What Is A Surrogate Parent?
advertisement

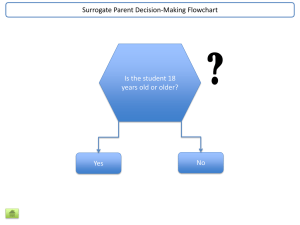
A presentation by the El Dorado County Office of Education Charter SELPA (adapted from a presentation developed by Riverside County SELPA) Training Objectives Examine basic roles, rights, responsibilities, qualifications, and qualities of surrogate parents Develop an awareness of the federal and state laws and regulations which safeguard the rights of children with disabilities and their surrogate parents Develop an awareness of the IEP process Examine the role and responsibilities of surrogate parents in the IEP process Discuss techniques for effective surrogate parents in the IEP process What Is A Surrogate Parent? A surrogate parent is a person appointed by the local education agency (LEA) or special education local plan area (SELPA): To represent a student for the purpose of their individualized education program (IEP) To ensure that the rights of the student to a free appropriate public education (FAPE) are protected What Are the Responsibilities of the LEA? The LEA is responsible for the assignment of an individual to act as a surrogate for the parent(s). This must include a method for: Determining whether a child needs a surrogate parent Assigning a surrogate parent to the child Who Can Be A Surrogate Parent? A surrogate parent must: Have knowledge and skills to adequately represent the student Be culturally sensitive to the student A surrogate parent must not: Be an employee of a public agency involved in the education or care of the student Be an employee of a private agency involved in the education of the student A LEA shall, as a first preference, select a surrogate who is a relative caregiver, foster parent, or court-appointed special advocate. What’s the difference between the surrogate’s role and the parent’s role? Local training requirements, as stipulated in the local plan The term of appointment The fact that the surrogate parent’s service may be terminated if a conflict of interest arises that may affect the child’s educational program Group Home Employees and Foster Parents Group home operators or employees are not eligible Foster parents are allowed to represent students unless They have a conflict of interest The placement is short-term (less than 6 months – not ongoing or long-term) There is a Minute Order assigning educational rights to a specific person A surrogate parent must not have a conflict of interest. If one arises, it is the responsibility of the surrogate to notify the LEA and the SELPA immediately. Conflict of Interest “An individual who would have a conflict of interest…Means a person having any interests that might restrict or bias his/her ability to advocate for all of the services required to ensure a free appropriate public education for an individual with exceptional needs.” (Govt. Code Section 7579.5(3)(e)) When Is a Surrogate Parent Appointed? Student does not have a parent, guardian or conservator, or one can’t be located Student is a ward or dependent of the court, the court has removed parent’s rights to make educational decisions and has not assigned anyone else Student is an unaccompanied homeless child or youth These children may be living in: Foster homes Private group homes State hospitals Other health facilities Residential treatment centers Legal Guardian If a child has a legal guardian, a surrogate is not needed If someone (grandparent, etc.) is “acting” as the child’s parent at the request of the natural parent, a surrogate is not needed IDEIA – Individuals with Disabilities Education Improvement Act Guarantees students with disabilities: Free Appropriate Public Education (FAPE) Placement in the Least Restrictive Environment (LRE) Fair assessment procedures Parent involvement in educational decisions IDEIA – Individuals with Disabilities Education Improvement Act Offers two major protections: Individualized Education Program (IEP) Due Process Procedures How Long May a Surrogate Represent a Student? A surrogate may represent the child until any of the following are determined: The child is no longer in need of special education The minor reaches 18 years of age Another responsible adult is appointed to make educational decisions for the minor The right of the parent or guardian to make educational decisions for the minor is fully restored The surrogate parent may resign from his or her appointment only after giving notice to the LEA Surrogate Parent Rights Same rights regarding educational decisions as the parent Surrogate is appointed to assure that the student’s rights are protected. These rights include: FAPE in accordance with their IEP Appropriate, nondiscriminatory educational assessment in the child’s primary language Educated in the LRE for his/her needs Surrogate Parent Rights (cont.) Inspect and have a copy of all educational records Request changes in inappropriate or inaccurate information in student records Be informed about assessment procedures, tests, and results Seek an independent assessment when appropriate Give written consent for nonemergency medical services, mental health treatment services, and occupational or physical therapy services when there is a need for local mental health involvement. Surrogate Parent Rights (cont.) Participate fully in planning the IEP Receive information about special education services Question the appropriateness of the student’s educational program Decide if a proposed placement is appropriate for the child Agree/disagree with parts or all of the IEP Participate in disciplinary (suspension/expulsion) hearings Surrogate Parent Rights (cont.) Talk with people involved with the student’s education and receive reports and communications Review, help make decisions and propose changes in the student’s educational program Request a parent/school conference, new evaluation, or planning meeting Have an outside person and student attend any meeting, if appropriate Request an IEP meeting if needed Surrogate Parent Rights (cont.) Receive information from the school about free or low cost legal services for legal guidance Initiate due process proceedings, when necessary Participate in resolution sessions Be informed if the school is beginning due process Be notified in writing when the school proposes any of the following: Assessment of the student Changing the student’s placement Changing the student’s IEP Calling an educational placement meeting Can a Surrogate Be Held Liable? Surrogate parents are held harmless when acting in their official capacity except in acts or omissions found to have been wanton, reckless, or malicious (California Government Code Section 7579.5(l)) Surrogate Parent Responsibilities Organize and maintain student records Participate in IEP meetings Share information about the student with the IEP team Monitor the student’s educational progress Work collaboratively with the school and other agencies involved with the student Represent the student in any complaint, due process, or ADR session Be familiar with the Procedural Safeguards Learn about the Student Learn about the student’s educational needs by: Meet the student at home, school, or in the community Review samples of the student’s work Talk with the student’s teacher(s) and other professionals Learn about the student’s area of disability Assessment Guidelines No one test result can be used to place a student in special education A team of people will conduct a multi-disciplinary assessment Tests and other assessments should examine all areas of possible learning difficulties Testing must be non-discriminatory IEP Participation The surrogate should: listen to the information shared regarding the student’s needs ask questions participate in the writing of the goals and objectives discuss the student’s strengths and needs identify concerns It takes all members of the IEP team to fully develop an appropriate IEP that truly meets the student’s needs. What to Expect at the IEP Meeting Student’s present levels of performance Data regarding whether goals and objectives from the last IEP were met New annual goals will be developed A transition plan will be developed if the student is 16 or older, or if the student will turn 16 before the next annual IEP Specific listing of program and services to be provided (offer of FAPE) Date for beginning and ending of services Discussion of any behavioral concerns and possible development of a behavior plan What Else to Expect… Discussion of… How student will participate in state and district assessments Graduation requirements Transition services (16 and older) The percentage of time the student will participate in general education or reason for not participating in general education Transportation Extended School Year Placement Options and LRE By law, students receiving special education services must be placed in the “least restrictive environment” (LRE) This means: Students in special education must be educated “to the maximum extent appropriate” with children who are not disabled Continuum of Services Least Restrictive • General education • General education with Related Services (RS) • General education with Resource Specialist Program (RSP) • Special Day Class at home school (SDC) • Special Day Class at another public school in the school district • Non-Public School (NPS) • Home and hospital instruction Most Restrictive • Residential placement • Institutional placement Is the Surrogate Involved in the Discipline Process? Positive Behavior Support Plan Functional Assessments Manifestation Determination Review Interim Alternative Educational Setting – 45 school days Signature A surrogate will be asked to sign all forms relating to the student’s special education program, including: Assessment plan IEP document Release of Information Make sure to ask questions regarding anything you do not understand. Confidentiality State and federal law protect the confidentiality of student records and limit the disclosure of such records. Confidential information includes: All personally identifiable information about a child in special education All special education records When the surrogate’s appointment ends, all records should be properly returned to the LEA or destroyed. What If I Have Additional Questions? Please feel free to contact the El Dorado County SELPA: 530-295-2462 Thank you for your time and dedication!