Lymphatic System and immunity
advertisement

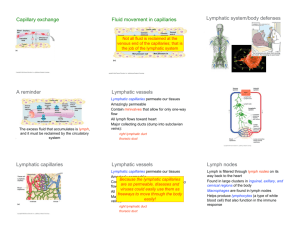
http://drmichaelljohnsonchiropractor.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/08/images3.png http://static.squarespace.com/static/511852bfe4b0cb217578137f/t/5133f01 3e4b0b73e5290c5d2/1362358292060/lymphatic_system.jpg http://static.ddmcdn.com/gif/lymph-system-1.jpg By Sheena Yvarra & Taylah Montgomery General Functions Removes excess fluid from tissues and transports it into the bloodstream Absorbs fats from small intestine Helps defend the body against disease-causing agents Major Organs Spleen Thymus Thymus Spleen http://www.savorylotus.com/wpcontent/uploads/2013/09/organs_of_the_lymp hatic_system.jpg Spleen Largest lymphatic organ FUNCTIONS: foreign particles and damaged red blood cells from blood http://img.webmd.com/dtmcms/live/webmd/consum er_assets/site_images/articles/image_article_collec tions/anatomy_pages/Spleen2.jpg Contains many macrophages, which filter Thymus Relatively large during infancy and early childhood; shrinks after puberty FUNCTIONS: Contains inactive lymphocytes and turn them into mature or active T cells T cells (T lymphocytes) leave thymus & provide immunity *Lymphocytes- white blood cell that attack invading viruses, bacteria, and other parasitic cells http://www.mskcc.org/sites/www.mskcc.org/files/imagecache/enlarge/n ode/4708/images/497816.jpg Lymphatic Pathway Lymphatic Capillary Lymphatic Vessel Lymph Node Lymphatic Vessel Lymphatic Trunk Collecting Duct Lymphatic vessels- transport lymph(fluid) throughout body Subclavian Vein Lymphatic Pathway Lymphatic Ducts: Thoracic Right Lymphatic **Thoracic duct is larger and longer; lower limbs, abdomen, left side of body *Right Lymphatic receives lymph from right side of head and neck Lymph Nodes Vary in size and shape Usually less than 2.5 cm long Bean shaped FUNCTIONS: Filters potentially harmful particles from lymph before returning it to the bloodstream Centers for production of lymphocytes, and they also contain phagocytic cells *Lymphocytes- white blood cell that attack invading viruses, bacteria, and other parasitic cells 5 Types of Antibodies (Immunoglobulins) Antibodies- special proteins that fight off and destroy disease-causing germs Antigen- foreign substance introduced into the body and causes immune response; molecules produced by the body 1. 2. 3. Immunoglobulin G (IgG) is in tissue fluid and plasma and defends against bacterial cells, viruses, and toxins and activates complement, a group of immune system enzymes Immunoglobulin A (IgA) is in exocrine gland secretions (breast milk, saliva, tears) and defends against bacteria and viruses. Immunoglobulin M (IgM) is found in plasma and activates complement and reacts with blood cells during transfusions. 5 Types of Antibodies (Immunoglobulins) 4. Immunoglobulin D (IgD) Found on surface of B cells, especially those of infants Activate B cells 5. Immunoglobulin E (IgE) is found in exocrine gland secretions and promotes allergic reactions http://www2.estrellamountain.edu/faculty/farabee/biobk/antigenAB.gif Immune Responses First reaction to an antigen is called a primary immune response during this response, antibodies are produced for several weeks some B cells remain dormant as memory cells Secondary immune response occurs rapidly as a result of memory cell response if the same antigen is encountered http://sphweb.bumc.bu.edu/otlt/mph-modules/eh/eh_immunity_b/AdaptiveImmunityMemory.png Active vs Passive Immunity Active immunity person produces antibodies in response to the presence of antigen Long-term immunity http://www.proprofs.com/flashcards/upload/q7118722.gif Passive immunity Person receives antibodies produced by another individual Short-term immunity http://www.stmary.ws/highschool/science/humanbio/q3/q3%20pictures/passive%20immunity.gif Vaccination Vaccine produces another type of active immunity helps protect against infectious disease by exposing you to a mild or dead version of the germ Makes your body build up protection in the form of antibodies Antigens that cause allergic response is called allergens Allergic response is an immune attack against a nonharmful substance, like chocolate Sensitize lymphocytes and antibodies may bind antigens Can damage tissues Can be dangerous and lifethreatening http://wondergressive.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/12/Peanut_Allergy-3.jpg Allergic Reactions http://foodimentaryguy.files.wordpress.com/2012/03/peanuts1.jpg Tissue Rejection Reaction Recipient’s immune system may recognize donor’s cell surfaces as foreign and attempt to destroy the transplanted tissue Matching donor and recipient tissues can minimize the rejection reaction Autoimmunity immune system fails to distinguish self from nonself antigens Produces autoantibodies and cytotoxic T cells that attack and damage the body’s tissues and organs **Self antigen- antigen that originates within the body ** Nonself antigen- foreign antigens not originally within the body http://alt-ternativeautoimmune.com/wpcontent/uploads/2014/01/cells.gif Lymphedema Chronic swelling of the limbs caused by the accumulation of lymph fluid Hodgkin’s lymphoma Type of cancer that typically occurs when the white blood cells become diseased or damaged http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/b/b3/Hodgkin_lymphoma_(1)_mixed_cellulary_type.jpg http://www.regionshospital.com/ucm/groups/public/@hp/@public/documents/webasset/dev_015219.gif Diseases Works Cited http://glencoe.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0218378151/student_view0/chapter14/study_outline.h tml http://www.livescience.com/26983-lymphatic-system.html