China, Mongolia, and Taiwan
advertisement
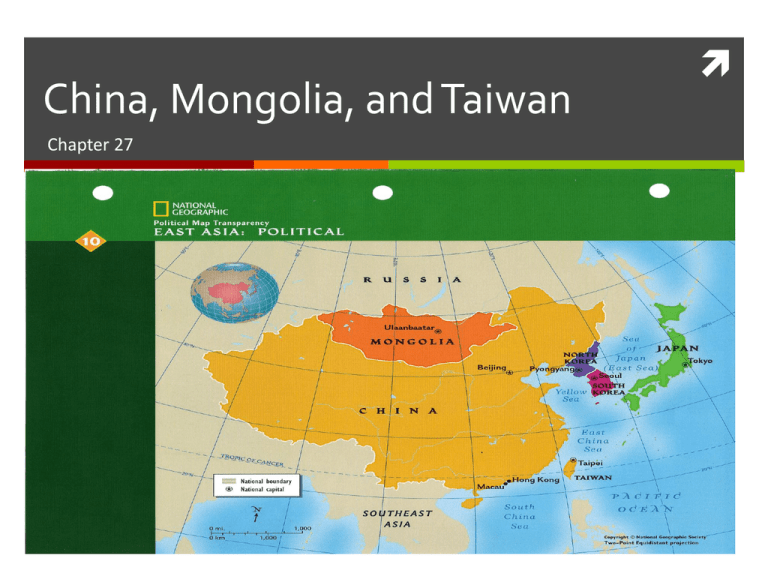
China, Mongolia, and Taiwan Chapter 27 Section 1 Objectives Identify the major landforms in this region. Describe the climates in this area. List the main natural resources. China is the 3 rd largest country in size Himalayans located in the Southwest Mongolia is landlocked/ Gobi Desert in North China/ Taiwan island are Tectonically active Climates Two major climates divide the China with Arid climates to the Northwest and Warm Humid climates in the Southeast. This causes distinct vegetation in these areas: NW Grasslands SE Tropical Rainforest Panda/ Chinese Alligator/ Chinese Paddlefish These are exclusive to China Natural Resources Hydroelectric Power Three Gorges Dam (World’s Largest) Agriculture 10% of land is arable Rice is the most heavily grown crop in China World’s Leading producer of: Coal Lead Tin Tungsten Section 2 Objectives Examine some important events in the early history of the region. ID the major political events that have affected the region’s modern history Describe some features of Chinese culture DYNASTIES OF CHINA SHANG 1ST dynasty from 1700-1100 B.C. QIN 1st Emperor started Great Wall (can be seen from space)/ 1st Imperial Dynasty/ “China” comes from this dynasty/ 1100-202 B.C. HAN 202BC-220AD/ Cities, arts, & architecture flourished/ after this dynasty China would not be unified until 618AD TANG & SUNG China becomes the more advanced during this time Mongols would invade and control this area within 80 years. Modern History of China China becomes popular due to trade done via the “Silk Road” During the 1800’s the British take control of Hong Kong (1842-1990) & Taiwan goes to Japan in 1895 1912AD Sun Yat-sen overthrows the last dynasty and forms Republic of China. He would be succeeded by Chiang Kai-Shek Communism in China Communists took control & form People’s Republic of China under Mao Zedong Farms become government owned Women = Men 1 child/family enforced to limit population growth New China under Deng Xiaoping Modernized technology/ agriculture/ & industry Changed China to a market economy Responsible for Economic growth, but no political reform China still has very strict limitations on its citizens Chinese Culture Population is over 1.3 billion people, close to 20% of the world’s population, Largest in population 70% speak Mandarin Chinese, making it the most spoken language in the world Buddhism and Taoism are the major religions here Confucianism was started in China 66% of the population lives in the East near water, this has caused rapid urbanization Section 3 Objectives ID China’s major regions. Describe Mongolia Discuss Taiwan’s relationship with China China’s Regions Southern Called the “Rice Bowl” Large percentage of the population lives here Highly industrial with Shanghai and Hong Kong located here SEZ Special Economic Zones. Area around Hong Kong where factories are located. North Where China’s culture 1st developed Very densely populated Beijing is located here Once contained “The Forbidden City”, was used to house the Emperor China’s Regions Northeast Manchuria located here Resource rich area West Harsh environment Dry/Cold/High altitude Tibet located here Palace of the Dalai Lama was here prior to Chinese occupation The official Chinese name for Tibet is Xizang Large Muslim population in Xinjiang Nomadic herding can be found here Mongolia 2X the size of Texas Least densely populated country in the world Food and Water Scarce Communist controlled till 1990, suppressed religion This is the birth place of Genghis Khan Leader of the Mongols Taiwan One of Asia’s richest & most industrialized countries Exports many goods Controlled by Chinese nationalists for 38 years under martial law Both Taiwan and China believe that their government controls the other They do trade with China, but political views cause tension between the two countries Put the country with its capital 1. China A. Ulaanbaatar 2. Tibet B. Beijing 3. Mongolia C. Lhasa 4. Taiwan D. Taipei 1. B 2. C 3. A 4. D











