computerappsenterprise_lectures6789

Computer applications in the modern enterprise
Επιχειρησιακές Εφαρμογές Η/Υ
Lectures 6-9: Get closer to what the real thing is –
Business Intelligence as IT application
Univ. of the Aegean
Financial and Management Engineering Dpt
Petros KAVASSALIS
<pkavassalis@atlantis-group.gr>
1
What you will learn in this course
A set of fundamental concepts and frameworks for understanding the potential impact of information technology (IT) on business strategy and structure
Computers and Information Systems (IS)
The business value chain
Business integration through Enterprise Application Integration
Information Systems in practice: How does the modern enterprise use
“Business Intelligence” (BI) systems to improve decision-making
Methods and BI examples
“Hands-on” experience: create business reports by using Eclpise BIRT Reporting Tool
( http://www.eclipse.org/birt/phoenix/ )
<pkavassalis@atlantis-group.gr> 2
Communication tools
e-mail: pkavassalis@atlantis-group.gr
Course web site: see FME web site
<pkavassalis@atlantis-group.gr> 3
Students evaluation
Class Participation (20%)
+
Assignments (20%)
+
Final Exam (60%)
<pkavassalis@atlantis-group.gr> 4
What I am going to say
Within the modern enterprise
Inter-organizational relationships
Intra-organizational relationships are supported by Information Technologies
It is about enterprise applications that inter-operate to move information around
Not only within existing business frontiers but also within the network of the collaborators and customers of an enterprise
Not randomly but in an organized way, within the enterprise architecture framework
<pkavassalis@atlantis-group.gr> 5
Enterprise Architecture Framework
or Enterprise Application Integration (EAI)
The organizing logic for) for aligning business operations and IT infrastructure reflecting priorities and other internal decisions (MIT
CISR …
For delivering goods and services to the customer
It is what makes businesses to differentiate from the competitors
IT as strategic business enabler
IT to improve operational efficiency
IT to meet existing and new business needs
IT need investments
<pkavassalis@atlantis-group.gr> 6
Enterprise architecture
<pkavassalis@atlantis-group.gr> 7
Why IT? more
You know:
Companies are moving aggressively to computerized support of their operations
Why?
Operational efficiency
Better serve customer needs o
Leverage new opportunities
More: o o o
Business pressures (BP)
Result of today's competitive business climate
Organizational Responses (BR)
To counter the pressures
Computerized Decision Support (CDS)
To better organize the process of decision making
<pkavassalis@atlantis-group.gr> 8
Decisions and Support
[Reference: E. Turban et al., 2011, Business Intelligence,
Pearson – chapter 1]
<pkavassalis@atlantis-group.gr> 9
Business Pressures (BP)
[Reference: E. Turban et al., 2011, Business Intelligence,
Pearson – chapter 1]
FACTOR DESCRIPTION
Markets Strong competition
Expanding global markets
Blooming electronic markets on the Internet
Innovative marketing methods
Opportunities for outsourcing with IT support
Need for real-time, on-demand transactions
Consumer Desire for customization demand Desire for quality, diversity of products, and speed of delivery
Customers getting powerful and less loyal
Technology More innovations, new products, and new services
Increasing obsolescence rate
Increasing information overload
Societal
Social networking, Web 2.0 and beyond
Growing government regulations and deregulation
Workforce more diversified, older, and composed of more women
Prime concerns of homeland security and terrorist attacks
Necessity of Sarbanes-Oxley Act and other reporting-related legislation
Increasing social responsibility of companies
10
Organizational Responses
Organizations should be
Reactive
Anticipative
Adaptive
Proactive
Support executives and work practice with exact knowledge on “what is going on” in each area of operation, process etc.
More general: Business action needs computerized support
Please give examples o
From a Bank o o
Insurance
Tourism industry
<pkavassalis@atlantis-group.gr> 11
Computerized Decision Support
Informing about the reality
See New York Municipality site (CPR)
Rationalizing and improving the decision-making process
Closing the gap between the current performance of an organization and its desired performance (i.e. where do we want to go?)
as expressed in its mission, objectives, and goals, and the strategy to achieve them
<pkavassalis@atlantis-group.gr> 12
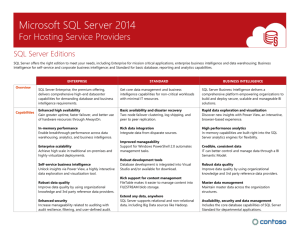
Business Intelligence: definition (1)
BI is an evolution of decision support concepts over time
Meaning of EIS/DSS… o o
Then: Executive Information System
Now: Everybody’s Information System (BI)
BI is an umbrella
Architectures
Tools
Applications
Methodologies
BI systems are enhanced DSS with additional visualizations, alerts, and performance measurement capabilities
The term BI emerged from industry apps
<pkavassalis@atlantis-group.gr> 13
Business Intelligence: definition (2)
BI's objective is to enable easy access to data (and models) to provide business managers and key workers with the ability to conduct analysis
BI helps transform data:
to information (and knowledge)
to decisions and finally to action
BI app components
Data warehouse, with its source data
Business Analytics, a collection of tools for manipulating, mining, and analyzing the data in the data warehouse;
User Interface (e.g., dashboard)
+ Business Performance Management (BPM) for monitoring and analyzing performance
<pkavassalis@atlantis-group.gr> 14
Business Intelligence: architecture
<pkavassalis@atlantis-group.gr> 15
BI from the Univ. of Michigan
[http://www.bi.umich.edu/learn/what.html?autoplay=true&tra nscript=true]
<pkavassalis@atlantis-group.gr> 16
BI example
[http://www.epagogix.com/]
<pkavassalis@atlantis-group.gr> 17
BI LifeCycle (1)
... Starts here
Planning
<pkavassalis@atlantis-group.gr>
ΗΠΑ:
Department of Defense
18
BI LifeCycle (2)
Planning / Tasking
Data Collection
Processing & Exploitation
Analysis
Iterative process
Production – Dissemination
Use
<pkavassalis@atlantis-group.gr> 19
BI LifeCycle: Planning & Data Collection
Planning
Why? Who will use it?
Expected Results o o o
Reports
Web Site
More?
Project Design
Time Plan
Data Collection
Preparation Phase o o
Data Sources
Collection Period
Familiarization with Data o o o
Data Cataloging
Sources Cataloging
Filtering
<pkavassalis@atlantis-group.gr> 20
Data from
External
Sources
BI LifeCycle: Processing & Exploitation
Howson:
Successful Business Intelligence
{ETL: extract, transform, load}
<pkavassalis@atlantis-group.gr> 21
BI LifeCycle: Processing & Exploitation
(cont.)
E Turban et al: Business Intelligence, Pearson
<pkavassalis@atlantis-group.gr> 22
BI LifeCycle: Analysis
[Business Analytics, BA]
Wikipedia
Business analytics makes extensive use of data, statistical and quantitative analysis, explanatory and predictive modeling , and factbased management to drive decision making . Analytics may be used as input for human decisions or may drive fully automated decisions.
Business intelligence is
Querying
Report Design (dashboards and scorecards)
Alerts
Cube Analysis ( OLAP )
<pkavassalis@atlantis-group.gr> 23
BI LifeCycle: Production & Dissemination
<pkavassalis@atlantis-group.gr> 24
S. Ottl: Emerging Trends in Business Analytics and Business Intelligence
In a nutshell
Process Time Analysis Time Action Time
Technical Staff
<pkavassalis@atlantis-group.gr>
Field Users
Managers
Executives
25
BA example
[http://www.quadbase.com/espressreport/help/examples/i ndex.html]
<pkavassalis@atlantis-group.gr> 26