OCR_B5_revision
advertisement

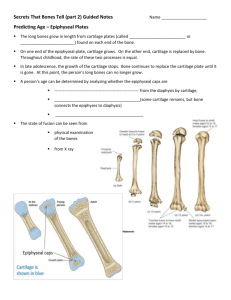
+ Biology Revision B5 The Living Body + 5a In good shape Skeletons No skeleton – e.g. worms Exoskeleton – e.g. insect made of chitin Endoskeleton – e.g. shark made of cartilage; human bone with some cartilage Advantages of endoskeleton: 1. Framework of body 2. Can grow with body 3. Easy to attach muscles 4. Flexibility Human skeleton starts as cartilage by is ossified by the addition of calcium & phosphorus. Amount of cartilage present determines growth stage + 5a In good shape Long bone structure: Head covering of cartilage Shaft, bone marrow with blood vessels Cartilage & bone are living tissue Bones are strong but easily broken Types of fractures: Simple Compound Green stick + 5a In good shape Joints Where 2 or more bones meet Joined by ligaments Bones moved by muscles, attached by tendons Synovial joints e.g. ball & socket, hinge Advantages & disadvantages of joint replacement? + 5a In good shape The arm Biceps & triceps are antagonistic muscles Arm is like a lever: Biceps contract, triceps relax -> arm raises + 5b The vital pump Circulatory Systems None – e.g. amoeba Open – e.g. insects Closed – single e.g. fish , 2 chambered heart Double e.g. mammals, 4 chambered heart Historical contributions about circulatory system: Galen – 200AD – believed blood flowed between heart & liver Harvey – 1628 – discovered blood vessels, valves & high pressure blood flows away from heart in arteries + 5b The vital pump Cardiac Cycle – controlled by SAN & AVN ECG Effect of adrenaline? Exercise? + 5c Running repairs Heart Conditions/Diseases Condition Effect Treatment Irregular heart beat Pacemaker Hole in heart Surgery Damaged or weak valves Replacement with artificial valves Blocked coronary artery Bypass surgery Heart attack Transplant – disadvantages? Lifestyle risk factors– diet, alcohol smoking, stress, drugs + 5c Running repairs Blood components Blood groups: A, B, AB, O Rhesus positive & negative Agglutinins – markers on the surface of red blood cells which make them Clump if they contact the corresponding antigen: Blood group Agglutinin on surface Antibodies in blood Can accept blood from A A Anti-B A or O B B Anti-A B or O AB A&B None Any O None Anti-A & Anti-B O + 5c Running repairs Blood donation – cards for everyone? Religious objections? Blood Clotting occurs: 1. When blood vessels are damaged 2. When blood comes into contact with air 3. To prevent too much blood being lost 4. To prevent pathogens entering through wounds Vitamins K & C are needed for healthy blood clotting Alcohol & cranberries slow it down Anti-coagulant drugs e.g. warfarin, heparin & aspirin reduce it Haemophilia is an inherited disease where a faulty protein stops blood clotting + 5d Breath of life Gas Exchange Simple organisms e.g. amoeba through skin Complex organisms through specialist organs Fish gills Respiratory System + 5d Breath of life Breathing Volume of chest cavity increases, pressure in lungs falls Volume in chest cavity decreases, pressure in lungs rises + 5d Breath of life Measuring Breathing Tidal air/volume – volume of air in a normal breath Vital capacity – maximum volume breathed in & out Residual air/volume – air that remains in lungs Respiratory Diseases Industrial e.g. asbestosis Genetic e.g. cystic fibrosis Lifestyle e.g. lung cancer Pathogenic e.g. pneumonia Asthma – irritated bronchioles narrow, muscles tighten, more mucus produced + 5e Waste Disposal Excretion – getting rid of waste e.g. CO2, urea, sweat Defecation – getting rid of solid waste through the anus Excretory organs: lungs, kidneys, liver, skin Skin structure: Excess water & salt are excreted as sweat, which evaporates + 5e Waste Disposal Kidneys Ultrafiltration – at bowman’s capsule – small molecules squeezed out under pressure Selective reabsorption – in tubules & loop of Henle – useful substances reabsorbed into blood + 5e Waste Disposal ADH – controls reabsorption of water in kidneys Made in pituitary gland Negative feedback: Water content low -> ADH released -> nephron tubules more permeable -> normal water level Dialysis Machine Waste diffuses from blood into dialysis fluid Sodium & glucose in blood replaced + 5f Life goes on Fertilisation – fusion of a male & female gamete Reproductive systems: + 5f Life goes on Menstrual Cycle Day 1-5 – menstruation Day 14 – ovulation Hormone Where Made Effect FSH Pituitary Stimulates egg to ripen & oestrogen release Oestrogen Ovary Uterus lining thickens, LH released LH Pituitary Ovulation Progesterone Ovary/c orpus luteum Preserve uterus lining + 5f Life goes on Infertility Fertility drugs – FSH injected to stimulate egg release Artificial insemination Egg donation – problem? Only has genes from one parent Ovary transplant Surrogacy – problem? Emotional attachment IVF – problem? low success rate, twins/triplets more likely Foetal Screening – for health of baby Ultrasound Anmiocentesis – tests cells from amniotic fluid using hypodermic needle, Ethical issues? Can cause miscarriage (1 in 200), termination? + 5g New for old Organ Donation Biological replacement e.g. blood, cornea, heart, lungs, kidney & bone marrow Organs must be: healthy, right size & age, tissue matched Can be from living donors e.g. kidneys or dead donors if they cannot regain consciousness & breath unaided Mechanical replacement e.g. Kidney, knee & hip joint, heart, eye lens Problems with mechanical Problems with Biological Size Shortage of donors Power supply Tissue match/ immunosuppresants Material used (non wearing) Rejection Body reactions e.g. allergic + 5h Size matters Growth – animals grow in the early stages of life, plants grow continually in areas called meristems e.g. shoot tips New cells for growth made by mitosis Human growth stages: 1. Infancy (up to 2) 2. Childhood (2 -11) 3. Puberty (11-15) 4. Adulthood (15 – 65) 5. Old age (over 65) Problems of living longer? Growth is measured as gain in height & mass Determined by: Genes Diet Exercise Hormones Health/disease Human growth hormone – made in pituitary gland – releases energy for growth from fat stores, stimulates growth of long bones