Trace Fossils - Geology Rocks
advertisement

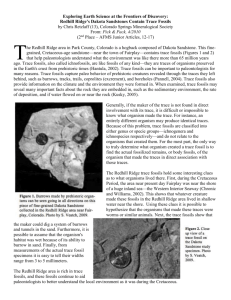
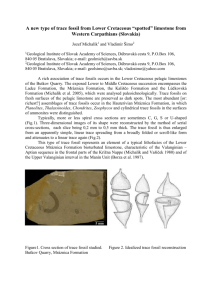
The specification states that you need to be able to: describe trace fossils: Tracks Trails Burrows and outline their use in interpreting palaeoenvironments. Trace fossils are traces left behind by an animals activity but the remains of the animal are not necessarily preserved. Excellent Environmental Indicators This is because behaviour is often influenced by environmental factors, trace fossils provide important clues to the original conditions of ancient environments. Environmental factors reflected by trace fossils include: Salinity Oxygen levels Energy Organismal interactions?????? Food supplies Tracks Footprints: Can indicate reptile/amphibian/bird or mammal activity formed in land/swamps or beach environment. The distance between footprints combined with finding out the length of the leg (from fossils) can allow you to work out the speed. The depth of the footprint can give a hint at the mass of the animal. Tracks Cruziana These are trails left behind by trilobites (which are arthropods with jointed limbs). As the trilobite moves along each pair of llimbs leaves a mark (like a centipede would if it walked over wet mud). Rusophycus This is the correct term for a “resting” trace formed as the trilobite settled into the sediment when resting. Trails (Feeding Trails) These include the burrows of sediment feeders usually with a distinct threedimensional shape. They may be dendritic or multibranched. Other feeding traces consist of large vertical and horizontal branching tubes. Burrows Many fossils burrow into sediment (infaunal) and will leave a trace. Often these are soft bodied organisms that otherwise would not be known. They may be single burrows. U-shaped (can indicate wayup). Or complicated 3D shapes. Fossil Poo Additionally, trace fossils inductive of feeding behavior (and diet) include predatory borings and fossilized excrement (called coprolites). Smaller fecal pellets (microcoprolites) are a common constituent in many sediments.