File
Hydrologic
Cycle 1
Hydrologic
Cycle 2
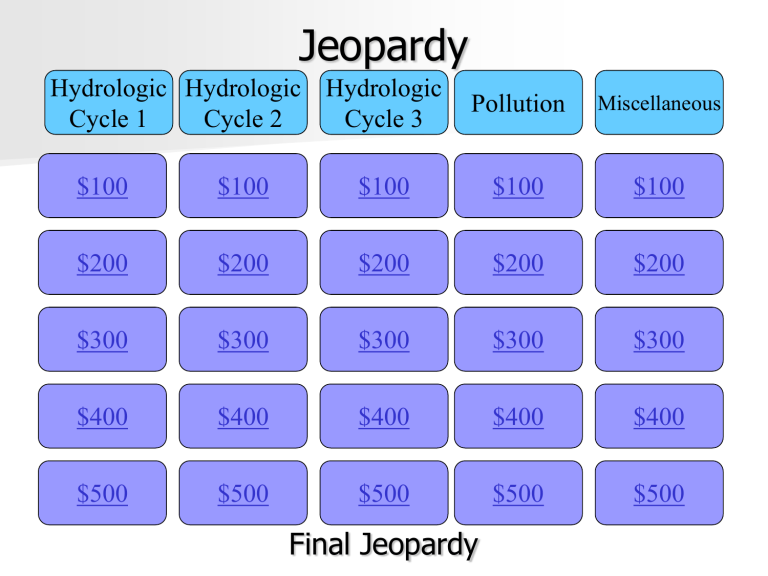
Jeopardy
Hydrologic
Cycle 3
Pollution Miscellaneous
Hydrologic Cycle 1 - $100
What keeps the hydrologic cycle going?
The sun
Hydrologic Cycle 1 - $200
Evaporation is when water changes from a
__________ to a __________.
Evaporation is when water changes from a liquid to a gas.
Hydrologic Cycle 1 - $300
What is the definition of runoff?
Water that moves or flows over Earth’s surface
Hydrologic Cycle 1 - $400
The picture shows which step of the hydrologic cycle?
Transpiration
Hydrologic Cycle 1 - $500
The step where water enters and filters through ground is known as __________.
Infiltration or percolation
Hydrologic Cycle 2 - $100
The hydrologic cycle begins with evaporation.
True or false?
False, there is no starting or ending point to the water cycle.
Hydrologic Cycle 2 - $200
Water in its gas state is called _________.
Water vapor
Hydrologic Cycle 2 - $300
Which state is where water turns from a gas to a liquid?
Condensation
Hydrologic Cycle 2 - $400
Deposition is water that changes from a
__________ to a __________.
Deposition is water changes from a gas (water vapor) to a solid (ice).
Hydrologic Cycle 2 - $500
Where would you find deposition taking place in the hydrologic cycle?
Cirrus clouds, which are high in the troposphere, turn from water vapor to ice crystals.
Contrails, clouds made from planes, also turn water vapor to ice crystals.
Hydrologic Cycle 3 - $100
What is groundwater?
Water stored underneath the ground
Hydrologic Cycle 3 - $200
Water that falls from the troposphere to Earth is called __________.
Precipitation
Hydrologic Cycle 3 - $300
These are all examples of which step of the hydrologic cycle?
Condensation
Hydrologic Cycle 3 - $400
Sublimation is water that changes from a
__________ to a __________.
Sublimation is water that changes from a solid
(ice) to a gas (water vapor).
Hydrologic Cycle 3 - $500
Give an example of something that undergoes sublimation.
Snow can turn directly to a vapor without melting first.
Dry ice goes from a solid carbon dioxide to its gas form.
Pollution - $100
If you contaminate water by accident it is not pollution. True or false?
False, if you contaminate water on purpose or by accident, it is still considered pollution.
Pollution - $200
What are the two types of pollution?
Point source- when pollution is put directly into a water source
Nonpoint source- when pollution is carried to a body of water by runoff, wind, or infiltration
Pollution - $300
Point source pollution or nonpoint source?
Point source because it is being dumped directly into the water
Pollution - $400
Point source pollution or nonpoint source?
Nonpoint source because it can be carried to body of water.
Pollution - $500
Which type of pollution is the bigger problem in the US- point source or nonpoint source?
Nonpoint source is a bigger problem because it is harder to monitor. Dumping pollutants into water (point source) is illegal.
Miscellaneous - $100
We will eventually run out of water. True or false?
False, the total amount of water on Earth never changes.
Miscellaneous - $200
What is water conservation, and why is it important?
Water conservation is using water responsibly. It is important because only 1% of the Earth’s water is fresh, non-frozen water. We have a limited supply of fresh water.
Miscellaneous - $300
Impermeable rock that contains a large body of groundwater is a(n) __________.
Aquifer
Miscellaneous - $400
List the steps that have an increase in thermal energy. List the steps that have a decrease in thermal energy. Choices: condensation, deposition, evaporation, sublimation, transpiration
Increase in thermal energy (gets warmer)evaporation, sublimation, and transpiration
Decrease (gets coolers- condensation and deopsition
Miscellaneous - $500
An area of land where all water drains into is a
__________.
Watershed
8.
Final Jeopardy
Label all the steps of the water cycle.
9.
Cirrus cloud
Snow on top of a mountain
1.
5.
Above ground
.
2.
6.
Underground
3.
.
4.
7.
Underground
1. Precipitation
2. Transpiration
3. Condensation
4. Evaporation
5. Runoff
6. Infiltration
7. Groundwater
8. Sublimation
9. Deposition