Complete PowerPoint - Coventry Public Schools
advertisement

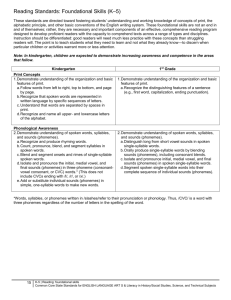
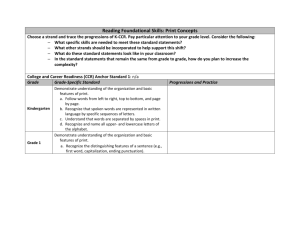
Study of the Standards using Common Core English Language Arts Expectations Participants will gain a common understanding of the Common Core State Standards and develop a strong working knowledge of the standards effect on teaching and learning. Session participants will learn…… • How to use a set of structured tools to promote conversations and collaboration around a common core State standards • How to use the common core State standards to guide decision-making about teaching, learning and assessment “To begin with the end in mind means to start with a clear understanding of your destination. It means to know where you are going, so that you better understand where you are now and so that the steps you take are always in the right direction.” Stephen R. Covey The Seven Habits of Highly Effective People The Common Core State Standards do not provide……. • A complete scope and sequence • A course outline • All the essential skills and knowledge students could have The Common Core State Standards do ……. • Outline the most important and essential skills and knowledge every student needs to master to succeed in college and careers. Common Core State Standards Development The Common Core State Standards initiative state-led effort coordinated by the National Governors Association Center for Best Practices (NGA Center) and the Council of Chief State School Officers (CCSSO) The standards were developed in collaboration teachers, school administrators, and experts to provide a clear and consistent framework to prepare our children for college and the workforce. Common Core State Standards Development • Aligned with college work expectations • In rigorous content occasion of knowledge through high order skills • Build upon strengths and lessons of current State Standards • Informed the top three countries so that all students to succeed in a global economy and society • Evidence and/or research-based As new research is conducted and implementation of the Common Core State Standards is evaluated, the standards will be revised on a set review cycle. http://www.coventryschools.net/Common_Core_Instructional_Materials/ELA_Video.htm Study of the Standards using Common Core English Language Arts Part 1B Structure The Common Core State Standards for English Language Arts are compromised of a set of anchor standards and corresponding grade-specific standards that are organized around 4 strands: • Reading • Literature K -12 • Informational Text K -12 • Foundational Skills K -5 • Speaking and Listening • Language • Writing The Common Core State Standards for Literacy in History/Social Studies, Science, and Technical Subjects are comprised of a set of anchor standards and Corresponding grade-specific standards that are organized around 2 strands: • Reading • Writing Structure Standards for ELA and Literacy Anchor Standards These are college and Career Readiness Standards that “anchor” the Common Core State Standards. They define general expectations that must be met to ensure students enter college and workforce training programs ready to succeed. Strand A broad idea that describes the area of focus for an English Language Arts standard. Organizing Elements Categorize ideas and standards within the strand Grade-Specific Standards Define end-of-the year expectations and cumulative progressions designed to enable students to meet college and career readiness expectations no later than the end of high school. Common Core State Standards: English Language Arts K-12 Strands and organizing elements Reading Writing (W) K -12 Literature (RL) K -12 Key ideas and details Craft and structure Integration of knowledge and ideas Range of reading and level of text complexity Test types and purposes Production and distribution of writing Research to build and present knowledge Range of writing Informational Text (RI) K-12 Key ideas and details Craft and structure Integration of knowledge and ideas Range of reading and level of text complexity Speaking and Listening (SL) K- 12 Foundational Skills (RF) K – 5 only Language (L) K - 12 Conventions of Standard English Knowledge of Language Vocabulary Acquisition and Use Print Concepts Phonological awareness Phonics and word recognition Fluency Comprehension and collaboration Presentation of knowledge and ideas Common Core State Standards: Literacy in History/Social Studies, Science and Technical Studies Strands and organizing elements Writing Reading History/Social Studies (RH) 6 -12 Key ideas and details Craft and structure Integration of knowledge and ideas Range of reading and level of text complexity Science and Technical Subjects (RST) 6 -12 Key ideas and details Craft and structure Integration of knowledge and ideas Range of reading and level of text complexity History/Social Studies, Science and Technical Subjects (WHST) 6 -12 Test types and purposes Production and distribution of writing Research to build and present knowledge Range of writing English Language Arts Appendices Appendix A: Research supporting key elements of the standards Glossary of key terms Appendix B: Text exemplars and sample performance tasks Appendix C: Samples of student writing Reading Standards: Foundational Skills (K – 5) Kindergarteners: Phonics and Word Recognition Grade 1 Students Strand RF Grade 2 Students Organizing Element 3. Know and apply grade-level phonics and 3. Know and apply grade-level phonics and 3. Know and apply grade-level phonics and word analysis skills in decoding words word analysis skills in decoding words. word analysis skills in decoding words. a. Demonstrate basic knowledge of onea. Know the spelling sound a. distinguish long and short vowels when to-one letter-sound correspondences by correspondences for consonant digraphs reading regularly spelled one-syllable words producing the primary or many of the most b. decode regularly spelled one syllable b. Know spelling sound correspondences frequent sound for each consonant. words. for additional common vowel terms. b. Associate the long and short sounds c. Know final –e and common vowel term c. Decode regularly spelled two-syllable with common spellings (graphemes) for the conventions for representing long vowel words with long vowels. five major vowels. sounds. d. Decode words with common prefixes c. Read common high-frequency words by d. Use knowledge that every syllable must and suffixes sight (e.g., the, of, to, you, she, my, is, are, do) have a vowel sound determine the number of e. identify words with inconsistent but d. Distinguish between similarly spelled syllables per word. common spelling-sound correspondences words by identifying the sounds of the letters e. decode two syllable words following that differ. basic patterns by breaking words into syllables Grade-Level Columns Fluency Standard 4. Read emergent-reader texts with purpose 4. Read with sufficient accuracy and fluency to and understanding support comprehension. a. Read on-level text with purpose and understanding b. Read on-level text orally with accuracy, appropriate rate and expression on successive readings. c. Use context to confirm or self-correct word recognition and understanding, rereading as necessary. 4. Read with sufficient accuracy and Reading Standards: Foundational Skills (K – Strand 5) Abbreviation Kindergarteners: Grade 1 Students Phonics and Word Recognition RF Grade 2 Students 1st Grade 3. Know and apply grade-level phonics and 3. Know and apply grade-level phonics and 3. Know and apply grade-level phonics and word analysis skills in decoding words word analysis skills in decoding words. word analysis skills in decoding words. a. Demonstrate basic knowledge of onea. Know the spelling sound a. distinguish long and short vowels when to-one letter-sound correspondences by correspondences for consonant digraphs reading regularly spelled one-syllable words producing the primary or many of the most b. Decode regularly spelled one syllable b. Know spelling sound correspondences frequent sound for each consonant. words. for additional common vowel terms. b. Associate the long and short sounds c. Know final –e and common vowel term c. Decode regularly spelled two-syllable with common spellings (graphemes) for the conventions for representing long vowel words with long vowels. five major vowels. sounds. d. Decode words with common prefixes c. Read common high-frequency words by d. Use knowledge that every syllable must and suffixes sight (e.g., the, of, to, you, she, my, is, are, do) have a vowel sound determine the number of e. identify words with inconsistent but d. Distinguish between similarly spelled syllables per word. common spelling-sound correspondences words by identifying the sounds of the letters e. decode two syllable words following that differ. basic patterns by breaking words into syllables Fluency 4. Read emergent-reader texts with purpose 4. Read with sufficient accuracy and fluency to and understanding support comprehension. a. Read on-level text with purpose and understanding b. Read on-level text orally with accuracy, appropriate rate and expression on successive readings. c. Use context to confirm or self-correct word recognition and understanding, rereading as necessary. 4. Read with sufficient accuracy and End of Part 1 Study of the Standards using Common Core English Language Arts Part 2 Curriculum Alignment : Basic Principle Written Taught Assessed Alignment Means Every Educator: • Understands what is expected of students • Understands these expectations in the context of the K-12 program • Accepts responsibility for these expectations Vertical Alignment – Investigation Activity • It is not about developing content knowledge. It is about learning a process to understand alignment and its implications for teaching and learning • It is not about demonstrating our content knowledge. It is about engaging in a collaborative process and constructing meaning using that process • It is not about specific grade-level content. It is about developing a K-12 perspective on alignment • It is not about “the product. “ It is about collegial conversations focused on the standards. Vertical Alignment Chart Writing Informative/Explanatory Text Concept (or Big Idea):_______________________________________ Grade Specific Standard 6 W.6.2 5 W.5.2 4 W.3.2 1 W.1.2 K W.K.2 Understanding Vertical Alignment: Reflection • How can the learning from this investigation affect the classroom teacher? • How can the learning from this investigation affect the conversations at the grade or department level? • How can the learning from this investigation affect the conversations at the school and district level? • How can the learning from this investigation guide our work toward our goals? • How will this impact the learning of all students? (at, above and below grade level) End of Part 2 Study of the Standards using Common Core English Language Arts Part 3 Writing Writing Grade 5 W.5.1 Write opinion pieces on topics or texts, supporting a point of view with reasons and information. a. Introduce a topic or text clearly, state an opinion, and create an organizational structure in which ideas are… • • • • • Grade 6 Grade 7 W.6.1 Write arguments to support claims with clear reasons and relevant evidence. a. Introduce claim(s) and organize the reasons and evidence clearly. Added distinguish between relevant and irrelevant information to make an argument Moved from opinion to argument Adding identifying credible sources of information Moving from less formal to formal writing style Concluding statement follows……….. W.7.1 Write arguments to support claims with clear reasons and relevant evidence . a. Introduce claim(s) and organize the reasons and…. • • Adding knowledge alternate or opposing claims Adding reasoning and organizing evidence to support claims logically. • Added support claims with logical reasoning using accurate sources…………… Most content should be approached from a developmental level of instruction since it is unique to the grade level. The instruction should then move through reinforcement with drill and practice as appropriate. Use what students know about: • Opinions as a basis to compare/contrast arguments • Building logical arguments and reason so that they can support claims • Logically ordering reasons so they can move to supporting claims The ELA standards are designed in an integrated way; therefore considered RI.8 Reflection: 1. What is the purpose of the Instructional Alignment Chart? 2. What is the difference between the Vertical Alignment Chart and the Instructional Alignment Chart? 3. Why are conversations with your colleagues an important part of this process?