The Practical SLP powerpoint 2007 copy
advertisement

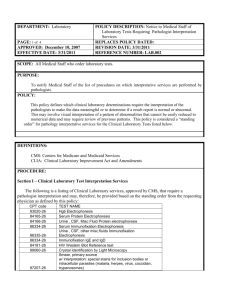
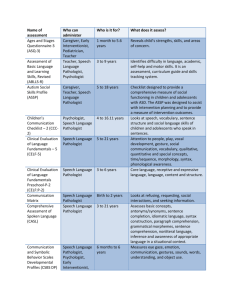
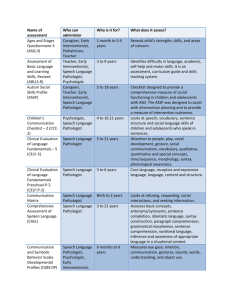
The Practical SLP: Middle School A Guide to the roles and responsibilities of the Middle School Speech Language Pathologist Forward The following power point is based almost solely on my 20 years of experience as a Speech Language Pathologist. I have spent the last 11 years working as a Middle School Speech Language Pathologist. I know what my role is in my student’s education. However, I never felt the administration, teachers, support staff and parents understood what I do. In some school systems, the speech language pathologist is just considered an articulation expert. We are much more than that. Parents and professionals often view us as the “speech teacher”. I have to admit that I have perpetuated this by referring to my self as the “speech teacher” (a throw back from my preschool days) or telling the kids it is “time for speech”. Our own professional group has given us a confusing name “Speech Language Pathologist”. Often shortened to Speech Pathologist. A pathologist that does therapy. The only pathologist most people know is a medical examiner. Our official title change actually occurred during my career. It is no wonder that there is often confusion as to what is the role of the speech language pathologist, the name alone is semantically confusing. Fortunately, teachers and parents usually only have to sit through one team meeting with us to realize we are not just experts in articulation but in language and communication as well. In my community, the first wave of integrated preschoolers graduated from high school, class of 2004. These students were successfully integrated into their local public school through out their school career. This happened in schools all over the country. Specialized programs and special education services increased drastically within the public school system during that time. The public school speech language pathologist’s caseloads grew and evolved to accommodate these students. A public school therapist was no longer working on only vocabulary, grammar and articulation. These students varied in their needs from mild language learning disabilities to severe physical and mental impairments. Along with this trend in public education, parents awareness of their children's special needs and their power to advocate for them grew. Both these factors effected the growth of the Speech Language Pathologists caseload. forward cont. We all know that middle school is a time of transition for students. Expectations for the older student increase and school becomes more challenging. This is no different with language/learning disabled students. By middle school most goals and objectives written by a speech language pathologist will focus on higher-level language needs not just articulation or When referring to language needs at the middle school level we are talking about teaching the skills needed to make students proficient listeners, speakers, writers, communicators and social beings. basic grammatical usage. I hope you find this power point helpful and informative. Teresa Sadowski MA/SLP-ccc AKA The Speech Teacher What does the Middle School Speech Language Pathologist Do? This power point will help to answer the following questions What are the common areas of language the speech pathologist addresses? What does the typical middle school speech and language caseload look like? What does the typical middle school speech and language student look like? What is the best way to service the middle school speech and language student? In class or pull out How does a student qualify to receive speech and language therapy? Does the middle school speech pathologist address articulation? When is a student ready to be discharged from therapy? When should a student be referred for a Speech and Language evaluation? Some of the common areas of language the Speech Language Pathologist might address at the Middle School level are: auditory perceptual abilities (memory, comprehension etc..) organization of language understanding of word relationships awareness and understanding of language needs higher-level vocabulary word retrieval understanding of ambiguous language understanding of figurative language pragmatic/social speech skills expanding language problem solving, reasoning, drawing conclusions and making inferences language difficulties due to hearing impairment The Typical Middle School Caseload Middle School caseloads have shown significant growth in the past several years. Every school system tends to deliver special need services differently depending on their population. Because of this, the speech language pathologist’s caseloads can be extremely diverse. Severely disabled students may be in a separate program either within the public school setting or in a separate facility. Those students have extremely unique needs, which requires even more of the speech pathologist’s time and expertise. Most Middle School Students on the speech pathologists caseload will fall into two specific categories Language learning disabled students Students with social pragmatic needs Or a combination of both The typical student on the Middle School Speech and Language caseload will probably: have a history of a language/learning disability from early on be integrated into the regular classroom setting for most of the day have received speech and language therapy through out grade school require additional support by either a special needs teacher or a teaching assistant through out the day. require other special services such as counseling demonstrate other academic and learning needs How are Speech and Language Services Delivered There is no ideal service model at the middle school level. The way the Middle School Speech Language Pathologist services students is extremely dependent on the type of special needs program the school provides, the type and size of the caseload, individual student needs and the therapist’s personal philosophy. Servicing Students within the Classroom Setting Many speech language pathologists and scholars will insist that the curriculum based co-teaching model is the only way to service middle school students efficiently Cons Pros Curriculum based Working on class work relevant to the student. Scheduling may be easier if several children can be serviced at one time Can work on developing compensation techniques within the classroom setting. During the course of a class there are fewer opportunities to interact, in a therapeutic manner with your student. The co-teaching model requires significant planning time with the classroom teacher and a significant amount of time servicing the student within the classroom setting. Unless this is a full time proposition it is almost impossible to co-teach effectively. SLP’s who attempt co-teaching as an alternative to direct therapy often fall into the trap of becoming a “glorified teaching assistant” rather that a therapist May end up working on getting through class work rather than focusing on goals The last thing most middle schoolers want is another adult hanging around them making them feel different Servicing Students with the Traditional Pull out Model. I prefer this model. A few other therapists and scholars also think this way. Pros The pull out method provides the therapist a good chunk of time to work directly on a specific language skill With a little planning class work and selected vocabulary can still be worked on Small group settings can provide structured social interactions for students who need it Students are more likely to work on improving specific weak skills if they are in a private or semi-private setting Work on specific skill development has a better chance of transferring to other settings. Cons Scheduling can be a nightmare. If they are taken out of core classes they might miss too much work. It is very difficult for special needs students to catch up on their work. Coming out of small group settings, specialists (art, gym, music etc) or support periods may be a little easier. However, specialists classes are fun, provide a little relief from academics and provide opportunities for social interaction. Some students do not want to be pulled out of class for any reason. How does a Student Qualify to Receive Direct Speech and Language Services? Most schools systems require the student to go through a pre-referral process to determine if specialized testing is necessary. Speech and language testing is completed focusing on the specific area of need and general receptive/expressive language abilities. Testing will determine if the student exhibits a language based learning disability. Other factors taken into account when determining a language based disability include: classroom performance, other areas of need and manner of performance during testing. Whether or not a student receives direct services is a team decision with specific recommendations from the Speech Language Pathologist. Very few Middle School students receive direct articulation therapy By middle school most articulation issues a student may have been remediate A few students may continue to have difficulty with later developing sounds such as s,z, and r. These are very difficult sounds to remediate, especially for young children. Some children will present with a history of severe oral motor dyspraxia and may continue to require specialized therapy. Many children are going through extensive orthodontia and articulation therapy may be counter productive. To successfully remediate articulation at the middle school level the student must be invested in therapy. Another consideration is whether or not articulation is effecting the child’s classroom performance. Students who present with intelligibility issues to the extent that it interferes with academic or social development may be candidates for continued articulation therapy. Discharge Criteria A student should be discharged from Speech and Language therapy when….. age level goals have been met evaluation results indicate that the student is within the average range of functioning. the student has developed compensatory skills that are functional in the deficit areas. the students deficit areas can be managed through classroom modifications. the student has shown little or no response or gains from direct speech and language therapy for the past school year the student has plateaued in the areas of development related to speech and language treatment. a parent requests that speech and language services be terminated. the students disorder is not considered amenable to remediation at this time attendance is an issue the team decides that it would be in the child's best interest to discontinue direct services. When Should a Student be Referred for a Speech and Language Evaluation? Most schools have a pre-referral process to determine if a speech and language evaluation is warranted At the middle school level a student should be recommended for the pre-referral process if concerns are raised in any of the following speech and language areas. Trouble following directions Trouble understanding new concepts Hearing acuity Poor vocabulary skills Difficulty organizing language Using inappropriate word order or grammar Difficulty staying on topic Difficulty understanding simple word relationships Has a hard time understanding jokes Inability to reason Has difficulty interacting with peers or adults If you have any questions or concerns about a students speech or language abilities…………Just Ask! It has been my experience that Speech Language Pathologists love to talk and talk about what they do! So ask away. We also love to give our opinion. Seriously……… The Speech Language Pathologist can also offer support to the general education curriculum as a consult whenever necessary. The Speech Language Pathologists works with kids in a therapeutic manner to remediate speech and language issues. The Speech Language Pathologist may offer suggestions from a different perspective. I am always happy to help colleagues and parents by offering any assistance around speech and language issues. So are most Speech Language Pathologists.