The Role of DSMBs in Clinical Research
advertisement

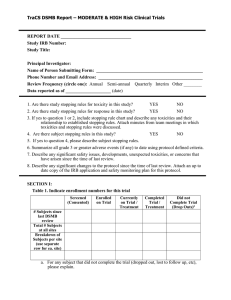
THE ROLE OF DSMB’s in CLINICAL RESEARCH Data and Safety Monitoring Data and Safety Monitoring Every clinical trial should have provision for data and safety monitoring The size of the monitoring committee depends upon the nature, size, and complexity of the clinical trial The Principal Investigator was expected to perform the monitoring function but may have had others to help Data and Safety Monitoring 1994 It was recommended that every clinical trial, even those that pose little likelihood of harm have an external monitoring body Data Safety Monitoring Boards 1998 Establishment of Data Safety Monitoring Board (DSMB) is required for multi-site clinical trials involving interventions that entail potential risk to the participants The functions and oversight of such activities are distinct from the requirement for study review and approval by an IRB A DSMB is your Friend Not your Enemy Definitions Data Safety Monitoring Plan (DSMP) describes how the study investigators plan to oversee research subject safety and how adverse events will be characterized and reported The intensity and frequency of monitoring should be tailored to fit the expected risk level, complexity, and size of the particular study Data and Safety Monitoring Board (DSMB/DMC) A group of individuals with pertinent expertise that review on a regular basis accumulating data from ongoing an clinical trial Advises sponsor regarding safety of current and future participants and validity and scientific merit of the trial DSMBs perform 3 fundamental functions Review accumulating clinical data relating to the efficacy and safety of the investigational product (drug, biologic and/or device). Conduct interim analysis of the clinical data to determine whether the study needs to be terminated for safety reasons. Ensure the continued scientific validity and merit of the study Roles of a Data Safety Committee Monitor adverse events Monitor enrollment Is Risk:Benefit is not altered Does Informed Consent need to be changed Is study meeting target? Can it be Completed? Potentially monitor subject outcomes Monitor new information relative to the study To be effective 1. 2. 3. Monitoring must be performed on a regular basis Conclusions should be discussed with PI if he/she not part of the committee Conclusions of the monitoring must be reported to the IRB Specifics of the plan will depend upon the nature, size, complexity and risk of the clinical trial Observation Study, no intervention Observation study, non-randomized intervention Randomized Controlled Trial using approved drugs/devices IND/IDE Studies Multi-center RCTs Observation Study, no intervention PI and 1-2 others Meet annually Report to IRB – enrollment status, recommendation to continue Observation study, nonrandomized intervention 2-4 Members, PI not Chair, at least 1 member not involved with the study If low Risk, meet annually Report enrollment, Adverse Events. Review SSS and ICS for needed changes Randomized Controlled Trial using approved drugs/devices 2-4 members, PI should not be a member but may attend meetings at discretion of chair Consider a biostatistician as member No member should be involved (Co-I) on study Meet semiannually depending on enrollement pace Report enrollment, Adverse Events. Review SSS and ICS for needed changes Review group outcome differences, if large may need to break blind in executive session May need to recommend discontinuation if: One group has significantly better outcomes Adverse events serious and mostly in one intervention IND/IDE Studies and/or Multi-center RCTs Require a formally constituted Data Safety Monitoring Board (DSMB) No conflicts of interest Formal Stopping rules Regular scheduled meetings Reports to IRB and FDA Generally set up by the study sponsor Data and Safety Monitoring Plan and Board A description of the plan and the composition of the monitoring board are required at the time of the IRB submission. SECTION IX: DATA SAFETY MONITORING PLAN For all research that is greater than minimal risk, a Data Safety Monitoring Plan (DMSP) must be developed. This is a plan to assure the research includes a system for appropriate oversight and monitoring of the conduct of the study to ensure the safety of subjects and the validity and integrity of the data. Monitoring Plan Checklist □ N/A. The research is minimal risk. □ The DSMP is contained in the protocol. State where in the protocol the description is located: NOTE: Ensure that all points outlined below are addressed in the description in the protocol. If any points are not addressed, within the protocol, they should be addressed below. □ The DSMP is NOT contained in the protocol; however, this is a repository/database protocol and the primary risk is that of loss of confidentiality; thus, I do not need to complete this section. □ The DSMP is NOT contained in the protocol. Complete the questions below. Section IX – A Who will be responsible for the data and safety monitoring? Examples include: a DSMC or DSMB, medical monitor, investigator, independent physician) Clarify if this individual or committee is independent from the sponsor and/or investigator. Section IX –B What will be monitored Examples include: data quality, subject recruitment, accrual, and retention, outcome and adverse event data, assessment of scientific reports or therapeutic development, results of related studies that impact subject safety, procedures designed to protect the privacy of subjects Section IX-C What are the procedures for analysis and interpretation of data, the actions to be taken upon specific events or endpoints, the procedures for communication from the data monitor to the IRB and site, and other reporting mechanisms Section IX – D What is the frequency of monitoring? The appropriate frequency of data and safety monitoring will be dependent on the nature and progress of the research; however, monitoring must be performed on a regular basis (e.g, at least annually). Section IX – E What information will be reported to the IRB? IRB requires the following information at the time of continuing review: 1) frequency and date(s) of monitoring; 2) summary of cumulative adverse events; 3) assessment of external factors (i.e. scientific reports, therapeutic developments, results of related studies) that impacted the safety of subjects; 4) summary of subject privacy and research data confidentiality outcomes; and 5) any changes to the risk-benefit ratio. Data and Safety Monitoring Plan and Board 1. 2. 3. 4. Description should include: DSMB chair and members How frequently the study will be evaluated The method of detecting adverse events How events will be scored Translational Research Ethics Consultation Service (TREX) Available to researchers to help clarify and address ethical issues that arise in planning, carrying out, and analyzing human subjects research. Areas for possible consults include but are not limited to: o Recruitment and informed consent issues o Vulnerable, pediatric, or impaired research subjects o Data sharing with research subjects or a broader community o Biobank construction and governance o Data Safety Monitoring Plans or Boards TREX Free of charge, offered by the IU Center the Bioethics (IUCB) as a service of the Bioethics and Subject Advocacy Program (BSAP), a part of the Indiana Clinical and Translational Sciences Institute (CTSI). Confidential and anonymous when appropriate. Conclusion of the consult is a memo issued as advice to the requestor. Researchers can request a consult by emailing Dr. Peter Schwartz (phschwar@iupui.edu), Director of TREX, or Dr. Eric Meslin (emeslin@iupui.edu), Director of IUCB. To learn more about the IUCB and BSAP go to www.bioethics.iu.edu/bsap