OTEC Environmental Impact Assessment & Monitoring
advertisement

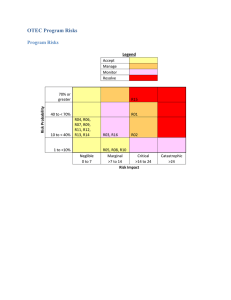
OTEC Environmental Impact Operational Noise OTEC Warm Water Intake: •Entrainment •Impingement Cold water intake: •Entrainment Biota attraction or avoidance Discharge Plume: •Redistribution of nutrients •Algae blooms •Altered temperature and pH •Where will it settle? OTEC Environmental Impact • 1981 EIS+: update to current oceanographic standards • What data do we need? Stakeholder meeting, June 2010 – Oceanography: baseline nutrients, carbon cycle, T, S, O – Plankton, fish larvae: distributions and density – Megafauna habitat use • What data is already available? NOAA. 1981. Ocean thermal energy conversion final environmental impact statement.” OME. NOAA. 2010. “OTEC: Assessing potential physical, chemical, and biological impacts and risks.” CRRC. 39pp. Discharge plume: what data is available? The Hawaii Ocean Time Series (HOTS) – 1989 – present – Temperature, Salinity, oxygen, pH, chlorophyll a Gaps in data: • Nutrients (1989-2001 only) • Alkalinity and DIC at deep depths • Trace metals Entrainment: Warm Water Pipe Boehlert and Mundy 1994. Mar Ecol. Prog. Ser. 107:1-13 +Seapy. 2008. Mar. Biol. 154(6): 985-995 ++Poe and Norenburg. 1999. Deep-Sea Res. (1 Oceanogr. Res. Pap.) 46(7): 1201-1220 Entrainment: Cold Water Pipe Entrainment: NELHA deep water pipe 2 months, 2009 18 Fish Flow rate of 0.8m3/s Crustaceans Compare to pilot plant: 25m3/s 21 30 Cnidarians 62 Other Invertebrates West Hawai’i Explorations Academy and commercial plant: 500m3/s Baseline monitoring • Stakeholder meeting++ – – – – Oceanography : 3 years Ichthyoplankton: 1 year+ Marine Mammals and turtles: 1 year Plankton: 2 years • Taking into account available datasets…. Baseline Monitoring Suggestions 1 year: Nutrients, trace metals, and deep water carbon cycle cafethorium.whoi.edu Discrete-depth sampling for bacteria, copepods, total biomass Consistent monitoring of CWP at NELHA Don’t forget: Background acoustics Fishing/backscatter for nekton Megafaunal habitat use