Ilias Iakovidis
advertisement

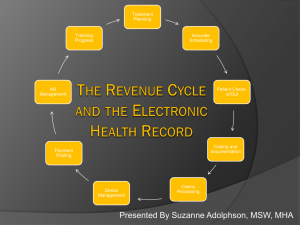
EHR Workshop Brussels 11 -12 October 2007 Introduction to the Workshop on Primary and secondary use of EHR Ilias Iakovidis Deputy Head - ICT for Health DG Information Society and Media EU Commission EHR Workshop Brussels 11 -12 October 2007 • Welcome • EU eHealth Agenda • EHR – situation on the ground • Why this workshop ICT for Health Unit Information Society and Media DG European Commission • European Union –ICT for health office established in 1989 , supported to date over 400 project, worth more than €1 Billion • The vision (since 1994): “eHealth enabled Citizen-centred care” or equivalently “eHealth enabled Continuity of care” • Major focus in 90’s: Regional Health Information Networks, Electronic Health Records, Homecare/telemedicine • Today’s focus – • Support to deployment of R&D results of 90’s • R&D in Personal health systems, Patient safety, modelling and simulation of human physiology (disease simulator) eHealth Vision of EC (since 1994): Enable Continuity of care/Patient centered care Through all the stages Across all the points of care HOSPITAL Prevention Diagnosis Care Rehabilitation PHYSICIAN HEALTH AUTHORITIES HEALTH INSURANCES PHARMACY How: Sharing information LABORATORIES Tools: Electronic health records Regional health information networks Link the healthcare institutions and provide applications to for health professionals (R&D Focus 1991-2001) Health Centre Emergency Hospital Pharmacy Secure Networks Region 3 Mobile, Wireless mobile PC & Broadband Region 2 Region 1 Home Mobility Link the people with the health Infrastructure/services (EC R&D focus since 01) Health Centre Emergency Hospital Pharmacy Secure Networks Region 3 Mobile, Wireless mobile PC & Broadband Region 2 Region 1 Home Mobility Current R&D focus: Towards full picture of individual’s health status (Molecular Medicine) Biochips Biosensors Environmental Data Genomic data Phenomic data Integrated Health Records Support to Deployment: eHealth Action plan: COM(2004) 356 final ‘ Main areas of activity • • • • • • National/regional roadmaps Common approaches for patient identifier Interoperability standards for EHR and messaging Boosting investments in eHealth Certification and labeling Legal framework, certification of qualifications • Yearly Ministerial conferences & exhibitions (next in Malaga, Spain 10-12 May, 2006) • World of Health IT yearly conference Support to Deployment of eHealth Priority for EU • DG INFSO ( + DG ENTR, SANCO, RTD, MARKT, COMP) • CIP Porgramme - pilots • Lead Market initiative ( follow up of AHO report) • ASP 2008 – Chronic Disease Management • DG SANCO • Initiative on health services • Initiative on Eu Health strategy • DG JLS • Privacy of data in Electronic Health Records Hospitals 2004: EHR systems Hospital EPR systems - Installed base - 2004 100% 80% 60% 40% 20% Medical document management Order communication Computer based storage of electronic patient records Knowledge Support Systems EU FI N DK SW NO CH AU NL BE ES IT EI RE UK / FR DE 0% (Hospitals in Germany) Medical Records – Medical Document Management Systems (France) (Hospitals in France) Main Storage Medium in Medical Records Library Main Storage Medium in Medical Records Library (Italy) Hospitals in Italy IT use among primary care physicians in seven countries www.medcom.dk Prescriptions 80% Disch. Letters 81 % Lab. reports 95 % Estimated cumulative benefit by 2008: ~ € 1.4 bil. Reimbursement Referrals 13290 = 95 % 40113 =80% EHR related activities around the World Accenture, 2007 Canada – Infoway set up to design and procure National EHR - $1.2 billion of government backing USA - ONCHIT promoting NHIN and RHIO’s. Government has invested $140 million to date. EHR Maturity High Medium Mexico: No EHR but aim for HL7 Integration Low Considering EHR Data N/A or No EHR Presence Chile: PACS in Santiago University Hospital Q2 2004. Denmark : National EHR for January 2006. England: Connecting for Health£6 billion until 2010. Netherlands: 88% of GPs have an EHR France: EHR Mandatory by 2007. Sweden: Developing a National EHR – Germany: EHealth card by January 2006. China: Plans to develop a national EHR Hong Kong: Territory wide Patient Master Index Singapore: EMR system tender expected Q1 2005 Australia: Malaysia: Brazil: HealthConnect is Lifetime Health National Health developing a Record (LRH) Card Project. National by 2010 st Information Argentina: 1 Network. adoption of a New Zealand: digital South Africa: National EHR system radiography No EHR – but in place. solution- 2004. infrastructure being developed. TOP standards HINE Survey (2004) Information standards meant to prevail - EU - 2003 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 HL7 33 XML/Web 27 12 DICOM Snomed CT ISO 35 11 7 • HL7, SNOMED CT, XML and DICOM are the favourites. Three countries reported not having decided yet. • All pointed out how critical is the usage of international accepted standards. • All requested more cooperation with health professionals (clinically oriented) to tackle semantic interoperability. • IHE initiative mentioned three times as major interoperability initiative (clinicians/vendors) Hospitals 2004: Standards Integration standards - 2004 (Europe) 100% 90% 80% 70,4% 71,3% 70% 63,7% 64,9% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 7,4% 10% 8,2% 0% HL7 HISA Currently Next 5 years DICOM Hospitals 2004: Standards Integration standards - 2004 (Europe) 100% 90% 80% 70% 60% HL7 50% HISA 40% DICOM 30% 20% 10% EU N FI DK SW NO CH AT NL BE ES IT EI RE UK / FR DE 0% Why this workshop (1/2) i) patient care - Primary purpose of EHR i) clinical research - Secondary usage of EHR data (other areas include public health, management, health system research) Patient care and clinical research need each other - and have potential for greater synergy: - Assisting each other in better performance/quality - Faster translation of R&D into practice - Learning from advances in information handling, knowledge representation But still are “different worlds” w.r.t. data modeling, knowledge representation and storage and communication standards, legal framework .. • in pharma limited experience with clinical care (e.g. HIS, EHR, RIS/PACS, LIS, HL7, ICD, SNOMED…) • In clinical care limited experience with clinical research (e.g. EDC, validation, ICH, MedDRA ..) Why this workshop (2/2) This workshop focuses on 3 specific topics of interest to Pharmaceutical industry where such synergy could be achieved 1) patient recruitment in clinical research, 2) electronic data capture (EDC) during clinical trials and 3) safety monitoring. 3 areas chosen where concrete recommendations could be achieved: A)Interaction model between actors of i) and ii) B) Practical solutions for interoperability between systems of i) and ii) C) Specific legal requirements regarding secondary use of EHR What do we want to achieve & how ? • Practical recommendations rather than ususal and universally known “diagnosis of problems” • focus on the 3 priority areas • Working workshop with limited competent people rather than formal communication event … we expect each participant to actively contribute • While the topics are primarily of Pharma interest they should meet concerns of different stakeholders and identify win-win situations • Clarify topics within the agenda • Provide pre-workshop material for reading (decision left for each of work stream co-chair) Structure of the workshop • • Start and finish with a plenary • Special attention should be devoted to practical suggestions such as • organisational issues for better adoption/use of EHRs, seamless and legal extraction of data for research, supporting the clinical research so it adds ( does not compete) with care processes, tracking post marketing experience to improve patient safety, … • Technical issues: terminologies, ontologies, standards, privacy enhancing technologies Three parallel streams to end up with Practical recommendations to be captured and reported on Friday afternoon Organizing Committee • • • • European Commission: • Ilias Iakovidis (ICT for Health), with the support of Veli Stroetmann (empirica research) European Federation for Pharma Industry Association (EFPIA): • Isabelle de Zegher (Novartis), • Jean Samuel (Pfizer), • Mats Sundgren (Astra Zeneca), • Bernard Ferre (EFPIA) Clinical Care: G. de Moor (Eurorec) IT Vendors: • G. Zhalmann (Siemens), • P. Wilson (CISCO) Interoperability • Concept with vast scope and many facets • Many research groups working for decades • Many international efforts with US, CA, and AUS • Major technical aspects are common with other areas But the semantic interoperability has to be done by the domain experts EC funds several projects on Semantic interoperability such as Semantic Health and RIDE Interoperability “Interoperability means the ability of information and communication technology systems and of the business processes they support to exchange data and to enable the sharing of information and knowledge”. Recommendation by EC to be published in 2008 Please review and update ( e.g. pg 10!) ICT for Patient Safety • Description of the upcoming projects Conclusions & Practical considerations • Coffee, lunch, timing • Permission to use presentation & written material • Focus and small concrete step rather than “boiling the ocean” • To find more on ICT for Health / eHealth? • Policy site: http://europa.eu.int/information_society/activities/health/index_en.htm • eHealth R&D Newsletter (monthly issues): http://europa.eu.int/information_society/activities/health/research/ newsletter/index_en.htm Thank you ilias.iakovidis@ec.europa.eu