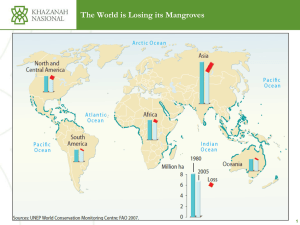
The Ramsar Convention on Wetlands
advertisement

Needs Assessment and Prioritisation Workshop EC ACP MEAs Programme – Africa Hub Overview of Capacity Building Needs Under the Ramsar Convention 16 to 18 September 2009 African Union Commission, Addis Abeba Abou Bamba Sr. Advisor for Africa www.ramsar.org About the Ramsar Convention • The Convention on Wetlands of International Importance (Ramsar, Iran; 1971), also referred to as the Ramsar Convention, is an intergovernmental treaty that provides the framework for national action and international cooperation for the conservation and wise use of wetlands and their resources. • • www.ramsar.org For more information on the Convention text and its history, joining the Ramsar Convention, and what the commitments are for the Contracting Parties: http://www.ramsar.org/cda/ramsar/display/main/main.jsp?zn=ramsar&cp=1-3138_4000_0__ http://www.ramsar.org/pdf/about/info2007-02-e.pdf What are wetlands? • Wetlands are areas where water is the primary factor controlling the environment and the associated plant and animal life • They occur where the water table is at or near the surface of the land, or where the land is covered by water. • Under the text of the Convention (Article 1.1), wetlands are defined as: « areas of marsh, fen, peatland or water, whether natural or artificial, permanent or temporary, with water that is static or flowing, fresh, brackish or salt, including areas of marine water the depth of which at low tide does not exceed six meters ». http://www.ramsar.org/cda/ramsar/display/main/main.jsp?zn=ramsar&cp=1-3637^7713_4000_0__ www.ramsar.org Contracting Parties’ commitments under the Ramsar Convention 3 “pillars” of action: 1. Wise use of all wetlands 2. Wetlands of International Importance designation and management (Ramsar List) 3. International cooperation (transboundary wetlands) www.ramsar.org 1. What is the “wise use” of wetlands ? “… their sustainable utilization for the benefit of humankind in a way compatible with the maintenance of the natural properties of the ecosystem” (Ramsar COP3, 1987) For more information on wise use of wetlands: • • www.ramsar.org http://www.ramsar.org/pdf/about/info2007-07-e.pdf http://www.ramsar.org/pdf/lib/lib_handbooks2006_e01.pdf 2. Designating wetlands for the Ramsar List • The document of adhesion to the Convention sent by the Head of State or Foreign Office to UNESCO must be accompanied by the designation of at least one wetland site for the List of Wetlands of International Importance. Thereafter, each Party "shall designate suitable wetlands within its territory for inclusion in the List" (Article 2.1). • Such designation(s) should include: a) a completed Information Sheet on Ramsar Wetlands (RIS) for each site; b) a map showing the boundaries of each designated site. For more information on the designation of wetlands: http://www.ramsar.org/pdf/lib/lib_handbooks2006_e14.pdf www.ramsar.org 3. And international cooperation for Ramsar ?... • There is extensive cooperation with: • • • • www.ramsar.org other environmental global and regional conventions; UN agencies; regional environmental organizations; NGOs and expert networks. • Ramsar has five International Organisation Partners that provide invaluable support for the work of the Convention at global, regional, national, and local levels, chiefly by providing expert technical advice, field level implementation assistance, and financial support, both from their headquarters units and from their national and regional offices and affiliates and from their expert networks. • BirdLife International; the International Union for Conservation of Nature; The International Water Management Institute; Wetlands International and WWF International. For more information on international cooperation: http://www.ramsar.org/pdf/lib/lib_handbooks2006_e17.pdf Facts and figures 159 Contracting Parties in the world • Africa: 47 Contracting Parties • Non-Contracting Parties in Africa: Swaziland, Zimbabwe, Angola, Somalia, Ethiopia. 1847 Wetlands of International Importance “Ramsar sites” in the world • • • • www.ramsar.org Largest global protected area network totaling 181 million hectares size: from <1 ha to >6 million ha A total of 282 Ramsar sites in Africa Capacity needs for various stakeholders www.ramsar.org National Focal Points or Daily Contacts • Understanding the Convention (issues and challenges) • Job description (what do they do between two COPs/MOPs?) • Negotiation capacities • Institutional framework • Language • Resource mobilization • Technology transfer • Communication and outreaching skils www.ramsar.org STRP National Focal Points • Understanding the Convention issues • Putting African issues on the Convention agenda • Networking • Language barrier • Advocacy skills • Resource mobilization to undertake research on the issue www.ramsar.org Other stakeholders • Judiciary and other law enforcement officers • Parliamentarians • NGOs • Private / business sector (e.g: oil and gas, extractives, etc.) • Journalists and other communication specialists www.ramsar.org Challenges for MEAs Secretariats • Synergy in implementation is weak • « Big » conventions v/s « Small » conventions • Working language is an issue • Many are not compliance-based • Domestication in national legislation • Monitoring and evaluating implementation • Overlaps • Funding to serve growing number of CPs www.ramsar.org THANK YOU! For more information on Ramsar and wetlands... www.ramsar.org http://www.ramsar.org