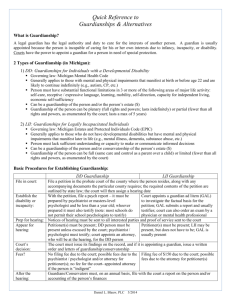
Options in Decision-Making Authority
advertisement
Options in Decision Making Authority Presented by Barbara J. Byram www.dussaultlaw.com Presumed Capacity When an individual turns 18, she is an adult in the eyes of the law. Adults presumed to be capable of making decisions on their own behalf. Parents lose the right to speak for their child, including… Health Care Driving Marriage Schools & Other Government Agencies Financial www.dussaultlaw.com Conferred Authority To make decisions on behalf of another adult, a person must be granted that authority by the adult, by the courts, or by operation of law. Ways to retain decision making authority Guardianship Power of Attorney Trust Representative Payee www.dussaultlaw.com Guardianship A “guardian” appointed by Superior Court upon a finding of incapacity. Types of Guardianship: Estate (financial) Person (everything else!) Scope of Guardianship Full Limited www.dussaultlaw.com Types of Guardianship •“Estate” Incapacity means “Person” Incapacity means “significant risk of financial harm based upon a demonstrated inability to adequately manage property or financial affairs.” “significant risk of personal harm based upon a demonstrated inability to adequately provide for nutrition, health, housing, or physical safety.” Duties include Duties include – Managing funds – Applying for benefits – Entering contracts – Informed consent (health care) – Decision on driving – Decisions on marriage www.dussaultlaw.com Scope of Guardianship Full Guardianship Estate, Person or both The individual loses the right to make most decisions The right to vote? Limited Guardianship Financial, Personal Care or both Tailored to fit individual’s unique needs and abilities www.dussaultlaw.com Scope of Guardianship (continued) Person Estate Full √ √ Limited √ √ www.dussaultlaw.com Establishing A Guardianship Court determines Incapacity Scope of the guardianship Who should be appointed as guardian Process: Day 1 – Petition the Superior Court to appoint a guardian. Day 1 - Guardian ad Litem (“GAL”) appointed to investigate the petition and report to the Court. By Day 5 – Service of Notice of the Petition to the Alleged Incapacitated Person (“AIP”) By Day 45 – GAL has: Conducted investigation Filed report from a physician or psychologist Filed GAL Report By Day 60 – Initial hearing before a judge or court commissioner www.dussaultlaw.com Rights of the AIP Right to be represented by counsel Represents the AIP’s expressed desires GAL represents the AIP’s best interests Right to a jury trial Presumed to have capacity until found incapacitated. www.dussaultlaw.com Who Should Serve As Guardian? Parents Siblings or other close family members Family Friends Certified Professional Guardian Public Guardianship? Stand-by Guardian Transition www.dussaultlaw.com Guardian’s Rights and Responsibilities Manage the Incapacitated Person’s assets Manage the Incapacitated Person’s financial affairs Making annual reports to the Court Up to triennial if less that $80,000 Incapacitated Person’s current condition Accounting for the Guardianship assets Is the Guardian responsible for the Incapacitated Person’s Debts? www.dussaultlaw.com Cost of Guardianship Filing fee Petitioner’s Attorney Guardian ad Litem AIP’s Attorney Less than $3,000 in the AIP’s name County will pay filing fee, GAL and probably AIP’s attorney. Petitioner responsible for their own attorney. More than $3,000 in the AIP’s name AIP’s assets will probably pay filing fee, GAL and his attorney. Petitioner’s attorney may be paid by AIP’s assets. www.dussaultlaw.com Power of Attorney (POA) A legal instrument in which a person (the “Principal”) grants another person (the “Attorney-in-Fact” or “AIF”) the right to make decisions on his or her behalf “Capacity” to sign the Power of Attorney required The Principal does not lose the ability to make decisions Substituted judgment rule Decisions of Principal “trump” POA is revocable Date of Effectiveness Immediately (terminates on disability unless otherwise indicated) Upon disability of the Principal Beware of the form! www.dussaultlaw.com POA Authority Scope of the AIF’s authority determined by language in the POA Broad language granting "all powers that the principal has" allows the AIF to make most decisions regarding the Principal's financial affairs and health care, including Financial Health Care Consent to most medical treatment Buy or sell things Enter contracts Language can be very specific and limited www.dussaultlaw.com Restrictions on POA Authority Powers that must be specifically mentioned in the document: The power to make gifts of the Principal’s money or property Change beneficiary designations Powers that cannot be given to an AIF at all: The power to vote in public elections The power to make or alter a will www.dussaultlaw.com POA vs. Guardianship Guardianship No retained rights Difficult to revoke Invasiveness Establishment On-Going Reports Psychological effect on AIP Can be expensive • • • • • • POA Retained Rights Easily revocable Privacy Does not protect against bad decisions Relatively inexpensive May be a “temporary fix” www.dussaultlaw.com Representative Payee An individual designated by the Social Security Administration (“SSA”) to act on behalf of a disabled person in dealing with the SSA Acts as a substitute to receive and handle a recipient’s benefits including SSI and SSDI Agrees to use the government benefits on behalf of the beneficiary for the beneficiary's personal care or well-being Who may serve as Representative Payee? Anyone concerned with the recipient’s welfare Individuals Organizations Parent Spouse Close relative Guardian Friend Institution such as a nursing home or health care provider; Public or nonprofit agency or financial organization Cannot be a convicted felon Role of Representative Payee Uses benefits for the recipient’s basic needs for food and shelter Provides an accounting, usually on an annual basis to the agency showing how the benefits were used. Communicates with the agency, including completion of agency requests and reports Advocates for the best interests of the disabled recipient to the agency including appeals Authority is limited to matters between the recipient and the agency. Trusts A written document allowing for management of money placed in the Trust by a selected individual (the “Trustee”) Usually for the benefit of another Less restrictive alternative to guardianship when there are concerns about the beneficiary’s ability to manage finances Types of Trusts Living (intervivos) Trusts Testamentary Trusts Allows the Trustee to dictate how money will be used, including how it is invested and spent Disclaimer & Notice This training and written materials are designed to provide accurate and authoritative information in regard to the subject matter covered. It is provided with the understanding that the presenters are not engaged in rendering legal, financial or other professional services. If legal advice or other expert assistance is required, the services of a competent professional should be sought. Please keep in mind all written materials and power point slides are the intellectual property of the Dussault Law Group. These materials may not be distributed without the express written consent of the authors. www.dussaultlaw.com