Green Ship - Intertanko
advertisement

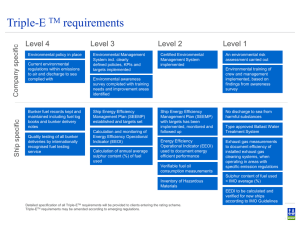
Developments in Green Ships Design/Technologies By Dave Iwamoto 15 October 2010 Tripartite Meeting 2010, Tokyo 1 Restriction of Emission from Ships NOx and SOx restricted Incinerator Ship recycle (not in force) Halon & CFC prohibited VOC prohibited in special port Noise restricted (in study) Oil discharge monitoring Sewage treatment Garbage disposal Bilge discharge Ballast water management (not in force) TBT prohibited Tripartite Meeting 2010, Tokyo 2 Green Ship Design Low GHG exhaust Ship operation Less fuel oil consumption at sea Diesel engine exhaust Low Nox and SOx Device for less energy Inventory Less hazardous materials Vapor emission control system for tanker Incinerator Noise Reduction Oil discharge monitoring for tanker Sewage treatment Garbage disposal TBT-free painting Gray-water treatment Bilge-oil discharge control Ballast water treatment Less ballast ship Best hull form & propulsion Less fuel oil consumption at sea Tripartite Meeting 2010, Tokyo 3 Green Ship Design Low GHG exhaust Ship operation Less fuel oil consumption at sea Diesel engine exhaust Propulsion Plant Low Nox and SOx – High efficient engine Inventory Less hazardous materials Vapor emission control system for tanker Incinerator– Hybrid diesel engine Development Noise Reduction in alternative engine – Electric motor driven (Fuel cells, electric batteries) – Dual fuel diesel engine Sewage treatment Garbage disposal – Bio fuel diesel engine Gray-water treatment – GTL, DME engine Bilge-oil discharge control Device for less energy Ballast water treatment Less ballast ship Oil discharge monitoring for tanker TBT-free painting Best hull form & propulsion Less fuel oil consumption at sea Tripartite Meeting 2010, Tokyo 4 Green Ship Design Low GHG exhaust Ship operation Less fuel oil consumption at sea Diesel engine exhaust Low Nox and SOx Operation Device for less energy Inventory Less hazardous materials – Optimized transport chain Incinerator – Route optimization (Weather routing) Vapor emission control system for tanker Noise Reduction– Optimized driving – Trim /ballast water optimization Sewage treatment Device for Less energy Garbage disposal – Cold ironing Gray-water treatment – Wind & solar energy Additional thrust (Kites) Ballast water treatment Bilge-oil –discharge control Less ballast ship Oil discharge monitoring for tanker TBT-free painting Best hull form & propulsion Less fuel oil consumption at sea Tripartite Meeting 2010, Tokyo 5 Green Ship Design Low GHG exhaust Ship operation Less fuel oil consumption at sea Hull form & propulsion Device for less energy Diesel engine exhaust – Less (Wave, Viscous, Wind) Inventory Low Nox and resistance SOx Less hazardous materials – High efficient propulsion, CRP Vapor emission Incinerator control system for tanker Less energy Noise Reduction– Less ballast ship, Weight saving of L/W – Optimized systems (Auxiliary machinery, Waste heat recovery, OilAirdischarge for tanker conditioning system, Electric motor driven deck machinery,monitoring etc.) Sewage treatment Garbage disposal – Less electric demand (LED illumination) – Micro bubble or air lubrication Gray-water treatment Bilge-oil discharge control Ballast water treatment Less ballast ship TBT-free painting Best hull form & propulsion Less fuel oil consumption at sea Tripartite Meeting 2010, Tokyo 6 Green Ship Concept • Sustainability and Expandability - based on stakeholders’ chain of responsibility • Rule Minimum + Something - ambitiousness and being ahead of legislations Tripartite Meeting 2010, Tokyo 7 Shipowners Challenge for Eco-friendliness Recently in Focus: • Optimized hull and propulsion • Optimized machinery efficiency - waste heat - domestic waste etc. • Waste minimization spirit reflected in operation manuals • Renewable energy • Drag during operation e.g.; NYK’s “NYK SUPER ECO SHIP 2030” MOL’s “ISHIN” Tripartite Meeting 2010, Tokyo 8 Schematic Outline of Promotion Proposal On Green Innovation KEIDANREN Japan, March 2010 (part of “Japan as Creating Country” Initiative) 1. Basic Vision • Use of technology …… 2. Policy on Latest Technology Pursuit • • • • Stimulating demand Education Regulatory framework towards model project International activities (GHG reduction included) 3. Green Innovation • • • Creating seeds (fund supporting element) Development (green technology platform) Actual use (support measures element) Tripartite Meeting 2010, Tokyo 9 Technical Challenges to Reduce Environmental Burden In Japanese Shipbuilding Industry • • Main engine and auxiliaries – Combustion efficiency – Waste heat recovery – Dual fuel main engine – Alternative fuel / Fuel cell / Batteries Hull and hull form – Larger hull body, lighter construction – Improved hull form – Reduced drag (resistance) continued.... Tripartite Meeting 2010, Tokyo 10 Technical Challenges to Reduce Environmental Burden In Japanese Shipbuilding Industry (cont.) • • • Propulsion – Improved propeller system – Energy saving appendages Operation and maintenance – Sophistication (e.g. Weather routing) – Support tools (e.g. Performance monitoring) – Change of mode (e.g. Slow steaming) Green Ship – Emission quality – Pollution prevention – Noise reduction Tripartite Meeting 2010, Tokyo 11 Summary • Green Ship is a concept that evolves and changes – Technology is the key element - careful follow-up is required • • Stakeholders need to understand the chain responsibility – Narrow minded concentration of own interest is discouraged – Close coordination and cooperation needed among stakeholders lead by private sector Regulation will follow but what can we seek beyond? – There are useful individually developed practices – Ambitious mind setting to go beyond rule requirements Tripartite Meeting 2010, Tokyo 12 Thank you for your attention. Tripartite Meeting 2010, Tokyo 13