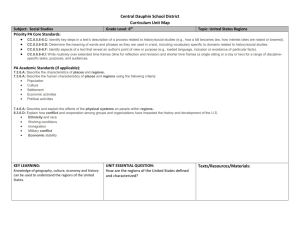
Introduction
Section 1:
The United States
Section 2:
Canada
Summary
Certain processes,
patterns, and functions
help determine where
people settle.
Studying the cultural
geography of the United
States and Canada will
introduce the peoples of
this region—their history,
how and where they live,
and the reasons behind
their choices.
Section 1:
The United States
What are three factors
that have influenced the
cultural geography of the
United States?
Section 2:
Canada
How have immigration
and physical geography
influenced the cultural
geography of Canada?
The United States
What are three factors that have
influenced the cultural geography of the
United States?
The United States
• immigration
• megalopolis
• Sunbelt
• Underground Railroad
• urbanization
• dry farming
• metropolitan area
• bilingual
• suburb
• literacy rate
• urban sprawl
• jazz
The United States
• discrimination
• expansion
• amendment
The United States
A. Los Angeles
B. New York City
The United States
What is the population of
the United States today?
A. More than 300 Million
A
0%
0%
C
C. Over 1 Billion
A. A
B. B
C.0%C
B
B. About 200 Million
Population Patterns
The United States is a country shaped by
immigration, with a continually shifting
population and densely populated urban
areas.
• Reasons for immigration:
– Political freedom
– Religious freedom
Population Patterns (cont.)
– Better economic opportunities
– Fleeing a war or natural disaster
• The population density of the United States is
about 87 people per square mile.
• Most populated areas:
– Northeast
– Great Lakes regions
– Pacific coast
Population Patterns (cont.)
• Least populated areas:
– Subarctic region of Alaska
– Great Basin
– Parts of the Great Plains
• Over the years, the United States has
experienced urbanization, mainly in coastal areas.
U.S Population Density
Which area is one of the fastestgrowing in the U.S. today?
A. The Great Plains
B. The Sunbelt
C. The Hawaiian Islands
D. The Midwest
0%
A
A.
B.
C.
0%
D.
B
A
B
C0%
D
C
0%
D
History and Government
Physical geography and a spirit of
independence influenced U.S. development.
• U.S. history has been influenced by:
– Native Americans
– European colonization
– A war for independence
– The creation of a new
government
History and Government (cont.)
– Westward expansion
– Industrial growth
– Technological change
• Modern challenges include:
– Terrorism
– War
U.S Expansion
Resources and the Civil War
Who were the next group of people
to immigrate to America after the
Native Americans?
A. Mexicans
B. Canadians
C. Europeans
D. Asians
0%
A
A. A
B. B
C.
0% C0%
D. D
B
C
0%
D
Culture
Immigration has influenced the diversity and
culture of the United States.
• Different aspects of culture in the U.S.:
– Language—mainly English
– Religion—mainly Christian
Culture (cont.)
– Education—public or private schools are
available.
– Health care—many people cannot afford
health care in the U.S.
– The arts—by the mid-1800s the U.S. started to
develop its own form of art, such as jazz.
– Family life—many families enjoy a high
standard of living due to the wealth in the U.S.
U.S Population by Age and Sex
What is second most
commonly spoken
language in the United
States today?
A. English
B. Chinese
C. French
0%
D. Spanish
A
A.
B.
C.
0%
D.
B
A
B
C
0%
D
C
0%
D
Canada
How have immigration and physical
geography influenced the cultural
geography of Canada?
Canada
• Loyalist
• Quebecois
• province
• North American Free
Trade Agreement
• Inuit
• dominion
• separatism
• Parliament
• financial
• eventually
Canada
A. Maritime Provinces
B. Prairie Provinces
C. Toronto
D. Montreal
E. Vancouver
F. Edmonton
G. Nunavut
Canada
Canada has how many
official languages?
A. Four
A
0%
0%
C
C. Three
A. A
B. B
C.0%C
B
B. Two
Population Patterns
Canada has a diverse mixture of ethnic
groups, densely populated urban areas, and
vast expanses of rugged terrain.
• Immigrants to Canada came for the following
reasons:
– Search for political and religious freedom
– Economic and educational opportunities
– Refuge from wars
Population Patterns (cont.)
• Average population density is about 9 people per
square mile.
• Most of Canada’s population lives in urban areas:
– Toronto
– Montreal
– Vancouver
– Edmonton
Canada’s Population Density
How much of Canada’s
population lives along
the U.S.-Canada border?
A. 25%
B. 50%
C. 75%
D. 90%
0%
A
A.
B.
C.
0%
D.
B
A
B
C
0%
D
C
0%
D
History and Government
Canada’s history has been influenced by its
French and English roots, a drive for
independence, and by immigration.
• Canada’s history has been shaped by:
– Great Britain and France feuding over land and
government
– The United States possibly gaining their land
History and Government (cont.)
– Native American cultures
– Immigrants from around the world
• Modern challenges:
– The effects of free trade with the U.S.
– French-speaking Canadians’ desire for
independence from the rest of Canada
Canadian Explorations
What type of government
does Canada have today?
A. A democracy
A
0%
0%
D
D. No government
A
B
C0%
D
C
C. A socialist government
A.
B.
C.
0%
D.
B
B. A constitutional
monarchy
Culture
European, Asian, and Native American
cultures have influenced Canada’s cultural
diversity.
• Language—two official languages, English and
French.
• Religion—Christians are the largest group.
• Education—public and private schools are available.
Culture (cont.)
• Health care—the Canadian government helps pay
for health care.
• The Arts—British, French, American, and native
cultures have influenced the arts.
• Family life—Canada is one of the wealthiest
countries in the world, so many families enjoy a
high standard of living.
Canadian Population by Age and Sex
Who makes up the largest religious
group in Canada?
A. Muslims
B. Hindus
C. Buddhists
D. Christians
0%
A
A.
B.
C.
0%
D.
B
A
B
C
0%
D
C
0%
D
Early History
• Native Americans are the
region’s earliest people.
• Europeans established
colonies in the region.
• Many Native American
cultures were destroyed
and people were displaced
by European colonization.
• The thirteen colonies won
their independence from
Britain in 1776 and created
the United States of America.
• The Dominion of Canada
was formed in 1867. Canada
became independent from
Britain in 1931.
Population Culture
• The United States and Canada include various groups
of native peoples and descendants of immigrants.
• The immigrant roots of the United States and Canada
contribute to their diversity.
• The region’s culture has been influenced by Native
Americans and immigrants from around the world.
• Population density and distribution in the region is
influenced by physical geography.
Industrialization and Development
• Cities in the region developed
along waterways.
• Proximity to natural resources
and transportation routes
fueled industrialization in the
region.
• Industrialization and
technology enabled westward
expansion and spurred social
change in the region.
• Prosperous economies have
allowed people in the United
States and Canada to enjoy
high standards of living.
immigration
the movement of people into one
country from another
Sunbelt
mild climate region, southern United
States
urbanization
the movement of people from rural
areas into cities
metropolitan area
region that includes a central city and
its surrounding suburbs
suburb
outlying community around a city
urban sprawl
the spreading of urban developments
on undeveloped land near a city
megalopolis
a “great city” that is made up of
several large and small cities such as
the area between Boston and
Washington, D.C.
Underground Railroad
an informal network of safehouses in
the United States that helped
thousands of enslaved people escape
to freedom
dry farming
farming method used in dry regions in
which land is plowed and planted
deeply to hold water in the soil
bilingual
speaking or using two languages
literacy rate
the percentage of people in a given
place who can read and write
jazz
musical form that developed in the
United States in the early 1900s,
blending African rhythms and
European harmonies
Loyalist
a colonist who remained loyal to the
British government during the
American Revolution
province
an administrative district or division of
a country
Inuit
a member of the Arctic native peoples
of North America
dominion
a partially, self-governing country with
close ties to another country
Parliament
in Canada, national legislature made
up of the Senate and the House of
Commons
Quebecois
a French-speaking inhabitant of
Quebec
North American Free Trade
Agreement (NAFTA)
trade agreement made in 1994 by
Canada, the United States, and
Mexico
separatism
the breaking away of one part of a
country to create a separate,
independent country
To navigate within this Presentation Plus! product:
Click the Forward button to go to the next slide.
Click the Previous button to return to the previous slide.
Click the Return button to return to the main presentation.
Click the Home button to return to the Chapter Menu.
Click the Help button to access this screen.
Click the Exit button or press the Escape key [Esc] to end the
chapter slide show.
Links to Maps in Motion, static maps and charts, and transparencies
appear near the bottom of slides as they are relevant.
Links to the Reference Atlas and Geography Online are located on
the navigation bar of most screens.
This slide is intentionally blank.