State Pollution Control Board Context
advertisement

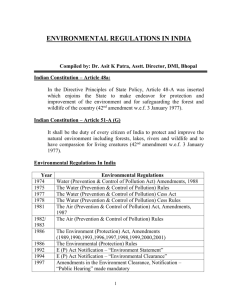
Compliance to Environment Regulations : State Pollution Control Board Context International Conference on Env. Governance and Enforcement WBPCB, Kolkota 19th, March, 2013 Dr. D. K. Behera Sr. Env. Scientist, SPCB, Odisha dk_behera@yahoo.com Environmental governance in India LEGISLATION IMPLEMENTING INSTITUTIONS PCB, DOEF, MOEF EXPERT ORGANISATIONS NEERI, TERI JUDICIARY CITIZEN Pollution Abatement Policy Enforcement Mechanism in India Policy Making Agency (MoEF) State Govt. Adoption of Acts Monitoring Agency (CPCB) Implementing Agency (SPCB) Project End Closure Regulation of Services Conviction Project Approval Consent to Establish Monitoring NonCompliance Court Compliance with Norms Public Suit Project Completion Detail Assessment (Consent to Operate) Project Continue Compliance Process New Units Project Conception Stage Application to SPCB for “CONSENT TO ESTABLISH” Consent Granted Permission for Trial Run Performance Evaluation by SPCB Construction Stage Operational Stage Change In Process / Raw material / Expansion of facility Not Satisfactory Grant Of CONSENT TO OPERATE Monitoring by SPCB Renewal Of Consent REGULATORY FRAMEWORK Consent to Establish Public Hearing CRZ Clearance Environmenta l Clearance Constructio n Phase Consent to Operate/Au thorization Monitoring and Review Operation Phase Major Functions of SPCBs Command & Control Principles • Formulation of preventive measures • Laying down env. Standards • Consent and authorisation Administration • Env. Friendly technology development • Control of pollution through inspection & monitoring of industrial units • Regulation of location of industries • Disposal of waste (hazardous, plastic, municipal, electronic etc.) • Collection and dissemination of information • Advise the State Govt. • Penal action against the violation Statutory Activities Planning, PW, E-wasteSES(P) • Consent to Operate, Cess – SEE(C) Authorisation • MEMBER SECRETARY CHAIRMAN Env. Monitoring (Air, Water, Soil etc.) Mines – SES(M) CTE, EIA, HW Authorisation – SEE(N) Site inspections for CTE, CTO, Regional Offices BMW, MSW - ES Central Laboratory SES(L) Administration - AO • Public Hearing • Grant of Consent <50 crores and compliance verification • District Level Meetings • Public Complain • Account Keeping • Closure Direction / SCN • Coordinate visits of CPCB, Committees, Expert Committee, Legal (LO) HO Officials RTI Compliance SPCB, Odisha Issues in functioning of SPCBs Manpower • Inadequate technical manpower – wide variation in the ratio of technical to non-technical among Boards • No norm of staffing • No fulltime Chairman • Expontial increase in no. of industries legislations Result-Env. Performance monitoring inadequate and Frequency of inspection and monitoring Red (L & M)- Once in 3 months Red (Small) – Once in a year Orange (L & M) – Once in a year Orange (Small) – Once in 3 years Green (L & M) – Once in 2 years Stone crusher, Brick kilns and hotels – Once in a year. ULBs and HCUs – Once in a year Inspection of units Units regulated per person, OSPCB Resources • Water Cess, consent and authroisation fees, sample testing fees, bank guarantee, grant-in-aid from Central & State Govt., project based grants etc. • Many of the SPCBs are self dependent • Wide difference in consent and other fees among SPCBs • Cess collection from ULBs • Not much expediture towards pollution prevention, R & D etc. Inventorisation • Data base on inventorisation of industries both under consent and authorisation administration still incomplete – addition of number of units, hotels, hot mix plants, HCEs, brick kilns etc etc… • Data management and periodical updation not standardised Jurisdiction • Vehicular pollution is beyond the jurisdiction of SPCB- source proportionate • 50-70% of urban air pollution caused due to vehicles • EC & consent to establish – almost similar function • Lack of Multi departmental coordination • Overlapping enforcing agencies Standards & Compliances • Monitoring frequency stipulated by CPCB not achieved • Standards do not allow percentage of deviation – except NAAQS – Impractical • Industries tempted to manipulate • Maintenance of PC equipment – not priority by industries • By passing – Sponge Iron Plant • Litigation – time consuming – more emphasis to the process of inspection • Domestic waste treatment – not adequate Information flow from Regional Offices of SPCBs • Poor linking. MIS is weak • IT based enforcement coming up • Support & accountability of ROs are not uniform – mechanism not standardized • SOPs are not well documented • SPCBs adopt different procedure of enforcement Others • Commutative impact studies (REMP, Carrying Capacity Studies) are not done as routine – quality of the report • R & D by SPCB is not a priority • Quantification of pollution load – studies are sporadic • Health Impact Studies missing INCREASE IN WORK LOAD in OSPCB Functional Indicators During 198687 During 199697 During 200607 Increase in 10 years 26 50 306 172 1199 639 4 times 3.7 times No activity No activity 1200 Additional responsibility No activity 0 No activity 0 774 103 Additional responsibility Insignificant Insignificant 296 Additional responsibility No. of inspections conducted 129 1159 4097 3.5 times No. of stack & ambient air monitoring 40 No. of public hearings / consultations Not existed 711 Not existed 2590 77 3 72 3.6 times Additional responsibility 24 times Rs. 1.38 crores Rs. 29.52 lakhs 4 Acts & 9 Rules 4 Rs. 5.56 crores Rs. 866.03 lakhs 4 Acts & 22 Rules 9 0 5 5 times Rs. 298.96 lakhs Rs. 839.12 lakhs 3 times No. of industries / mines under admn. a.Consent cases b.NOC cases No. of misc. industries (stone crusher & brick kiln) No. of health care units under admn. Nos. of ULBs No. of public complaints handled No. of legal cases Amount of cess collected Amount of consent fees collected No. of Acts & Rules notified No. of Regional Offices No. of external technical projects Annual budget of the Board Total Technical Manpower Nos. of units regulated/person 3 0 Rs. 10.95 lakhs 3 Acts & 3 Rules 0 0 Rs. 28.0 lakhs 08 9.5 35 13.6 55 71 4 times 29 times 2.5 times 2.5 time 1.5 5.2 Recommendation, Planning Commission, Govt. of India • To levy spot fines in case of violation (5-10 times operational cost of running ETP for the period the last visit) (Quaci – Judicial Power) • For arrest / detention of persons responsible for toxic waste pollution • Scientific & technical documentation of pollution • Record statement • Stepping up of institutional arrangement for creating env. awareness • Benchmarking of frequency of monitoring • Detail performance study of ETP & PC equipment • Transparency in Consent & Authorisation administration Strength of SPCBs Experienced subject specific man power Infrastructure in terms of laboratories for field investigation Competent technically qualified pool of Scientists and Engineers Exposure and updating on env. Sound technologies Promote clean technology Developing real time monitoring data management Awareness creation Status of Pollution in India Trends in pollution • Levels of SO2 and lead in ambient air : decreasing • PM10 beyond norms in majority of cities and NOx is the emerging pollutant • Medium level cities are front runners in air pollution • Number of polluted river stretches increasing Database Issues • 43 Critically Polluted Industrial Clusters Identified :REFINEMENT • 17 categories of highly polluting industries & grossly polluting industries shortlisted: GAPS IN DOCUMENTATION & REPORTING • Red/Orange/Green categories : NEED FOR HARMONISATION Status of Compliance • 17 categories: compliance 71%; GPI: compliance 68% - INTEGRITY OF DATA TO BE ENSURED • SSI Compliance-- STATUS NOT ASSESSED: 70% of pollution load CAG Audit Findings on Water Pollution • Legislative & Policy framework – Water pollution has not been adequately addressed in any policy in India, both, at the federal & provincial level • Planning for control of pollution in rivers, lakes & ground water – Inadequate planning – No complete inventory of rivers/lakes and keystone species associated with them – no identification of existing pollution levels in rivers and lakes in terms of biological indicators etc Audit findings • Implementation of programmes for control of pollution – Projects for pollution control of rivers was unsatisfactory 82 % were completed after the scheduled date of completion – 28 projects costing ` 251.27 crore were constructed but not utilised as yet – States implementing the projects faced problems in land acquisition, forest clearances, technical problems, problems from contractors etc. – Programme to prevent pollution of lakes also ineffective as only 2 of the sampled 22 projects had been completed and the rest were either continuing beyond the sanction date of completion or had been abandoned Audit Findings • Monitoring of programmes – Inspection and monitoring was inadequate at all three levels, i.e., local level, provincial/State level and federal/Central level. – There was paucity of network for tracking pollution of rivers, lakes and ground water as there were inadequate number of monitoring stations, no real- time monitoring of water quality and the data on water quality had not been disseminated adequately. Audit Findings • Results of programmes for control of pollution in India – Data on the results of programmes not very encouraging as majority of rivers remain polluted and continue to be plagued by high levels of organic pollution, low level of oxygen availability for aquatic organisms and bacteria, protozoa and viruses which have faecal-origin and which cause illnesses – Most lakes are under threat from nutrient overloading which is causing their eutrophication and their eventual choking up from the weeds proliferating in the nutrient-rich water. • Implementation programmes for preventing pollution of these lakes has had no discernible effect Pollution Management-SPCBs 1.Environmental Planning (a) Development of standards and guidelines (b) Development of laws, rules and regulations 2. Environmental Monitoring (a) Environment surveillance (General) (b) Ambient Monitoring (c) Maintenance of data base 3. Environment Impact Assessment/Audit (a) Identification and inventory of source of pollutant (b) Impact Assessment on different components of environment (air, water, land and other natural resources) 4. Laboratory Management (a) Quality control (b) Research and development 5. Pollution Control Enforcement (Facility Specific) (a) Inspection (b) Prosecution (c) Direction 6. Technological Intervention (a) Design and development of appropriate technology (b) Dissemination of appropriate technology 7. Environmental Awareness/Information (a) Support to NGOs/Education Institutions (b) Capacity building through training programs (c) Mass awareness through media Vision of SPCBs Strategic Planning- Broad Institutional goal, assesses the performance and develop overall strategy Operational PlanningFramework of implementing strategy derived from Strategic planning Uniform staffing and enforcement mechanism Laboratory- Nucleus of SPCs- More credible Comprehensive monitoring planning and execution Development of industry specific pollution control guideline and inspection protocol IT Based functioning THANK YOU