Aeration
advertisement

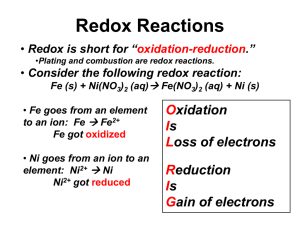
Reading Assignment Chapter 7: Soil Aeration and Temperature Too much water for too long Aeration relates to: Ventilation of soil with air (moving in and out of soil) The rate of gas exchange with atmosphere Proportion of pore spaces filled with air Composition of soil air Potential for oxidation and reduction (“redox”) within soil Moisture status of soil Temperature of soil Survival of plants or vegetation Composition of Air & Soil Atmosphere Oxygen (%) Carbon Dioxide Nitrogen (%) Relative Humidity Air Well-aerated soil Poorlyaerated soil 21 15-21 0-10 0.0375% (375 ppm) 0.1-0.5% (1000–5000) 1-10% 78 78 78 Low Near 100% Near 100% GASEOUS EXCHANGE Mass flow (quicker, at shallow depth) Diffusion (concentration gradient, more important) Soil properties affecting aeration - Structure - Texture - Compaction - Drainage Effect of poor aeration on plants and soil properties - As gas exchange is slowed, CO2 produced by organisms cannot escape fast enough and O2 required by organisms cannot enter fast enough - Other gases (H2S, methane, ethylene, etc.) produced by organisms can accumulate and maybe harmful to organisms and change soil chemical properties • If soil contains < 15% O2, plant roots begin to suffer • < 10% O2, toxic substances may be produced Nutrients Bright Color.................................... Dull Color Fe+3 (oxidized) -------------------- Fe+2 (reduced) Mn+4 (oxidized) --------------------- Mn+2 (reduced) NO3- (oxidized) ---------------------- N2 (reduced) Well Oxidized: sufficient Oxygen Insufficient oxygen Oxidized form Reduced form O2 H2O NO3- N2 Fe3+ Fe2+ SO42- S2- Mn4+ Mn2+ How to improve Aeration? • • • • Improve drainage breakup impervious layers improve aggregation (crumb structure) prevent crusting REDOX POTENTIAL Oxidation reduction (REDOX) • Soil REDOX potential is a measure of a soil's ability to lose or gain electrons • Oxidation is the major mechanism of energy generation by organisms – Oxygen is required for respiration by plants and animals • The consumption of oxygen by biota is what reduces the REDOX potential in soil Oxidation from divalent to trivalent (loses an electron) (2+) (3+) 2 FeO + 2 H2O < = > 2 FeOOH + 2H+ + 2eFe(II) Fe(III)