Public Administration in Slovakia (Eleonóra Marišová)
advertisement

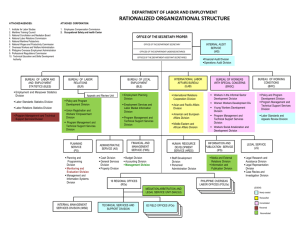
PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION in SR Eleonora Marišová SAU in Nitra, Faculty of European Studies and Regional Development Chapter VIII Public Administration in Slovakia Subchapters: System of public administration (dual, integral) State administration (central, regional, local authorities) Competencies of state administration Self government (regional, local) Competencies of self - government Decision-making process Public administration • Since 1989 major social and political changes • decentralisation - political decentralisation, - decentralisation of powers - financial decentralisation Public administration system • Devision of powers under the Constitution – „dual model“ of public administration • Self-government under the Constitution • Territorial devision of SR – 3 levels of public administration – Separate model Public administration reforms • Up to 1989 – national comitees • Act No. 369/1990 on municipalities – Separate model of public administration – Abolishment of regional state administration • Public administration establishment Main aim of the reforms : move from „govern“ to „governance“ Organisation of public administration • 1990 – political will for decentralisation • 1992 – dealing with the disintegration of CSFR • 1993 – SR • 1993-1998 – changes to state administration – SG – some competence, no financial covering – 1996 Act 221/1996 on Territorial and Administrative Division od SR and Act 222/1996 on Organisatiom of Local Self-government • 1998 – adoption of a decentralisation concept (effective from 1January 2004) Government Ministries(18) and central authorities Regional offices with units of general and specialised state administration(8) District offices with units of general and specialised state administration(79) Government Ministry of interior affairs Other ministries(13) Regional offices of general administration(8) Regional offices of specialised administration District offices of general administration(50) District offices of specialised administration(from 36 to 50) Regional self government offices(8) Municipalities - 2891 Nižňanský, V.: Verejná správa na Slovensku.2005, Úrad vlády SR.ISBN 80-969459-4-7 State administration • character of SA bodies • 3 levels: 1. government, ministries and other central bodies of state administration 2. regional state administration 3. local state administration Government - Ministries in the field of: 1.)national economy: - economy, agriculture, finance, construction and regional development, mail and telecommunications, environment 2.) national administration and management : - interior,foreign affairs, defence, justice 3.) culture and social affairs : education, culture, labour, social affairs and family, health Competences of State Administration • General local authorities of SA • Act No. 515/2003 Coll. • Regional offices – Competence – 2nd level of SA (appeal, coordination, control) – Abolished from 1st October 2007 • District offices – 1st level (local level) • Former Regional offices (8) - cancelled from 1.10.2007 – Competence – 2nd level of SA (appeal, coordination, control) - Units for general interior administration, entrepreneurs, civil security, citizehship - Powers - Ministry of Interior, Regional offices • District offices (50) Units for entrepreneurs, general interior administration, civil security, citizehship – 1st level Government Ministry of interior affairs Other ministries(13) Regional offices of specialised administration District offices of general administration(50) District offices of specialised administration(from 40 to 50) Regional self government offices(8) Municipalities – 2891 Cities 138 (out of them) Nižňanský, V.: Verejná správa na Slovensku.2005, Úrad vlády SR.ISBN 80-969459-4-7 Specialised Local authorities of SA • Regional offices – Competence – 2nd level of SA (appeal, coordination, control) – Organisation • District offices – 1st level SpecialisedLocal authorities of SA Act No 534/2003 .: • Regional offices for transport and territorial communications (8) • District offices for public transport and territorial communications (46) Powers of Local offices for public transport and territorial communications (46) - Licence for car schools - Instructors licences - Technical testification of cars - Rejection of cars from traffic - Offences in oversized cargo Road transport and roads Offices Boundaries of the SR Establishment of Regional Offices for road transport and roads (8) Establishment of District Offices for road transport and roads (46) Scope of Regional Offices of Environmental Offices Boundaries of Districts SpecialisedLocal authorities of SA Act No 518/2003 .: • Regional land offices (8) • District land offices (44) Powers: - Restitution process - Land consolidation organisation - Coordination of renewal of land registration Land Consolidation authorities and agricultural soil protection Offices Boundaries of the SR Scope of Regional Land Office Boundaries of Districts Establishment of Regional Land Offices (8) Establishment of District Land Offices (44) Specialised Local authorities of SA Act No 519/2003 .: • Regional forest offices (8) • District forest offices (40) Powers: -charge of managing of forests (private, state) - exemtion of forest land - construction in forests - huntinggrounds recognition Forestry Offices Boundaries of the SR Scope of Regional Forestry Office Boundaries of Districts Establishment of Regional Forestry Offices (8) Establishment of District Forestry Offices (40) SpecialisedLocal authorities of SA Act No 525/2003 .: Environmental Inspectorate (4) • Regional offices for environment (8) • District offices for environment (46) Powers: - Industrial waste water emission - Placing of large and middle sources of polution • geological works, public water pipes, drainage, industrial accidents prevention - Environmental Offices Boundaries of the SR Boundaries of Districts Establishment of District Environmental Offices (46) Establishment of Regional Environmental Offices (8) Scope of Regional Offices of Environmental Offices Specialised Local authorities of SA Act No 453/2003 : • Principal Office for work, social affairs and family (1) • Territorial offices for work, social affairs and family offices (46) Powers : -state social aid -register of unemployed people -re-qualification courses -activation subsidies to employers Labour, Social Affairs and Family Offices Boundaries of the SR Boundaries of the Regions Boundaries of the Districts Labor, Social Affairs and Family Office (1) Establisment of the Labour, Social Affairs and Family Offices (46) SpecialisedLocal authorities of SA Act No 578/2003 : • Office for public health care (1) • Regional offices for public health care(36) Powers: - permission of work in dangerous environment - quarantine - state health control Public Health Offices Boundaries of the SR Boundaries of the Regions Boundaries of the Districts Establishment of Public Health Office (1) Establisment of the Regional Public Health Offices (36) Specialised Local authorities of SA Act No596/2003 : • Regional offices for education (8) • no local offices (powers were delimitated to selfgovernment) - Powers: - Coordination of education of basic and secondary shools in region - Recognition of foreign secondary education certificates Education Offices Boundaries of the SR Establishment of the Regional Education Office (8) Specialised Local authorities of SA • Regional offices for construction (8) • no district offices (powers were delimitated to selfgovernment) • Powers: - approval of regional plans of municipalities - decisions on appeals in 2nd stage - replacement of powers of municipalities Specialised Local authorities of SA • Act No. 150/2001 Coll.: • Principal Tax Office (1) • external work places of this body (8) • District Tax Offices (101 districts) • Powers: • tax administration • tax assesments, tax claims • fines Construction Offices Boundaries of the SR Establishment of the Regional Building Offices (8) Boundaries of the Districts Specialised Local authorities of SA • Act No. 49/2002 Coll. • Monuments Board (1) • Regional Monuments Offices (8) Powers: - keep an archive in the field of the protection of monuments and historic sites; - protection of cultural monuments - archeological research - re-constructions Government Protection of Monuments Fund Boundaries of the SR Establishment of the Historical Monument Office Establishment of the Regional Historical Monument Office (8) Conception of State administration for future VARIANT A) • Cancellation of specialised regional offices • Competences to be moved to ministries • Merge of ministries (environment) • District offices – 1st level VARIANT B) • Reintroduction of general state administration - no special offices, regional and district special units under „one umbrella“ Organisation of local self-government 1. Municipalities Act no. 369/1990 - cities - villages 2. Higher territorial units Act no. 302/2001 - Bratislava, Nitra, Trnava, Trenčín, Banská Bystrica, Prešov, Košice, Žilina Municipalities - structure Nižňanský, V.: Verejná správa na Slovensku.2005, Úrad vlády SR.ISBN 80-969459-4-7 Municipalities • Legal entities (2891 villages, from that 138 cities) • Single-level self-government • Execution • Elected bodies (4 years, auditor 6 years, elected by assembly) • Citizens´ voting • Local referendum: (major outvoting,petition 30% of citizens, merge or secession of municipality) • Assembly (3-41 members – from 40- 100 000 inhabitants) - generally binding regulations (VZN) Municipal office (mayor, + manager appointed by mayor) • Original powers v. transferred powers Competences of municipalities • Original – local roads, public transport, public areas, green areas, cleanness, nature and environment protection, water management, sewer system, municipal waste, territorial planning, local development, housing, preschool and school establishments, social establishments, policlinics, certain hospitals, culture, certification of documents, certain offences, municipal police, collection of local taxes and fees, participation in regional planning • Transferred – registry offices, the construction order and a section of duties in the education sector Higher territorial units of Slovakia Higher territorial units - structure Nižňanský, V.: Verejná správa na Slovensku.2005, Úrad vlády SR.ISBN 80-969459-4-7 Higher territorial units characteristics • Legal entities • Single-level self-government • Execution • Elected bodies (4 years, auditor 6 years, elected by assembly) • 1 member of Assembly 12-16 000 inhabitants - generally binding regulations (VZN) • Citizens´ voting • Original powers v. transferred powers Competences of HTU • Original – 2nd and 3rd class roads, territorial planning, regional development, own investment activities, secondary schools, hospitals, certain social service establishments (retirement homes, social services for children, crises centres, children’s homes, etc.), cultural establishments (galleries, museums, theatres, certain libraries, etc.), participation in civil defence, licensing of pharmacies and private physicians • Transferred – section of powers in the education sector, healthcare sector and road transport Problems of public administration of Slovakia 2 different expert opinions and critisism of administrative division: • Too many administrative regions and selfgovernment regions • Expierences show that optimal administration execution is in 3-6 regions (1960-1990) • More effective and economic Opposite opinion • Current administrative regions and selfgovernment regions regions are too big units • Natural units - historical division optimal 16-20 regions • better „governance“ of population Decision –making process in Public administration – Administrative order • State and self-government offices (general and specialised) – on the 1st and 2nd level • Decision –making process on rights and duties of individuals and legal persons • Act No 7l/l967 Coll. on administrative procedure as amended by Law No. 527/2003 Coll. Stages of decision –making process (1st instance proceeding • l). Beginning the procedure (ex offo,application of the party) • - oral hearing (notice to appear) • - delivery of a call • 2). Identifying documents necessary for the decision • - interrogation of witnesses, • - expert opinions, • - documents, • - examination Stages of decision –making process (1st instance proceeding) • Rights of parties: • - propose evidences • -put questions to witnesses, experts • -to comment the basis and way of its investigation and decision • -propose amendments of procedure • 3). Decision on the case - in merito (immediately, within 30,60days) Requisites of the decision • 1. verdict • 2. justification (it is not necessary if all the parties are fully accommodated) • 3. guidance on appeal Forms of decisions review: Decision issued in 1st level may be reviewed by its governing body on the 2nd level: Ordinary remedies: • 1. Appellate proceedings • 2. Review proceedings Extra ordinary remedies: • 3. Renewal of proceedings • 4. Review of decisions outside appellate proceedings Specific remedies: • 5. Prosecutor’s protest proceedings • 6. Review of administrative bodies decisions by court. Execution • a decision in monetary or non- monetary terms fails to discharge such duty in time-limit • Administrative body in the first instance • the party may also apply for execution to be exercised by the court or a licenced executor • Administrative body is obliged 2 announce the beginning of execution • deadline for fulfilling the duty Problems of decision making process • Disintegration of legal norms • Subsidiarity of Administrative order • No consequences for holding – out of decisions making process • No codex Organisation of public administration: summary - 1990 Act 369 on Communal Establishment on SR, as amended by the act - 1995 Act 270 on National language of the Slovak Republic, as amended by the act - 1996 Act 221 on Territorial and Administrative Division on SR, as amended by the act - 1996 Act 258 on Government Regulation No. 258/1996 Coll Laws, which issued a list of municipalities and districts making up the individual military districts, as amended by the act - 2001 Act 302 on Higher Territorial Units, as amended by the act - 2003 Act 515 on Regional Offices and District Offices, as amended by the act - 2007 Act 254 on Abolition of Regional Offices and amending Act No. 515/2003 Coll. The Regional Offices and amending certain laws, as the Constitutional Court of the Slovak Republic no. 263/2006, as amended by the act (Source: http://www.civil.gov.sk/archiv/p11/p11-01.shtm) Literature • Belica, M.: Európska únia chce mať silné regióny. Verejná správa, 15-16, 2006, str.2- 4 • Belica, M: Finančná decentralizácia. Unpublished. • Marišová, N. – Ilková, Z. – Belicová, J.: Správne právo hmotné a procesné. 2002, Nitra. SPU v Nitre. ISBN 80-8069-127-4 • Nižňanský, V.: Verejná správa na Slovensku.2005, Bratislava. Úrad vlády SR.ISBN 80969459-4-7 • Nižňanský, V.: Verejná správa na Slovensku.2005, Bratislava. Úrad vlády SR.ISBN 80969447-1-1 • Z. 460/1992 Zb. Ústava SR • Z. 369/1990 Zb. o obecnom zriadení • Z. 302/2001 Z.z o samospráve vyšších územných celkov • http://www.government.gov.sk/decentralizacia/dokumenty/vniznansky_en.rtf • http://www.oecd.org/dataoecd/40/1/34990164.pdf • http://www.innovations.harvard.edu/showdoc.html?id=8363 • Druhý dych samosprávnych krajov –Verejná správa, č. 8/2005, str. 20-23 Thank you for your attention