Senior-Graduate Design Project 26.518 Plastics Product Design
advertisement

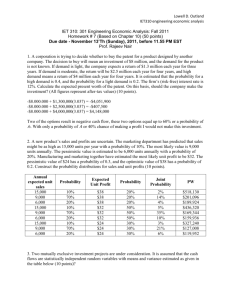
Service-Learning Integrated throughout a College of Engineering (SLICE) The vision of the project is to integrate service learning[1] into a broad array of courses so that students will be exposed to service-learning every semester in the core curriculum in every program in the entire college of engineering at U Mass Lowell. [1] Service-learning is the integration of academic subject matter with service to the community in credit-bearing courses, with key elements including reciprocity, reflection, coaching, community voice in projects. (Jacoby and Associates, 1996, p. 5) Examples of Community Partners • Tsongas History Center of National Park Service • Cambodian Mutual Assistance Association • St. Francis, Lowell General, and Spaulding Rehab Hospitals • Clinics, schools, town governments in 24 villages in remote Andes • City of Lowell • Coalition for a Better Acre, Lowell • Many local schools Assistive Technology Program, Profs. Donn Clark and Alan Rux •Example projects: Voice-controlled apartment [individual] . Talking telephone training aid [Perkins School for the Blind] . Sip-Puff pinball arcade game [New England Sinai Hospital & Rehab. Center] . Environmental control device for child [Franciscan Children’s Hospital] . Voice-controlled electric wheelchair [individual] . Suction control switch interface [individual] . Single switch talking scanning device [Franciscan Children’s Hospital] . Time switch control radio training device [Kennedy Day School, Boston] . Telephone switchboard interface device [Perkins School for the Blind] Program is 15 years old with hundreds of partners, many sponsors Example: Playground Safety • Sophomore required course in kinematics in ME • Forty-two students Spring 2004 • Analyze kinematics of children on different rides and impact from falls, test surface. • Write report to responsible party on safety of playground From textbook to reality: Village Empowerment Project 60 student-designed systems installed in 26 villages in Peru; 15 trips; 70 students Dilemma: Should we provide TV for Andean Villages? Engineering Ethics Course, 180 engineering students Prof. Gene Millican Miniproject (pros and cons essay for takehome exam) Senior-Graduate Design Project 26.518 Plastics Product Design (Carol Barry) • Client • Objective – Replace cement grave vaults with plastic or composite systems • Challenges – Learning about soil loading • Prof. Pradeep Kurup – Designing for 100 years + – Meeting cost requirements • Final design presentations – Dec. 17 at 11:30 am http://www.cem.va.gov/index.htm Mahanth, Rios, Truong Service Learning in a College Wide Introduction to Engineering Course 270 students + open ended problem = Museum exhibit with 60,000 grade school visitors (Prof. Dave Kasmer) 14.460 Water Resources Eng. • Homework Project: Design an open channel structure for irrigation villagers in Peru. Expected Outcomes: Students • Attraction of underrepresented groups into engineering, • Sufficient knowledge to solve “real world” problems, • Enhanced motivation, active learning, experience with serving others, while covering the same course material, • More practical applications in the courses, • Treatment of the sociological and environmental consequences of engineering decisions, • Application of “good engineering practice” for community “customers” for quality improvement, • All the positive cognitive and affective benefits found in previous studies. Expected Outcomes: Community • technical design and testing services available that otherwise would not be, • infusion of new ideas, • exposure to innovative, efficient, environmentally appropriate engineering systems, • assistance in attaining the goals of the particular community group, • transfer of knowledge and skills to community groups and vice-versa, • transfer of perhaps donated equipment to those in need. Expected Outcomes: Faculty • Revitalization in teaching and service • Coincidental generation of ideas for research and service through course projects • Enhanced cooperation and unity among departments • Engaged students, departments, and college • Promotion and tenure Expected Outcomes: Institution • Reform of many courses, • Increased economic and social benefit to the region, which is in the charter of the university, • Improved community relations and support, • Increased recruitment and retention of students, • Graduates with more civic responsibility