What is US Foreign Assistance?
advertisement

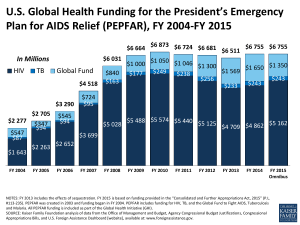
Alleviating and Addressing Hunger U.S. Foreign Assistance 101 U.S. Development or Foreign Assistance • The international affairs budget “150 Account” • Foreign aid • Official development assistance (ODA) • Poverty-focused development aid What is U.S. Foreign Assistance? WHO ? • Transfer of resources from the USA -> developing countries and to some strategic allies What is U.S. Foreign Assistance? HOW ? • Money (via loans or grants), • contributions of goods (i.e. food aid), • and technical assistance What is U.S. Foreign Assistance? WHY ? • For a variety of reasons, not all having directly to do with development... What is U.S. Foreign Assistance? WHAT ? (the Categories) • National security and foreign policy interests i.e.. Uzbekistan and Pakistan in exchange for use of their territory for military operations in Afghanistan. What is U.S. Foreign Assistance? WHAT ? (the Categories) • Political development and stability – conflict prevention, to build peace after conflict, and to strengthen failing states Camp David Accords – Egypt and Israel Humanitarian crises to countries and people suffering famine, recovering from a natural disaster, or displaced by conflict Long-term development purposes – • • • • • • • fight poverty support agriculture build roads educate children build health care capacity create small businesses spur economic growth “Foreign Aid” - broad category of grants • Economic development • Emergency response to disasters ----------------------------------------------• Security and military assistance • Counter-narcotics and terrorism activities • Programmes to fight corruption and increase public transparency Foreign Aid – funds to military and political allies for strategic purposes • Israel, Egypt and Jordan – US strategic interests in the region • Pakistan – cooperation against terrorism • Colombia – counter-narcotics programmes (some programmes may benefit the poor, but this is not their primary purpose) U.S. INTERNATIONAL FOOD AID PROGRAMMES: BASIC DESCRIPTIONS • P.L. 480 (Titles I, II, III & V) • Food for Progress Act of 1985 • Agriculture Act of 1949, Section 416 (b) • McGovern-Dole International Food for Education and Child Nutrition Programme • Bill Emerson Humanitarian Trust US National Security Strategy – the Three Pillars: 1. Defense 2. Diplomacy 3. Development (Post 9/11 – since 2002) - Millennium Challenge Corp (MCC) - President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR) MCC – Millennium Challenge Corporation Five year grants - Countries rewarded = Conceptual Basis for effectiveness of aid (eligibility criteria): 1. Good governance 2. Economic freedoms 3. Investments in people MCC - $ 7.9 billion programmes in 22 countries to date • Countries must design programmes themselves • Benchmarks of progress to receive each round of funding • US Congress impatient with slow disbursement rates PEPFAR • $ 15 billion for 5 years to target 2 million people on anti-retroviral treatment • 15 Focus countries • Broad support within US Congress US Official Development Assistance by Agency CY (calendar year) 2006 NET OFFICIAL DEVELOPMENT ASSISTANCE IN 2009 Source: OECD, 14 April 2010 Percentage spent on Foreign Aid from the US Federal Budget ? • 30 percent ? • 13 percent ? • Total International Affairs Budget (including diplomacy, development, etc.) – i.e. 150 Account equals... • 1.3 percent of US Federal Budget Percentage (poverty-focused portion) = Less than 1 percent...(0.55 %) • for programmes that improve livelihoods and create lasting solutions to world poverty • Canada - 0.30 % (double the US %) • UK – 0.51 % (triple the US percentage) Lawns vs. Foreign Aid Americans spend as much on maintaining their lawns—$30 billion annually—as the US government spends on foreign aid Pets vs. Foreign Aid Americans spend more on caring for pets—$45 billion annually—than the US government spends on foreign aid Candy vs. Foreign Aid Americans spend as much on candy—$30 billion annually— as the US government spends on foreign aid. US Foreign Aid • At $ 30 billion, US largest bilateral (plus multilateral!) donor in absolute terms • But, compared to the US income, aid levels have fallen over the past 40 years • Increases in the past few years, due to PEPFAR, MCC and debt relief (Iraq and Nigeria, plus Afghanistan, Pakistan...) NET OFFICIAL DEVELOPMENT ASSISTANCE IN 2009 Source: OECD, 14 April 2010 US ODA as percentage of gross national income GNP = Gross National Product GNI = Gross National Income COMPONENTS OF DAC DONORS’ NET ODA Source: OECD, 14 April 2010 Current Events • The US Global Development Policy • Feed the Future • USAID Forward Foreign Aid has increased in last 5 years, but... • Despite new resources and renewed attention, US ODA system remains: • Fragmented (too many players/agencies) – USAID – overseas only 45 % of US Foreign Aid • Cumbersome/bureaucratic – US laws on foreign aid = 33 different goals, 12 Departments, 25 different agencies, 60 separate Gov’t offices U.S. Leadership • Key Issue – given the absolute amounts of foreign aid • When the US fights poverty, everybody wins... (beneficiaries, host countries, Aid agencies around the world, the planet...)