outline
• Background
Amcor
Blow Molding
Recycling
• Fluid Mechanics
Temperature
Molecular Weight
• Bottle Processing
Purification
Preforms
Bottles
• Conclusions
Background: AMCOR
• Global Company
– Australian
• 1860 as Australian Paper
Manufacturers
• 1986 changed name
– 90% Food industry
– 43 countries
• West EU and NA
– 180 plants
– 27,000 employees
• Ames
–
–
–
–
1997
175 Employees
10% of Ames Power
Primarily Preform
Background: Blow Molding
• Blow Molding:
Using gas pressure to expand a
polymer to a desired shape.
• History [1]:
Developed: 1800s (baby rattles!)
1st PET bottle: December, 1942
• Today [1]:
30-40 billion plastic bottles/year
(US alone)
Figure 1: Blue baby rattle [2]
Background: Blow Molding
• General Process [1]:
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Melt thermoplastic resin
Extrude through die head
Form hollow Parison
Drop Parison through mold halves
Mold halves close around Parison
Plastic solidifies inside mold
Mold opens to get final component
Figure 2: Blow molding [1]
Background: Blow Molding
• Variations [1]:
1.
2.
3.
4.
Injection blow molding
Stretch blow molding
Extrusion blow molding
Reheat and blow molding
Bolded: involved in beverage bottle processing
Background: Recycling
•
•
1.
2.
3.
•
•
‘PCR’: post-consumer recycled
Advantages:
Less amount of waste in landfills
Less carbon footprint than ‘virgin’
Less natural resources needed
Disadvantage: Food residue
Solution: Heat to sterilize,
Use pure PET
Figure 3: Pellets [3] flakes [4] PCR
Fluid Mechanics: Temperature
• PET Tmelt: 250-260 °C [8]
Equation 1: Temperature dependent viscosity
• Viscosity:
Optimize T,
just above
Tmelt, low
enough for
PET to flow
(but not too
easily)
[9]
Fluid Mechanics: Molecular Weight
• PET Typical Mw: ~20-40K g/mol [10]
Equation 2: Temperature dependent viscosity
• Viscosity:
The lower the
MW the less
viscous. PET
critical MW is
unknown
[9]
Bottle Processing: Overview
• Simply known as:
Injection Stretch Blow Molding
• Injection (Preform):
Inject hot PET into cavity
• Stretch (Bottle):
Blow preform to get bottle
Figure 4: Preform [5]
Figure 5: Final product [6]
Bottle Processing: Purification
• PET pellets come by railcar
Moved into Silos by Suction
• Dried for 6-10 hours
Rate limiting step for the process
~ 0.2 % Moisture
• Additives
Colorant, Plasticizers, Release Agents
Bottle Processing: Preform
• Injection Stretch Blow Molding:
Summarized in 4 steps
Figure 6: First two steps involved in injection stretch blow molding
[7]
Bottle Processing: Bottle
• Injection Stretch Blow Molding:
Summarized in 4 steps
Figure 7: The rest of steps involved in injection stretch blow molding
[7]
Conclusions
•
•
•
•
AMCOR Makes PET Preforms/ Bottles
Receive PET pellets and dry them
Preforms made via injection molding
Bottles made from preforms by blow molding
References
[1] Manufacturing: Plastic Molding & Forming. Engineer's Handbook. Web.
[2] Blue Baby Rattle Shower Favor Holders. Factorydirectcraft. Web.
[3] Recycled HDPE Resins. Envision Plastics. Web.
[4] PCR PET Flakes Decontamination. Viscotec. Web.
[5] PET Preform Injection Molding Machine: SZ-1600A. Web.
[6] Pepsi Introduces New Shape for Bottle After 16 Years. Designboom. Web.
[7] Injection Stretch Blow Moulding. Plastipedia. Web.
[8] Polyethlene Terephthatate: Melting Point. Web.
[9] Mendoza, J. D., Mat E 453 Lecture, Iowa State University.
[10] Pearl Engineering PEPLEPET B-103C PET Bottle Grade. MatWeb.