code compliance
advertisement

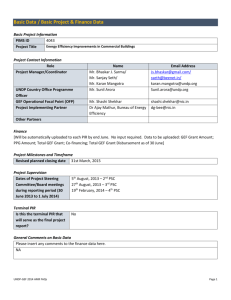
Best Practices in Building Energy Code Implementation NRDC India Initiative 1 Building Energy Consumption in India Commercial and Residential Buildings Everything else 70% of India’s building stock in 2030 are yet to be built. 2 Benefits of Building Energy Efficiency • Save $696 billion worldwide by 2030. • Reduce lifetime operating costs of buildings. • Reduce peak electricity demand. • Reduce need for more power plants. • Reduce greenhouse gas emissions. • Spur innovation in the construction and building materials sector 3 Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC) • A set of standard energy efficiency measures • Save 1.7 billion kWh of electricity in India annually • Applicable to commercial buildings, offices, hospitals, IT parks, and high-rise residential buildings • Applicable to buildings with loads larger than 100 kW or 120 kVA Walls and windows Building envelope Lighting Electric motors 4 Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC) • Voluntary at national level • Champions States for ECBC adoption: Rajasthan, Orissa, Delhi, Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh, Haryana, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, and West Bengal. * Source: United Nations Development Program (2011) 5 Steps for Implementing ECBC 1. Adopt energy efficiency measures into building bye laws 2. Form steering committee to oversee implementation 3. Train and certify third-party inspectors 4. Create checklists, certify software to evaluate energy efficiency 5. Use innovative strategies for implementation: – Break down EE measures and roll out in phases – Have a locally adapted code; national-level quality control – Engage utilities – Support local bodies by providing policy guidelines, legislative guidance, and promoting local programs (e.g., Town and Country Planning Organization) 6 BEE publishes ECBC. Min. of Urban Dev. Issues a directive to state and local level bodies to start implementing ECBC. Urban Development Departments (UDDs) develop General Development Control Regulations (GDCR). Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) write bldg codes compliant with ECBC. BEE approves any provisions in local GDCRs and bye laws where they are different from ECBC State legislature approves GDCRs and bye laws. Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) enforce those codes at city and town level. Urban Development Departments (UDDs) oversee the activities of ULBs within each state. Local Level State Level National Level ECBC Enforcement System Town Development Offices (TDOs) include provisions of GDCR into local bye laws. 7 ECBC Development System Technical advisory and consultancy of MoUD Urban and regional planning and development strategies Research. Monitoring, and appraisal of central government schemes and development strategies Oversee the activities of ULBs within each state. Regulate urban development; Town planning; regulation of construction buildings, roads, etc. Legend Organization Central Government National Action Plan on Climate Change Min. of Urban Development National Mission on Sustainable Habitat ECBC Town and Country Planning Organization Urban Development Departments (UDDs) Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) (e.g., Municipal Corporations, Municipalities, Nagar Panchayats) General Development Control Regulation (GDCR) (a framework for building regulation) Town Development Offices (TDOs) Building Bye Laws (Individual plot level building regulation) ULB Subcommittee for proposing bye law Document Comment State Legislature 8 US Example: California Building Code Implementation Certificate of Construction Design -Builder, homeowner, or code consultant prepares and submits application materials - Building Department or contracted third party reviews the design Certificate of Occupancy Construction Occupancy -During the construction, Building Department representatives or contracted third party may make site visits to make sure the construction conforms to approved design - Remaining building components such as lighting and solar hot water that were not approved during the design phase are reviewed and approved 9 Strategies to Scale Up ECBC Development System (1/2) • Roll out the requirements of the code phases – Give time to designers, builders, and code officials to obtain knowledge and experience – Break down the energy efficiency requirements of the code into multiple phases (tiers), based on the energy saving potential and level of skill training required • Hire Third Party Contractors for Inspection and Plan Review – Provide training, certification, and quality control for third parties. 10 Strategies to Scale Up ECBC Development System (2/2) • Allow local building authorities to modify EE measures based on local conditions; perform quality control on national level – Monitor progress towards national compliance targets with regular progress reviews and random inspections. – Example: China has a three-level code enforcement system: project-level, local-level, and national-level. • Engage utilities and local entities – Utilities can support customer driven energy efficiency and create demand. – Support local bodies by providing policy guidelines, legislative guidance, and promoting local programs (e.g., Town and Country Planning Organization). 11 Thank you! Natural Resources Defense Council Anjali Jaiswal and Radhika Khosla ajaiswal@nrdc.org and rkhosla@nrdc.org http://www.nrdc.org/international/india/ 12