PowerPoint Presentation - Week 5: Primary Hemostasis
advertisement

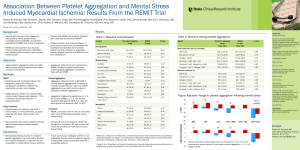
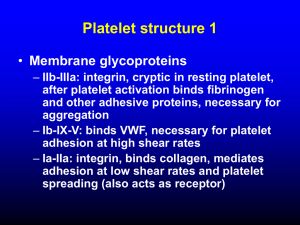
Week 5: Primary Hemostasis Hemostasis Platelet function Platelet anatomy Megakaryocyte Platelet kinetics Platelet count Aggregation studies Von Willebrand’s Bernard-Soulier Aspirin (salicylate) Vascular problems Allergy Viral infection Collagen disorders Vitamin C deficiency Ehlers-Danlos Render-Osler-Weber telangiectasia Petechiae, ecchymoses Bleeding time Vascular Injury Serotonin and thrombaxane A2 (TxA2) for vasoconstriction Prostacyclin PGI-2 for arteriole relaxation to increase blood flow Exposure of basement membrane and collagen (negatively charged surface) Inside of a vessel SEM x 2,500 Process of Hemostasis Vascular injury Platelet adhesion and activation Platelet aggregation (1o hemostatic plug) Fibrin formation via cascade (2o hemostasis) Clot retraction (thrombasthenin) Fibrinolysis and healing Role of Platelets Surveillance for vascular integrity Formation of 1o hemostatic plug Activation of 2o hemostasis Healing Platelet Formation Megakaryoblast undergoes endomitosis Intermiediate stage promegakaryocyte without granules Megakaryocyte (2N to 64N) with over 100µ diameter IL3, GM-CSF, thrombopoietin 20% of platelet stored in spleen Platelet 2 - 4µ diameter Round or oval Hyalomere - clear peripheral zone Granulomere - highly stained area with granules Platelet Anatomy Peripheral zone with glycoprotein receptors Structural zone with contractile microtubules (thrombasthenin) Organelle zone with granules Membrane with open cananicular and tubule systems for increased surface area and rapid release Electron micrograph of a platelet x 25,000 Longitudinal peripheral microtubule (brown), endoplasmic reticulum (blue), mitochondria (green), glycogen (black) Platelet Function Adhesion to basement membrane or collagen with vWF and GP-Ib Activation Shape change from discoid to distorted Exposure of GP-IIb/IIIa and other receptors TxA2 synthesis (cyclo-oxygenase dependent) Membrane phospholipid Arachidonic acid Arachidonic acid TxA2 and prostaglandins Platelet Function: Glycoprotein Group or Gene Families Integrins Leucine rich glycoprotein family Selectin family Quadraspanin family Immunglobulin supergene family Integrins Integral to membrane Ca++ dependent GPIIb/IIIa most abundant Cell-cell or cell-substrata interaction Receptor to Fib, vWF, vitronectin, fibronectin Leucine Rich GP Family Adhesion to subendothelial collagen (COL) mediated by vWF by transmembrane complex GPIb/IX Stabilizes PLT membrane by interaction with cytoskeleton Selectin Family GMP-140 mediates adhesion of neutrophils and monocytes to PLT Quadraspanin Family Plasma membrane protein p24/CD9 interacts with GPIIb/IIIa, modulating adhesion molecules Leads to Ca++ increase and subsequent PLT activation and aggregation Immunoglobulin Supergene Family Functional role unclear Has role in cellular interactions Platelet Activation 1o aggregation with agonists: ADP, epinephrin, serotonin, PF4 (anti-platelet) Release or secretion facilitated by TxA2 o Dense body for 2 aggregation and vasoconstriction (ADP, Ca++, serotonin) -granule for heparin neutralization and clot Platelet derived growth factor (PDGF) for healing Retraction Signs and Symptoms of 1o Hemostasis Problems Ecchymoses Petechiae Mucus membrane bleeding Hematoma Prolonged bleeding after minor surgery Hereditary Vascular Problems Hereditary (spider) telangiectasis (OslerRendu-Weber): dilated superficial capillaries Ehlers-Danlos: collagen disorder Marfan syndrome: connective tissue Osteogenesis imperfecta Acquired Vascular Problems Senile purpura (Bateman’s): altered connective tissue support Cushing syndrome: metabolic Scurvy: abnormal collagen Allergy: vascular inflammation Viral infection Bleeding Time For vascular and platelet functions Duke (1910) on earlobes Ivy (1941) on arm with 1mm x 3mm incision Mielke (1969) with 1mm x 10mm template 1980’s: disposable devices (e.g., Simplate, Surgicutt) Bleeding Time Quantitative Platelet Disorders Thrombocytopenia <100,000/ml BT prolonged ≈10,000 Bleeding in trauma or OR <10,000 Spontaneous, CNS bleeding Thrombocytopenia due to destruction ITP (acute in children, chronic in young women) with anti-glycoprotein Drug reaction Heparin induced thrombocytopenia DIC and TTP About Thrombotic Thrombocytopeneic Purpura (TTP) Disorder of systemic platelet aggregation in microvasculature Stimulus: unusually large vWf In children: likely to be deficiency in vWf metalloproteinase to break down vWf In adults: vWf metalloproteinase inhibited by autoantibodies Low PLT count, intravascular hemolysis, RBC fragmentation, high LDH Quantitative Platelet Disorders Thrombocytopenia due to decreased production Aplastic anemia (e.g., Fanconi’s) Fibrosis Acute leukemia Megaloblastic anemia Hereditary (e.g., May-Hegglin, Wiscott-Aldrich, Bernard-Soulier) Splenic sequestration HELLP syndrome (hemolysis, elevated liver enzyme, low PLT) in pre-eclampsia Dilution (massive transfusion) Platelet Satellitosis in EDTA Quantitative Platelet Disorders Thrombocytosis Primary with dysfunctions (e.g., CML, ET) Post splenectomy: also see HJ, etc. Hemolytic anemia Acute hemorrhage and surgery Pseudo Thrombocytosis Red cell abnormalities HJ bodies Clumped Pappenheimer bodies nRBC Malaria Microspherocytes and schistocytes White cell abnormalities Unlysed WBC WBC fragments and necrobiotic cells Platelet Count Rees-Ecker with brilliant cresyl blue Brecker-Cronkite with ammonium oxalate Unopette: similar to BC Electronic counters Qualitative Platelet Disorders Berhard-Soulier: GP-Ib deficiency, adhesion problem Von Willebrand’s: vWF deficiency, adhesion problem Glanzmann’s thrombasthenia: GP-IIb/IIIa deficiency, aggregation problem -- cannot bind vWF and Fib Storage pool disease: dense body defect, secretion problem Qualitative Platelet Problems Aspirin: inhibits cyclo-oxygenase (COX), secretion problem, no TxA2 Plavix (Clopidogrel) inhibits ADP receptor Other medications affect GPIIa/IIIb interaction with Fib Uremia, secretion problem Gray platelet syndrome: -granule defect Hypofibrinogenemia Aggregation Studies ADP reversible 1o wave o if ADP is released, then 2 wave abnormal with aggregation and release problems Epinephrin similar to ADP Collagen direct release so only one wave of aggregation Ristocetin antibiotic aggregation only with vWF and GP-Ib Platelet Aggregometry Platelet Aggregation