VistA Service Assembler
advertisement

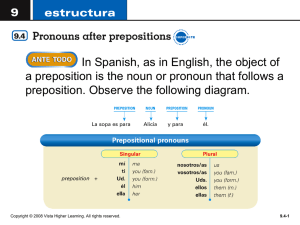
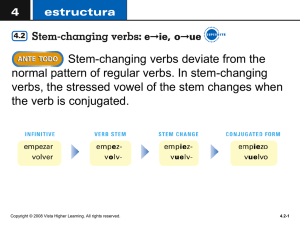
VistA SOA Services VistA Service Assembler (VSA) Conceptual and Technical Overview VSA Development Team April 2014 The VSA “Narrow Focus” “How is VistA supposed to integrate with external systems / applications in the Service Oriented Architecture (SOA) environment?” VistA SOA Services 2 Common Legacy SOA Interpretations VistA Encapsulation / Encasement HealtheVet VistA Notes Service Ordering Service Rx Service CP&E Service Consumers Atomization / Re-Hosting – Major retooling and investment – Subjective interpretation – Inability to anticipate future consumers – Tendency to build too much, to build too little – Perpetuates shortcomings and dependencies on legacy systems – Inhibits individual application replacement – Granular logic, “chatty” communications exacerbated by the middleware layer MDWS/VIA VistA Notes Rx Ordering Consumers CP&E VistA SOA Services 3 VSA precepts VistA Service Assembler (VSA) is not an “adaptor”. It positions VistA as a direct provider of SOA web services. This is a paradigm shift in VistA system integration approach VSA is not a collection of ‘services’, it is a set of utilities that facilitate the structured creation of VistA-based, SOA compatible services With minimal technical orientation, VSA facilitates the automated creation of VistA based web services to support system integration and the implementation of SOA in the VA VistA SOA Services 4 VSA Objectives and Outcomes Technical— • Position VistA as a direct provider of SOA services – Maintain/enhance existing security, auditing and role based access – Ensure implementation of the ‘user identity communication’ design pattern, generalizable for all VistA connectivity middleware solutions – Maintain VistA data integrity and VistA application-based provision/interpretation of data – Ensure SOA architectural principles (e.g. authoritative services, nonredundancy, loose coupling) – Standardize VistA SOA service design to support improved maintainability and sustainability Organizational— • Facilitate effective and reliable VistA SOA development – Simplify organizational orientation related to development that involves both legacy VistA and OO environments – Facilitate VistA SOA service development efficiency through automation – Enable community development participation and VSA product utilization (e.g. ‘open source’) VistA SOA Services 5 Major Elements of the VSA Solution • VistA SOA service infrastructure – – – – VistA Service Assembler Wizard Service descriptors database Federating platform and federating logic M environment components for ‘service’ execution • Definition of Policy and Process – VSA infrastructure distribution – VistA SOA service distribution • External component integration and implementation** – VistA SOA ‘reference implementation’ services – VSA “Pre/Post” action logic components **Collaboration with/contribution by external groups VistA SOA Services 6 VistA Service Assembler (VSA) High Level 1 2 3 4 5 VistA A M Developer or System Integrator identifies existing or new M routine(s) to be called by a new or existing VistA SOA Service. The M Developer or System Integrator executes the Assembler Wizard providing required information such as operation names, mumps routines to be called, and parameter mappings. VistA SOA Federating Services Platform - Regional (Java) 2 M Hosting Platforms MUMPS Caché Hosting Platform (Intersystems or open source (Intersystems or Open platform (ie. GT.M),Caché 130+ instances Source Platform (ie. in production in Graystone)) VA) VistA Service Assembler Wizard A VistA SOA Service descriptor is generated and stored in the VistA SOA Federating Service Platform. M Code and Data All Other Packages A new VistA SOA Service is auto-generated and published. Organizations using VSA as an ‘open source’ solution can engage VSA services directly if SOA infrastructure (e.g. ESB) is not implemented. 3 6 Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) 4 VistA Service Assembler SOA Service Descriptors (generated by the Assembler Wizard) VSA Package Site Specific VistA M Routine Calling Adapter (VMRCA) Registry and Repository Core ESB VistA SOA Services VistA SOAbyServices (generated the (Websphere Registry and Repository) (Websphere Message Broker) (generated by the Assembler Wizard) Assembler Wizard) VistA SOA Service Registry Entries VistA SOA Service Proxies 6a VA integration approach 6b Consuming Applications Consumers 6a 5 ‘Open Source’ connectivity Routines Private Interface Site Specific VistA M Routine Calling Service (VMRCS) 6 VA integration approach – ESB is deployed to production 6a Registry entries and service proxies created for the VistA SOA Services. 6b 1 The Consuming Applications integrate with the VistA SOA Service proxies published on the ESB and the direct connection to the VistA SOA Services published on VistA are retired. 7 VSA “Pre/Post” Logic (Future Implementation) SOA Services Environment Consuming Applications “Pre” logic 1. 10. ESB / eMI “Pre” logic 3. 2. 4. VSA 5. core logic 9. 8. “Post” logic VistA M Environment 6. 7. “Post” logic VistAs & RPCs Solution Attributes • Cost Effective – – – – Able to rapidly expose broad VistA functionality as ‘services’ Rapid development and incremental approach Minimal retooling of VistA applications or retraining developers Low impact organizationally • Addresses SOA objectives – – – – – – Security and system performance Semantic and syntactic compatibility Reusability and non-redundancy System maintainability, sustainability and replaceability Provides value before full SOA infrastructure is in place Complete integration and compliance with SOA architecture • Enables major consumers (e.g. mobile computing) • Alleviates ‘vendor dependence’ concerns while exponentially expanding VistA extensibility and ‘open source’ product development opportunities VistA SOA Services 9 Current Status • VSA ‘proof of concept’ delivered December 2014 • VSA ‘design time’/’run time’ components are operational, development underway to complete “essential” functionality features and prototype deployment • Major dependencies include ESB/eMI implementation, ‘user identity’ design pattern (incl. ‘user provisioning’), multiple “user” types, ‘consuming application’ authentication, service consumption governance, etc. • VSA Phase II (Feb. – January 2015)— • • Increment 1 – Development focused, initial implementation Increment 2 – Implementation focused, remaining development • Collaboration with ConnectedHealth effort • • Implementation of actual business use cases related to VPS Kiosk, etc. Non-production/”production ready” implementation of VSA ‘run time’ capabilities targeted NLT summer 2014 VistA Service Assembler 10 Navigate to a directory location and select or create a Service Descriptor file. Service Descriptor File <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?> <serviceDescriptor xmlns="http://vsa.med.va.gov/schema/service-descriptor-0.0.1"> <serviceName>ZzMkoMyService</serviceName> <serviceType>soap</serviceType> <version>1.0.1</version> <serviceNamespace>http://gov.va.med.zzmko</serviceNamespace> <javaPackage>zzmko.med.va.gov</javaPackage> <operation> <name>tiuLongListClinprocTitles</name> <rpcName>TIU LONG LIST CLINPROC TITLES</rpcName> <responseType>json</responseType> <parameter> <name>from</name> <type>string</type> </parameter> <parameter> <name>dir</name> <type>string</type> </parameter> </operation> </serviceDescriptor> Testing the Deployed Service Test Results Example of a RESTful service invoking the same RPC Questions / Comments VistA SOA Services 18 Backup Slides VistA SOA Services 19 Paradigm Shift: VistA as an SOA Service Provider Encased Leveraged VistA is encased as a system to isolate and then replace in the future VistA packages are leveraged and extended as building blocks for legitimate SOA services Adapter Integration Service Integration ‘Consumer applications’ are integrated with adapters that encase VistA ‘Consumer applications’ are integrated with SOA services exposed by ‘provider applications’ Rip and Replace Plug and Play Legacy VistA is encased with adaptors as a monolithic system, then replaced VistA applications expose SOA services, allowing application-by-application replacement Fine Grained Coarse Grained Chattiness due to business logic in adaptors, fine grained VistA methods All business logic positioned in VistA applications to produce coarse grained service logic modules Built from ‘scratch’ Built from existing components SOA services, environment and governance built “from the ground up” Existing VistA methods and data used to build SOA services, reducing development, testing, etc. VistA SOA Services 20 VistA SOA Services Runtime View Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) VistA Site 1 M Code and Data M Routines for Progress Notes Registry and Repository (Websphere Registry and Repository) Progress Notes Service Registry Entry Outpatient Meds Service Registry Entry Allergies Service Registry Entry VistA SOA Federating Services Platform Regional (Java) Progress Notes Service Outpatient Meds Service Consuming Consumers Applications Core ESB (Websphere Message Broker) Allergies Service M Routines for Outpatient Meds M Routines for Allergies VMRCA VMRCS Site N M Code and Data M Routines for Progress Notes M Routines for Outpatient Meds Progress Notes Service Proxy M Routines for Allergies Outpatient Meds Service Proxy VMRCA Allergies Service Proxy VMRCS VistA Service Assembler 21 VSA National Production Deployment Configuration Region 1 RDC 2 Region 2 RDC 2 Region 3 RDC Region 4 RDC WSRR WSRR WSRR WSRR VistA SOA Service Registry Entries VistA SOA Service Registry Entries VistA SOA Service Registry Entries VistA SOA Service Registry Entries WMB WMB WMB WMB VistA SOA Service Proxies VistA SOA Service Proxies VistA SOA Service Proxies VistA SOA Service Proxies VistA VistA VistA VistA VistA SOA Federating Services Platform VistA SOA Federating Services Platform VistA SOA Federating Services Platform VistA SOA Federating Services Platform 1 VistA SOA Services VistA SOA Services 1 2 VistA SOA Services VistA SOA Services 1 1 VistA SOA Services VistA SOA Services VistA SOA Services VistA SOA Services Site 1 to M Site M+1 to N Site N+1 to O Site O+1 to P M Code and Data M Routines M Code and Data M Routines M Code and Data M Routines M Code and Data M Routines VMRCA VMRCA VMRCA VMRCA VMRCS VMRCS VMRCS VMRCS Federated VistA SOA Services communicate with each other to produce a national view of information. WSRR = WebSphere Registry and Repository WMB = WebSphere Message Broker ESB = Enterprise Service Bus SOA = Service Oriented Architecture VMRCA = Site Specific Generic Mumps Routine Calling Adapter VMRCS = Site Specific Generic Mumps Routine Calling Service VistA Service Assembler 2 2 Chatty communication within an RDC is optimized on high speed network. 22 VSA Security Integration VistA Site 1-N Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) M Code and Data M Routines Supporting VistA SOA Services Registry and Repository (Websphere Registry and Repository) https Ensures user authentication and audit logging. VistA SOA Service Registry Entries VistA SOA Federating Services Platform Consuming Applications Core ESB https (Websphere Message Broker) https VistA SOA Services VistA SOA Service Proxies https Authorization is handled by application M routines. VMRCA In process communication VMRCS VistA Service Assembler 23 VistA Service Assembler (VSA) High Level Component Descriptions VSA Component Description VistA Service Assembler Wizard Java web application - auto generates VistA SOA Services VistA SOA Federating Services Platform Java application server such as Tomcat or WebLogic, to which VistA SOA Services are deployed M Hosting Platform A runtime system supporting ANSI standard M such as Intersytems Caché or GT.M VistA SOA Service An SOA compliant service generated by the VistA Service Assembler Wizard with federating capabilities. Implemented in the Java Spring Framework. VistA Service Assembler SOA Service Descriptors Meta data XML document created by the VistA Service Assembler Wizard used to auto generate VistA SOA Services Site Specific VistA M Routine Calling Service (VMRCS) A REST/SOAP web service deployed to each site that delegates requests to run M routines to VMRCA. Implemented in vendor specific technologies.. Site Specific VistA M Routine Calling Adapter (VMRCA) VSA M routines that handle M routine calling VistA SOA Service Registry Entry Entry in the Registry and Repository used to govern a specific VistA SOA Service VistA SOA Service Proxy Proxy on the ESB used to abstract the service endpoint. VistA Service Assembler 24 VSA Deployment and Rollout System Component VA Deployment and Rollout Mechanism Site Specific VistA M Routine Calling Adapter (VMRCA) Standard VA M patch release process via KIDS VSA Site Specific Generic Mumps Routine Calling Service (VMRCS) VMRCS is deployed in its own Caché database file at each site deployed to a region. M routines from other packages Standard VA M patch release process via KIDS VistA Service Assembler Wizard and Service Descriptors Deployed to development and not production. Service descriptors are versioned in source control. VistA SOA Services Each service is packaged as a WAR file. The service provider promotes a service through development, test and production environments. Service Registry Entries and Proxies ESB registry entry and proxy creation processes defined by operations are followed. VistA Service Assembler No Issues Foreseen 25 VSA Technology Stack (VA vs. Open Source) System Component VA Technology Stack Open Source Technology Stack VSA Site Specific Generic Mumps Routine Calling Adapter (VMRCA) ANSI Standard MUMPS hosted on Caché ANSI Standard MUMPS hosted on Caché or GT.M M routines from other packages ANSI Standard MUMPS hosted on Caché ANSI Standard MUMPS hosted on Caché or GT.M VistA SOA Services, VistA Service Assembler Wizard and Service Descriptors Java/Spring Framework/Open Source Web Technologies deployed to WebLogic Java/Spring Framework/Open Source Web Technologies deployed to Tomcat or JBoss VSA Site Specific Generic Mumps Routine Calling Service (VMRCS) Caché Server Pages (CSP) and Caché Objects hosted on Caché, CSP Gateway hosted on IIS Enterprise Web Developer (EWD) hosted on Apache/IIS/CSP and Caché stack or on Node.js and GT.M stack VistA Service Assembler VA/Open Source Integration Issues? 26