Lecture 11
advertisement
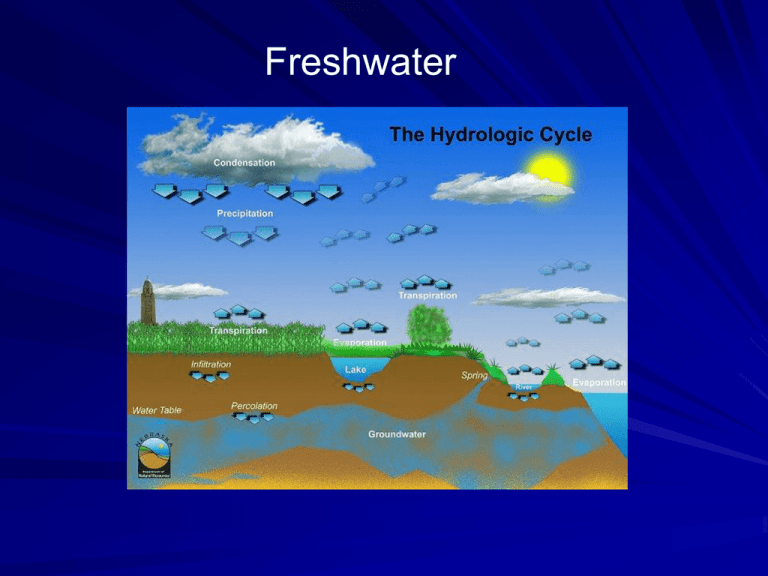
Freshwater Where is all the Water? Water source Percentage of total water Oceans, Seas, & Bays 96.5 Ice caps, Glaciers, & Permafrost 1.80 Groundwater 1.70 Lakes 0.013 Soil Moisture 0.001 Atmosphere 0.001 Wetlands, Swamps 0.0008 Rivers Biological Water 0.0002 0.0001 70% of fresh water on earth exists as ice South pole – 2 miles deep North pole – 15 feet deep Melting = 200 ft sea level increase + 45 ft - 375 ft If all the atmospheric moisture fell to the earth at once the sea level would rise only one inch Available Freshwater Groundwater Lakes Soils Wetlands Rivers 0.775% 0.8% er e RiR v eiv Ri resr ve s rs Fr esE Lhwar Ic Fre i quatthe e s i an h d r w Ic G d G a e ro anu n lacter d dw ier G a s lac te ie r Li rs Su qu rfa id Gc roe Li n qu G uW ro dawteid Su u nd atrer r w Su fac ate rfa e W r c e La a t Wk e er at s e La r At ke m o L s At p ak s At m oshe eres m ph os e ph re acre-feetof ofwater water acre-feet acre-feet of water Water on on Earth Liquid Water onEarth Earth Freshwater 1E+15 3E+13 1E+13 9E+14 9E+12 3E+13 8E+14 8E+12 7E+14 7E+12 2E+13 6E+14 6E+12 5E+14 2E+13 5E+12 4E+14 4E+12 1E+13 3E+14 3E+12 2E+14 5E+12 2E+12 1E+14 1E+12 00 0 Resource Resource Resource Groundwater provides 98% of all available freshwater Total Water Withdrawals 21% United States Surface Water 62% Florida Groundwater More than 90% of Florida’s drinking water is from groundwater Geographic Distribution Location, Location 6 countries possess half of the world’s total renewable freshwater supplies. Brazil Colombia Russia Canada Indonesia China Water Availability and Location South America: 3 of the 10 largest rivers 25% of fresh river water 5% of world population Greenland: 8 million gallons/person/day Alaska: 1 million gallons/person/day Congo: 130,000 gallons/person/day Gaza: 37 gallons/person/day Gaza has the lowest per capita water availability in the world. Asia has 2/3 of world population, but 1/3 renewable water Water Demand The three major factors causing increasing water demand over the past century •population growth •industrial development •expansion of irrigated agriculture. Agriculture accounted for most freshwater withdrawal in developing economies in the past two decades Population expected to grow to 9.3 billion by 2050 2 billion people will be “water scarce” (UNFPA, 2002) Industry and Income Country Agriculture Industry High income 30% 59% Middle income 74% 13% Low income 87% 8% Industrial use in China is expected to increase 5-fold . Agricultural Production 1% world energy Food production has grown with population 70% of all water used Irrigated land expected to expand by 23% in 25 years Overall Consumption Irrigation for crops uses 65- 70 percent of fresh supplies It takes over 528 gallons of water to produce enough food for one person for one day Over the past 30 years, the area of land under irrigation has increased by about 30%. Industry uses 20-25 percent of available freshwater Steel and other raw materials for industrial products annual industrial water use in China could grow from 52 billion tons to 269 billion tons (5X) within the next two decades Domestic use accounts for about ten percent of water use average consumption per person is five gallons a day (WHO, UNICEF), but in the U.S., Canada, and Western Europe the total consumption rises dramatically (>50 gal/day) Supply and Demand Turning to Groundwater Turning to Groundwater Use Local, On-demand Availability, Drought Resistance, Good Quality Heavy investment in groundwater exploration 50% of the world’s drinking water 40% of industrial water 20% of agricultural water 1.2 billion urban citizens worldwide depend on groundwater Turning to Groundwater Use India China Pakistan ½ the world’s total agricultural groundwater use In India, 80% of domestic supply and 70% of agricultural supply is from groundwater Extra Credit: 1. _______% of fresh water on earth exists as ice 2. _____% of readily available freshwater is in groundwater 3. ___ has the lowest per capita water availability in the world 4. 70% of all water used is for ________________________ 5. One of the 3 countries that account for 50% of world agricultural groundwater use. Growing Pains This part of China is mostly flat and the soil, replenished by silt carried down by the Yellow River, is well-suited to agriculture Shallow sand, gravel, rock North China Plain ½ China’s wheat, 1/3 corn Shallow aquifer largely depleted (renewable) 99,900 wells were abandoned Shift to Deep fossil aquifer (non-renewable) Agricultural well depths can exceed 1000 feet ($) Municipal well depths can exceed 3000 feet Aquifer Levels dropping 3 ft/year China’s grain production has fallen from its historical peak of 392 million tons in 1998 to an estimated 358 million tons in 2005 (34 million tons-8%) China largely covered the drop-off in production by drawing down its once vast stocks until 2004, at which point it imported 7 million tons of grain. India Population 1,132,446,000 21 million wells water table is falling by 6 meters (20 feet) per year falling water tables have dried up 95 percent of the wells owned by small farmers drilling 3000ft to reach water agriculture is rain-fed and drinking water is trucked in Pakistan Punjab Quetta Pakistan is growing by 3 million people per year In the Punjab plain, the drop in water tables appears to be similar to that in India. In the province of Baluchistan, water tables are falling by 11 feet per year. within 15 years Quetta will run out of water if the current consumption rate continues Israel Cenomanian-Turonian Mountain Aquifer Besor highly permeable recharged from the West Bank Coastal Aquifer Width between 3 and 20 km depth to groundwater 60 m to 8 m chief resource of water for Gaza Besor Negev Gaza has the lowest per capital water availability in the world . 80-100 sites lack infrastructure and mitigation measures Saudi Arabia Disi Conveyance Project al-Disi aquifer Sandstone aquifer not subject to recharge Partly in Jordan 1984 Saudi national survey reported fossil water reserves at 462 billion tons Wheat on 2.5 million acres of desert ½ has been depleted irrigated agriculture could continue for perhaps a few decades The Sahara: Libya 1953 Nubian Sandstone Aquifer “fossil” water Formed 145.5 to 65.5 million years ago two million square kilometers world's largest fossil-water reserve equivalent to the flow of 200 years of water in the Nile River located near the center of the world's largest continuous stretch of desert The Great Man-Made River Project the largest underground network of pipes in the world 1300 wells more than 500 m deep 10,000km³ 6,500,000 m³ water/day 4,800km³ Tripoli, Benghazi, Sirt 20,000km³ 4 major basins Water is 1/10 cost Of desalinization United States Wettest United States Rhode Island Florida Land (mi2) 3,618,770 Water (mi2) % water 79,481 2.2% 1,545 500.6 32.4% 65,975 11,808 17.9% North Carolina, Maine, Louisiana, Minnesota, Massachusetts Driest? New Mexico 121,593 243 0.2% Arizona 114,000 364 0.32% 24,232 145 0.6% West Virginia Surface water 79% Texas California Idaho Illinois Groundwater 21% California Texas Nebraska Arkansas Groundwater and Surface Water Use #1 irrigation #2 public Supply #1 power generation #2 irrigation Groundwater Surface water Surface Water Groundwater Agriculture and the Ogallala Aquifer Irrigation 1930s 1970s 600 wells 200,000 wells ¾ of wheat traded on the world market Slowly replenished: Water tables have fallen By up to 100 ft 5 – 25”/yr Rainfall Pumping has declined by ½; new wells banned irrigated Below is a link for a story on NPR http://www.npr.org/templates/story/story.php?storyId=12595774 Surface Water Groundwater Summary Surface water 79% of withdrawals Ground water 21% of withdrawals #1 use of groundwater is for irrigation #1 use of surface water is for power generation Both ground and surface water withdrawals peaked in 1980 Texas uses the greatest amount of surface water California uses the greatest amount of groundwater Florida 1700 rivers and streams (Feet to miles wide) One of the most productive Aquifer systems in the world 8 Bgal/d Water Withdrawn