Smoking Ban Legislation in Public Places in China
advertisement

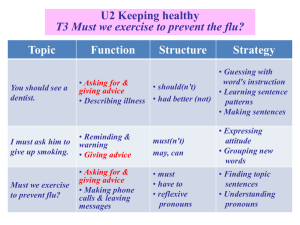
Smoking Ban Legislation in Public Places in China----Development and Improvement Prof. Chen-guang Wang, Ph.D. Yan Cheng School of Law, Tsinghua University A) General introduction on smoking ban legislation and its evaluation before FCTC (a) National Smoking Ban Norms in public places 1. smoking ban norms was developed from the central to the local during this period, the Ministry of Health (MOH), the National Patriotic Health Champagne Committee has developed a series of regulations and norms to promote the local’s efficient carrying out ● 1979, approved by the State Council , the MOH and other ministry decorated the Notice on smoking harm and tobacco control initiate ● 1981, National Education Committee set clear in the Students’ Regulations: No smoking ● 1985, the National Patriotic Health Champagne Committee together with the Ministry of Railways set regulations Ban on spitting, littering and smoking in smoke-free compartments on train ● 1987, the National Patriotic Health Champagne Committee together with the MOH and other ministries decorated Notice on no smoking initiate in places for children play ● 1987, the State Council promulgated the "public places, health regulations" to prohibit smoking in public places ● 1991, the Ministry of Health issued "Rules for the Implementation of Public Health regulations," provides in theaters, video halls, concert halls, dance halls, music cafes, recreation room, gymnasium, libraries, museums, art galleries, museums, shopping malls, bookstores, public transport waiting rooms and other 13 categories of smoking bans in public places; ● 1991, the Patriotic Health Campaign Committee, the Ministry of Health and other eleven ministries jointly issued "in public places and public transport to carry out in depth the activities of nonsmoking notice"; ● 1991, the "China Tobacco Monopoly Law" states: "State and community to strengthen publicity and education on health hazards of smoking, prohibited or restricted in public transport and smoking in public places.“ ● 1991 years " the PRC Law on the Protection of Children" twentyseventh article: No person shall smoke in schools, kindergartens, nursery teachers’, bedroom, and other health-focused activities rooms. ● 1997, the National Patriotic Health Campaign Committee, Ministry of Health issued "on public transport and its ban on smoking in the waiting room", putting forward stricter requirements on it. 2 Characteristics and shortcomings of the national legislation during this period: (1) a lower level law, mainly administrative regulations, government regulations, rather than the NPC law. (2) there is no specific national tobacco control laws regulate smoking in public places rather than scattered in other laws and regulations, lack of a systematic system of norms and the corresponding penalties. (3) notice, the main provisions of advocacy, lack of legal stability and authority. (B) local legislation China's large-scale public smoking ban legislation set up from the 1990s until the end of 2005, China Wuhan, Shaoguan, Nantong, Wenzhou, Jinan, Fushun, Hengshui, Weifang, Zhengzhou, Xining, Guiyang, Chongqing, Hohhot, Yinchuan, Urumqi, Dalian, Shanghai, Beijing, Nanchang, Qingdao and many other regions have promulgated specific smoking rules in public places within local specification file. During this period local legislation has the following characteristics: 1. The force of law in this period mainly regulate smoking in public places all over the local government regulations, only a handful of cities as local laws and regulations, such as Qingdao, Zibo, Urumqi, Shijiazhuang, Zhengzhou, Tianjin. Legal effect is relatively low. 2. Standardize the structure, during this time over smoking in public places is similar to the structure of norms, have largely adopted the legislative purpose, definition of nonsmoking places, social advocacy, self-management, passive smokers rights, smoking places on the unit where the punishment impede job processing, review and litigation, the requirements for health managers, non-smoking places on the individual smoking punishment system of norms. In the specific technical aspects of legislation, the definition of smoking area adopts listing mode, the majority of areas in order to compensate for list-style may lead to the extension of undistributed taken a fallback style requirements, listed in the last paragraph, "state laws and regulations No Smoking in other public places, “ " according to actual needs, determined by the municipal government banned smoking in other places ", etc., for the expansion of public places possibilities. 3 entity content: (1) smoking places limited mainly to the limited indoor places, workplaces and hotels, restaurants and other public places are not included in the scope of outdoor public places, smoking ban is not clear. (2) generally set smoking area (3) the implementation of the main provisions are not uniformed, single executive body does the work lacking of maneuverability. During this period the there are two categories carry out main provisions of law enforcement : Shanghai, Nanchang and so are managed by the provincial health bureau, penalty carried out by the local health bureau; Nanjing, Dalian and other places managedd by the provincial Patriotic Health Campaign Committee, while the Office of the competent authority, city, district, county Patriotic Sanitation is the executing agency for punishment. 4 clear focus on penalties object, clear legal position, but the legal representation is not accurate, not so conducive to public’s understanding and acceptance. Smoking in public places throughout the legislative intention is to control secondhand smoking damages the health of others, regulate smoking places emphasis on the specification and the performance of duties on non-smoking places, but are unified throughout the expression "smoking in public places," and used till now . Order-driven legal defination and the way of expressd is not conducive to an accurate grasp of the community spirit of the law and the core, are prone to psychological and emotional conflict Appendix: Convention on smoking in public places before the main legal directories 1. Wuhan ban on smoking in public places (2005 Amendment) (2005.11.09) 2. Shaoguan City, the ban on smoking in public places (2005.09.09) 3. Nantong ban on smoking in public places (2004.07.20 Amendment) (1998.08.12) 4. Wenzhou ban on smoking in public places (2004.01.17) 5. Jinan ban smoking in public places (2001 modified) (2001.06.15) 6. Fushun Provisional Regulations on smoking bans in public places (1999.05.25) 7. Hengshui city smoking bans in public places management practices (1998.08.30) 8. Weifang smoking regulations in public places (1998.08.27) 9. Zhengzhou smoking regulations in public places (1998.07.24) 10. Xining City, the ban on smoking in public places (1998.07.24) 11. Guiyang Provisional Regulations of smoking bans in public places (1998.06.17) 12. Chongqing ban smoking in public places [fail] (1998.06.01) 13. Hohhot ban smoking in public places (2009 Amendment) (1998.05.22) 14. Yinchuan Provisional Regulations on smoking bans in public places (1998.03.18) 15. Urumqi ban on smoking in public places (1998.01.06) 16. Dalian Provisional Regulations on smoking bans in public places (1997.12.31 Amendment) (1995.08.30) 17. Shanghai Provisional Regulations on smoking bans in public places (1997.12.19 Amendment) (1994.09.19) 18. Nanchang Provisional Regulations on smoking bans in public places (1997 amendments) 19. Qingdao city ban on smoking in public places (1997 modified) (1995.12.14) 20. Anshan City smoking ban smoking in public places Provisional Regulations (1997.7.23) 21. Smoking bans in public places Suzhou management practices (1997.04.12) 22. Benxi City, the ban on smoking in public places (1997.04.11) 23. Shijiazhuang city banned smoking in public places (1997.01.22) 24. Harbin ban on smoking in public places (1996.12.28) 25. Chengdu ban on smoking in public places (1996.10.14) 26. Xiamen ban on smoking in public places (1996.09.24) 27. Changchun Provisional Regulations of smoking bans in public places (1996.08.09) 28. Tianjin smoking regulations in public places (1996.07.10) 29. Shantou SEZ city smoking bans in public places Provisional Regulations on the implementation details (1996.06.11) 30. Jilin city ban on smoking in public places (1996.04.23) 31. Ningbo Provisional Regulations on smoking bans in public places [fail] (1996.04.18) • 32. Lanzhou implementation methods of smoking bans in public places (1996.03.01) 33. Huainan Interim Provisions of smoking bans in public places [fail] (1996.01.29) 34. Beijing banned smoking in public places (1995.12.21) 35. Hefei ban on smoking in public places (1995.12.15) 36. Haikou City, on the prohibition of smoking in public places of the Interim Provisions (1995.10.05) 37. Nanning Provisional Regulations on smoking bans in public places (1995.09.22) 38. Nanjing Provisional Regulations on smoking bans in public places (1995.09.20) 39. Guangzhou on the prohibition of smoking in public places notice (1995.08.09) 40. Chongqing Municipal People's Government ban on smoking in public places, the notice [fail] (1995.08.04) 41. Shenyang Provisional Regulations on smoking bans in public places (1995.07.24) 42. Zibo ban smoking in public places (1995.06.14) 43. Suzhou "ban on smoking in indoor public places, several provisions" (amended in 1997) (1993.12.30) B) General introduction on smoking ban legislation and its evaluation after FCTC Legislation of this period showing a bottom-up features: local legislation for the first, the department standard as assistance, to jointly promote the of national legislation. 1 local legislation: Typically, in 2008 the Beijing Municipal Government issued the "Beijing banned smoking in public places the scope of certain provisions" will be extended to public places, workplaces, and restaunts. In 2010 "second-hand tobacco smoke Nanchang Control Ordinance (draft)" first use "secondhand tobacco" expression. In 2011, "Harbin to prevent second-hand tobacco smoke regulations" of China is the first local law and regulation in line with the requirements of the UN Framework Convention on Tobacco Control. • (2) national legislation: the Ministry of Health, Ministry of Education issued the relevant regulatory documents. In 2009 "decision to ban smoking included in the 2011 national health system ",in 2010 "Ministry of Education, Ministry of Health issued “advice on the strengthening of school tobacco control efforts," respectively, and university health systems of these two major public places in the smoke standard control vertical advance, echo the local legislation. This May 1, 2011 "public places, Health Implementation Rules,“ took effect, Article 18 clearly states indoor smoking bans in public places. • Appendix 2:2006 smoking in public places since the main legal directories: 1. Public places, Health Implementation Rules (2011.5.1) 2. Ministry of Education, Ministry of Health advice on the strengthening of school tobacco control efforts (2010.6.12) 3. About 2011 the national health system decision to ban smoking (2009.5.20) 4. Guangzhou Smoking Control Ordinance (2010.9.1) 5. Lhasa Patriotic Health Regulations implementation measures (2009.11.05) 6. Anshan City, the Interim Provisions of smoking bans in public places (1997.07.23) 7. Shenyang Provisional Regulations on smoking bans in public places (1995.07.24) 8. Luzhou Municipal People's Government on Further Strengthening the views of health education (2010.03.12) • 9 control smoking regulations in public places in Shanghai (2009. 12.10) 10. Wuhu Municipal People's Government on Further Strengthening the health work of the patriotic views (2009.11.19) 11. Jingzhou Provisional Regulations on smoking bans in public places (2009.10.09) 12. Hohhot ban on smoking in public places (2008 Amendment) (2008.11.19) 13. Maanshan smoking regulations in public places (2008.10.18) 14. Huaihua ban on smoking in public places (2008.06.24) 15. Yichang City ban on smoking in public places (2008.06.14) 16. Qingdao Municipal People's Government on Further Strengthening the Work of smoking bans in public places notice (2008.05.29) 17. Luohe ban on smoking in public places (2008.05.28) 18. Shenyang notice smoking bans in public places (2008.05.14) 19. Meizhou implementation of smoking bans in public places (2008.04.09) 20. Yichang City ban on smoking in public places (2008.04.01) 21. Beijing banned smoking in public places certain requirements range (2008.03.31) 22. Dalian Provisional Regulations on smoking bans in public places (2008 Amendment) (2008.03.31) 23. Hanzhong ban smoking in public places (2007.12.17) 24. Daqing ban smoking in public places (2007.10.31) 25. Shaoyang ban smoking in public places (2007.05.26) 26. Tongchuan Provisional Regulations of smoking bans in public places (2006.12.28) 27. Xianning Xianning City People's Government on smoking bans in public places Interim Provisions (2006.04.30) C) Progress &shortcomings of the national legislation after the implementation of the FCTC (A) the progress of smoking ban covered areas 1 has been expanding the range of public places. (1) some of the outdoor spaces into public places range. There are two different methods of provision. The first is: "control smoking in public places in Shanghai regulations" non-smoking places in the range, including nurseries, kindergartens, schools and Children's Palace, the indoor and outdoor youth activity center area; MCH (the), Children's Hospital, children's Welfare Institute of indoor and outdoor areas. The second: Beijing, Yinchuan and other places only a few institutions express provision for indoor smoking, other smoking places not distinguish between indoor and outdoor areas. (2) specific non-smoking places more detailed list . Such as increasing the cafe, elevator and waiting area, the state authorities provided public services, work places, public utilities, financial institutions and other business premises. (3) further extension of the indoor public places and improvement of circumspect, indoor public places, smoking is clearly written "public places, Health Management Implementation Rules", in the workplace are gradually incorporated into the scope of public places, (2) smoking and smoke-free zoning problems are gradually improving. "Harbin regulations to prevent second-hand tobacco smoke," a change in the traditional division of smoking and smoking areas of practice, while taking a progressive path, provides: Bill comes into force, Harbin hotels, dining room place in a certain period within the designated smoking floors, rooms, after the expiration of non-smoking. Specific duration and scope, determined by the Harbin municipal government. 3, law enforcement agencies to improve the setting, to further clarify the division of responsibilities. Around the new formulation and revision of laws and regulations, and staffing in the implementation of the system has become more refined. A Case of Shanghai, "Shanghai Provisional Regulations on smoking bans in public places," 1997 edition of the implementing agencies provided only a simple as: "the prohibition of smoking in violation of the places where the unit, district or county Health Department at the following shall be punished ... "; and the new" control of smoking regulations in public places in Shanghai, "is more detailed and informative on the different areas of supervision and law enforcement to take the division of labor model. 4. Punishment has enhanced, more operational, but also conducive to the realization of legal deterrence. The modified units and individuals around the penalties were all improved. Penalties for violations of the no-smoking places from the initial range of 500-5000 yuan, up ten thousand dollars for the 2000-3; the individual smoker's punishment from the initial $ 10, adjusted to 50200 per month. 5. Legal effect level has improved, more authoritative. Before 2006, the majority of our local legislation of local government regulations, lower level. In this round of changes, Shanghai, Yinchuan, Guangzhou, regulate smoking in public places were up for the effect of higher local laws and regulations. (B)major shortcomings 1 the range of public places is still a gap with the requirements of the Convention. (1) the lack of "public places" and general definition, still in use liststyle approach is not conducive to "public places" extension of the comprehensive. (2) outdoor smoking in public places yet to be fully realized. From all over the legislative point of view, although in different places around the outdoor smoking or have different standards, but overall, indoor and outdoor smoking area is included in the scope of the need for specialized, explicit nature of the regulations, an outdoor public place Smoking not fully realized. (3) setting apart smoking and non smoking areas are still common practice. Followed around the smoking legislation places more restrictions on smoking places with distinction, the catering, entertainment and other places designated as smoking rooms can be set (area) place restrictions on smoking. The concept of misleading the public, as they can not recognize the so-called passive smoke, no "safe exposure" level. 2. Lack of unified national laws regulate smoking in public places to local laws and regulations and local government regulations based legal system, resulting in a series of questions. (1) The legal effect of low level lead to restricted types of administrative penalties. (2) differences in local law is not conducive to the formation of a unified concept of smoking in public places and practices 3. Name of legal norms can not accurately express the legislative intent. Modifications of some local laws and regulations "No Smoking" to "tobacco control", although such statements can be eased to some extent due to the general public to express the original legislative intent of the misunderstanding, still with the Convention to promote the "secondhand tobacco smoke control ", "law to prevent exposure to tobacco smoke," the expression of a considerable gap • 4. Government health administration authorities, non-smoking places, smokers and passive victims of rights and obligations related to the definition be further clarified. Smoking status and responsibilities of the designed site should be legislation to reexamine and solve problems. What is law enforcement smoking places the object is the subject of law enforcement, or "law enforcement facilitator"? Different roles in different settings will correspond to the responsibilities and authority, and its violation of obligations or duties of the legal consequences of the very different nature. Operational level, in the first-line anti-smoking non-smoking places lack the power of administrative punishment in the case, how to protect the immediacy of punishment? Related to lack the immediacy of the post-law enforcement can do bell? Smoking place concrete manifestation of violation of duties which include, in particular, is not to discourage smokers, the extent to which such acts should be punished? How to protect non-smoking places obligations on the immediate supervision of the situation? These operational issues were not involved in legislation, regulations and legal consequences of the generalized system of nonconvergence of law enforcement will inevitably lead to the penalties for not effectively implemented (C)suggestions • 1. According to the spirit and requirements of the Convention, to further clarify the meaning and extension of public places. First, a clear definition of public places, using the general style and the modalities of the list-style co-exist. Second, indoor workplaces have not yet fully incorporated into smoking areas around the key areas to promote. Third, the outdoor smoking ban in public places should be further clarified, specific. Fourth, the abolition of distinction between workplace smoking restrictions on smoking places and practices, the progressive realization of a total smoking ban in public places. A high concentration of people dining, and entertainment venues to establish a comprehensive smoking ban norms, a real sense of the standardization of tobacco control in public places. 2. Promote a national unified legislation for the implementation of local anti-smoking legislation and to provide more specific references and more authoritative legal basis. 3. scientific and unified naming of Tobacco control laws and regulations 4. Clear distinction between government health administration authorities, non-smoking places, smokers and the tobacco control law in the relationship of passive smoking victims have specific rights in the burden of specific obligations, the implementation of specific powers to take specific responsibilities, and these terms, responsibilities, rights and obligations between the specific association, protection of the law enforcement system to establish reasonable arrangements at the top set.