Kingdom: BACTERIA AND ARCHAEA
advertisement

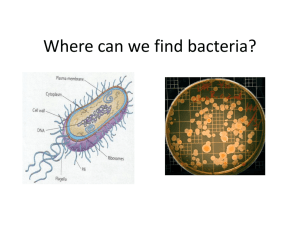
Kingdom: BACTERIA AND ARCHAEA These are Prokaryotes!! Bacteria Bacteria are literally everywhere. Skin, air, door handles, water fountains, ponds, desks, on food, in your intestines, ect Your skin has on average 100,000 bacteria per square centimeter. Bacteria a variety of environments from 0*C to 100*C and above. To us Americans that temperatures between 32*F and over 212*F Binary Fission Bacterial replication – Extremely simple It is a form of asexual reproduction The bacteria divides and to form an exact copy of itself. Some rare cases – bacteria will exchange genetic information through a tube. This is a form of sexual reproduction that gives some genetic diversity. (“grab-bag recomb”) Bacteria Shape: Coccus Simplest bacteria shape Spherical or ball shaped Typically grouped together Staphylococcus Streptococcus Bacteria Shape: Bacillus Rod-shaped bacteria Almost always Gram negative. Typically have thin cell walls E. coli is the most well known Bacilli bacteria Bacteria Shape: Spirillium Typically are spiral shaped, but can come in a variety of shapes. Aerobic vs. Anaerobic Require oxygen to breakdown food. Metabolism is similar to most animals. Found in temperate climates and habitats. Shallow waters as well. Do not require oxygen to breakdown food. Several forms of anaerobic bacteria can be found in your intestines. Found also in deep water and deep soil. Gram Negative vs. Gram Positive Gram negative – – Thin cell wall, very little peptidoglycan Gram negative bacteria stain “Pink” when a Gram stain is done Gram positive – – Thick cell wall, high in peptidoglycan Gram positive bacteria stain purple or very dark blue Cyanobacteria Producer eubacteria. They make their own food by “photosynthesis.” Normally blue or green in color, but can be red, yellow, or black Normally group together in chains. – They can do this because they are covered in jelly like substance that lets them stick to each other. Positive uses of Bacteria Pasteurization of thinks like milk and juice Culturing foods such as cheeses. Cleaning up waste Bioremediation Saprophytes and Nitrogen fixers “Consumer bacteria” – – Saprophytes use dead and decaying matter as their food source. They are responsible for nutrient recycling Nitrogen fixing bacteria – – These bacteria change nitrogen gas to a form that plants and animals can use. Found typically in the soil, around the roots of plants Bioremediation What is Bioremediation?? Bioremediation is the completely safe and natural process of cleaning up organic contaminants through the use of microbes. EZ Definition: Using bacteria to clean up waste Harmful bacteria: Pathogens Bacteria that can make you sick. Produce toxins, which are chemicals that are poisonous to the body. Botulism, TB, Pneumonia are examples. Vaccines…..remember them. They help prevent many bacterial diseases. Kingdom: Archaebacteria EXTREME-O-PHILE BACTERIA – Thermophiles “ Heat lovers” – Methanophiles “Methane lovers” – “Sulfur lovers” – “Salt lovers” Archaea features No nucleus No membrane bound organelles Live in the most extreme conditions Were considered in Bacteria kingdom, until the 1970’s Researched by Dr. Carl Woese and colleagues at Univ. of Illinois